Chapter 2 Preamble to the Constitution
Textbook Questions and Answers
1. Find the following words in the grid:

Question 1.
A sense of ‘we-feeling’ and empathy towards fellow citizens
Answer:
Fraternity.
Question 2.
A system in which sovereign power is in the hands of the people
Answer:
Democracy.
Question 3.
Introduction to the Constitution
Answer:
Preamble.
Question 4.
A system in which all religions are considered equal
Answer:
Secular

2. Answer the following questions.
Question 1.
What are the provisions in a secular Constitution?
Answer:
- In a Secular State, all religions are considered as equal.
- No religion is considered to be the state religion. The citizens are free to follow their own religion.
- The state cannot discriminate among citizens on the basis of religion.
Question 2.
What is meant by adult franchise?
Answer:
- Adult franchise means all citizens completing 18 years of age have the right to vote in the elections.
- This enables equal participation of citizens in the running of our country.
Question 3.
What right does economic justice ensure?
Answer:
Economic justice ensures our right to a source of livelihood so as to look after oneself and one’s family.
Question 4.
How will human dignity be established in a society?
Answer:
When every individual respects another and honours their freedom and rights, dignity of the individual will be established.
3. How should we make use of our freedom ? Write your views about it.
Answer:
- Pandit Jawaharlal Nehru has rightly said. ‘We have to assume the responsibility ourselves of what we do’.
- Freedom must be exercised with care, with a sense of responsibility.
- Our freedom and independence which we gained after innumerable sacrificies must be safeguarded.
- We should use the different freedoms endowed on us by our Constitution to bring out the best in us and build a better nation, a better world
- The future lies in our hands.
4. Explain the following concepts.
Question 1.
Socialist State
Answer:
- A Socialist State is such a State where the gap between the rich and the poor is minimum.
- All have a right over the wealth of the country.
- It is ensured that wealth is not concentrated in the hands of a few people.
Question 2.
Equality
Answer:
(i) The Preamble guarantees the Indian citizens equality of status and there will be no discrimination based on caste, creed, race, sex, place of birth, etc.
(ii) The guarantee of equality means that there should be no discrimination between people in terms of high-low, superior-inferior.
Question 3.
Sovereign State
Answer:
The word sovereign means that a state is not under the control of a foreign power. The most important goal of our freedom struggle was to acquire sovereignty. ‘Sovereignty’ means the ultimate authority to govern oneself. In a democracy, sovereignty rests with the people
Question 4.
Equality of opportunity.
Answer:
Equality means the state of being equal in status, rights or opportunities. Equality of status, and of opportunity means that all have equal human status and there will be no discrimination based on caste, creed, race, sex, place of birth, etc. All will get the opportunities for development without any discrimination.
5. Make a list of the key words in the Preamble. Look for their meanings in a dictionary. Prepare a chart in the following way:

Answer:
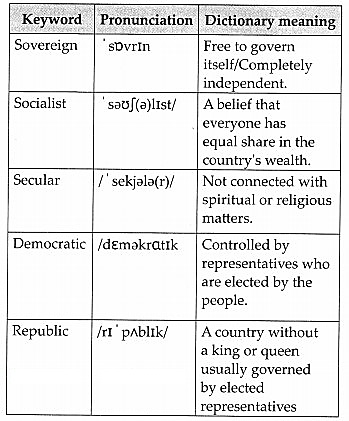
Activities:
- Visit your Tehsil office with your teacher to understand how a vote is cast and how the electronic voting machine works.
- Make a list of newspapers available in your locality.
In Text Questions and Answers
Answer the following concepts:
Question 1.
Liberty
Answer:
(i) Liberty implies that there should be no coercive, unfair restrictions upon us and that ’ there should be an atmosphere conducive to the development of our inherent capacities.
(ii) In a democracy, citizens enjoy liberty. In fact, democracy becomes mature only if the citizens enjoy freedom.
Discuss:
Question 1.
Some statements regarding freedom have been given below for discussion. Express your views.
(a) While publicly celebrating our festivals, we need to follow some rules. That does not restrict our freedom,
(b) Freedom means behaving in a responsible way, not as per our whims and fancies.
Answer:
Yes, With freedom comes responsibilities. Rules should be followed while exercising freedom for a smooth life and to ensure that we work towards responsible citizenship.
Question 2.
Read what Deepa has written on the topic: “My Family’.
Answer:
Democracy does not only imply elections. My parents do all the household work together. We also participate in it. We ensure that we talk cordially with each other. Even if we happen to fight, we try to listen to each others views by stopping the fight as soon as possible. If any change has to be made, even the grandparents are consulted. Anuja wants to take up agricultural research as her career. Her decision was appreciated by everybody.
Question 3.
Do you think that Deepa’s house functions in a democratic way? Which features of democracy can be found in this passage.
Answer:
Yes. They function in a democratic way and the features of democracy displayed here are:
- Carrying out responsibilities collectively as a unit.
- Mutual respect.
- Honouring opinions which are not in line with our views.
- Consensus in decision making.
- Freedom of thought and expression.
- Freedom of occupation.
Activities:
Question 1.
Visit your Tehsil office with your teacher to understand how a vote is cast and how the electronic voting ntachine (EVM) works.
Answer:
The voting machines used in India are a combination of two components. First component is called the Balloting unit on which the voters press the button. The other part is called the Control unit. This unit gives supervising power to the polling officer stationed at the poll booth.
The two units are connected by a five-meter cable. The voter places his /her vote on the Balloting unit which is placed inside the Voting compartment.
An EVM runs on 6-volt batteries to eliminate the need of any external power source. It is designed to record 64 candidate names and 3,840 votes at the max. The 64 candidate names can be split across (a maximum of) 4 balloting units connected in parallel, with 16 candidate names on each of the unit.
Question 2.
Make a list of newspapers available in your locality.
Answer:
English News Papers:
- The Times of India
- Economic Times
- Financial Express
- Indian Express
- Mumbai Mirror
- Mid-day
- DNA (Daily News and Analysis)
- Business- Standard
- Hindustan Times
- Free Press Journal
Hindi News Papers (Including Urdu Daily):
- Hindi Mid-Day
- Tehalka News
- Navbharat Times
- Humara Mahanagar
- Aaj Ka Anand
- YashoBhoomi
- Dopahar
- Saamna
- Hindmata
- Mumbai Sandhya
Marathi News Papers:
- Loksatta
- Maharashtra Times
- Navshakti
- Navakal
- Vartahar
- Saamna (saamana)
- Sakai
- Sandesh
- Lokmat
- Divyabhaskar
- Mumbai Mitra
- Sandhyanand
- Punya Nagri
- Samrat
Additional Important Questions and Answers
Complete the sentence by choosing the appropriate words from the options given below:
Question 1.
The _______ to the Indian Constitution is called the ‘Preamble’. (Preface, Preview, Annexure)
Answer:
Preface
Question 2.
The Preamble sets out the ______ of our Constitution. (declaration, objectives, theme of the Articles)
Answer:
objectives
Question 3.
It talks about the resolve of the Indians to constitute India into a ‘Sovereign, Socialist, _______ Democratic Republic’. (Theocratic, Autocratic, Secular)
Answer:
Secular
Question 4.
Our country became independent on _______. (15th August 1947, 26th January 1950, 26th November 1949)
Answer:
15th August 1947
Question 5.
The word _______ means that a state is not under the control of a foreign power. (Sovereign, Secular, Socialist)
Answer:
Sovereign
Question 6.
A Socialist State is such a State where the gap between the rich and the poor ______. (is maximum, is minimum, does not exist)
Answer:
is minimum
Question 7.
In _________ State, all religions are considered equal and no religion is considered as a State religion. (secular, socialist, sovereign)
Answer:
secular
Question 8.
In a _______ the sovereign power is in thehands of the people. (democracy, autocracy, monarchy)
Answer:
democracy
Question 9.
Elections are conducted in India after a fixed period when voters elect their ______. (President, Vice-president, Representatives)
Answer:
Representatives
Question 10.
The Parliament or Legislature and the Executive take decisions for the entire population as per the procedure laid down by the ______.(High Court, Supreme Court, Constitution)
Answer:
Constitution
Question 11.
________ implies removal of injustice and ensuring that everybody has the opportunity for progress. (Liberty, Justice, Equality)
Answer:
Justice
Question 12.
________ ensures that as human beings all have the right to the same dignity and respect, the same status. (Political justice, Social justice, Economic justice)
Answer:
Social justice
Question 13.
Since we have adopted universal adult franchise, all citizens completing ________ years of age have the right to vote in the elections. (18, 20, 21)
Answer:
18
Question 14.
The liberty of belief, faith and worship implies ______ freedom. (economic, social, religious)
Answer:
religious
Question 15.
_____ implies a ‘we-feeling’ towards one another. (Fraternity, Empathy, Sympathy)
Answer:
Fraternity
Question 16.
________ implies equal respect to each (Human Rights, Equality, Dignity)
Answer:
Equality
Match the following:
Question 1.
(1) Sovereignty (2) Socialist State (3) Secular (4) Democratic | (a) Equal right over the wealth of the country. (b) No discrimination on the basis of religion. (c) Sovereign power is in the hands of the people. (d) Public positions elected by the people. (e) Ultimate authority to govern ownself. |
Answer:
1 – e
2 – a
3 – b
4 – c
Name the following:
Question 1.
The fundamental and the highest law of the land which is an important document clarifying the rules of the administration.
Answer:
Constitution.
Question 2.
A systematic arrangement of all the aims and objectives of a law which is the preface to the Constitution.
Answer:
Preamble
Question 3.
The words with which the Preamble begins,
Answer:
’We, the people of India’.
Question 4.
The word that means that a State is not under the control of a foreign power.
Answer:
Sovereign
Question 5.
A state where the gap between the rich and poor is minimum.
Answer:
Socialist.
Question 6.
A state wherein all religions are considered equal.
Answer:
Secular state.
Question 7.
In this form of governance, the sovereign power is in the hands of the people.
Answer:
Democracy.
Question 8.
Institutions in India created by our Constitution.
Answer:
- Parliament
- Legislature
- Executive.
Question 9.
In this form of government, all positions are elected by the people and no public position is occupied on the basis of hereditary succession.
Answer:
Republic.
Question 10.
Three types of Justice talked of in the Constitution.
Answer:
Social Justice, Economic Justice, Political Justice.
Question 11.
This implies that there should be no coercive, unfair restrictions upon us and that there should be an atmosphere conducive to the development of our inherent capacities.
Answer:
Liberty
Question 12.
The most fundamental freedom of an individual.
Answer:
Freedom of Thought and Expression.
Question 13.
The liberty of belief, faith and worship implies this value.
Answer:
Religious freedom.
Question 14.
The goal which is included in the Constitution which implies a ‘we-feeling ‘ and feeling of empathy.
Answer:
Fraternity.
State whether the following statements are true or false with reason:
Question 1.
The Preamble begins with the mention that the people of India have given the Constitution to themselves.
Answer:
False : The Preamble begins with the words ‘We, the People of India’.
Question 2.
In a democracy, the sovereign power is in the hands of the people.
Answer:
True: Democracy is the Government of the people, by the people and for the people.
Question 3.
In a democracy, citizens enjoy liberty.
Answer:
True : In fact democracy becomes mature only if citizens enjoy liberty.
Answer the following questions:
Question 1.
The Preamble guarantees the Indian citizens equality of status and of opportunity. Explain.
Answer:
- It means that all have equal human status and there will be no discrimination based on caste, creed, race, sex, place of birth, high or low status or superior-inferior.
- The Preamble has given great importance to equality of opportunity as well.
- Each one gets the opportunities for development without discrimination.
Answer the following concepts:
Question 1.
Constitution and Preamble
Answer:
- Our Constitution is the fundamental and the highest law of the land.
- There are definite aims or purposes in making any law.
- Basic provisions in the law are made, after clarifying these objectives.
- A systematic arrangement of all the aims and objectives of a law is the Preface to the law.
- The Preface to the Indian Constitution is called the ‘Preamble’. The Preamble sets out the objectives of our Constitution.
Question 2.
Republic and how is it different from Monarchy.
Answer:
- Along with being a democracy, we are a Republic. All public positions in a Republic are elected by the people.
- No public position is occupied on the basis of hereditary succession.
- The position like the President, the Prime Minister, the Governor, the Chief Minister, the , Mayor, the Sarpanch, etc. are public positions.
- Any Indian citizen fulfilling the prescribed age criterion can get himself/herself elected to any of these positions.
Question 3.
Fraternity
Answer:
- Fraternity implies a ‘we-feeling’ towards one another.
- It creates a feeling of empathy.
- People become more understanding towards each other’s problems and needs.
Explain the terms:
Question 1.
Justice
Answer:
- Justice implies removal of injustice and ensuring that everybody has the opportunity for progress.
- Establishing justice is adopting such policies that will promote public good.
Question 2.
Social Justice
Answer:
- There should be no discrimination among individuals on the basis of caste, creed, race, language, region, place of birth or sex.
- As human beings, all have the right to the same dignity and respect, the same status.
Question 3.
Economic Justice
Answer:
- Poverty leads to the evils of hunger, hunger -deaths or malnourishment.
- If poverty is to be eradicated, everyone should have the right to a source of livelihood so as to look after oneself and one’s family.
- Our Constitution has given this right to every citizen without any discrimination.
Question 4.
Political Justice
Answer:
- We have adopted universal adult franchise to enable equal participation in the running of the country.
- Accordingly, all citizens completing 18 years of age have the right to vote in elections.
Give reason:
Question 1.
India is a sovereign state.
Answer:
- India was ruled by Britain for a long period.
- The British rule ended on 15th August, 1947. Our country became independent and India became sovereign i.e a state not under the control of a foreign power.
Question 2.
India is a secular state.
Answer:
- In India, all religions are considered as equal.
- No one religion is considered to be a state religion. The citizens are free to follow their own religion. So, India is a secular state.
Question 3.
Freedom of thought and expression is the most fundamental freedom for an individual.
Answer:
- Freedom of thought and expression is the most fundamental freedom for an individual.
- Everyone is free to express their own views and opinions. A give-and-take of ideas enhances the spirit of cooperation and unity amongst us.
- Similarly, it also enables us to understand the various dimensions of any problem.
Question 4.
Promotions of fraternity has been included in the Preamble as a goal.
Answer:
- The makers of the Constitution believed that merely guaranteeing justice, freedom and equality would not lead to establishing equality in Indian society.
- No amount of laws would help us achieve these goals if fraternity is lacking among Indians.
- Hence the promotion of fraternity has been included in the Preamble as a goal.
Question 5.
Fraternity is closely related with human dignity.
Answer:
- Human dignity implies equal respect to each individual as a human being. .
- It does not depend upon the criteria of caste, creed, race, sex, language, etc.
- Just as we would like to be treated with dignity and respect by others, we should treat others with the same dignity and respect.
- When every individual respects another and honours their freedom and rights, dignity of the individual will get established.
- This will also develop fraternity, a ‘we-feeling’ towards one another.