Chapter 1 Basics of Information Technology
1. Complete the following activity.
Question 1.
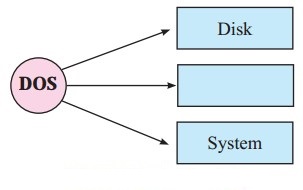
Answer:
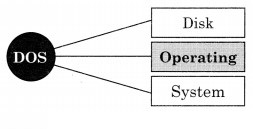
Question 2.
Tick the appropriate box.
Internet is a ____________ network connecting millions of computer.

Answer:
Global
Question 3.
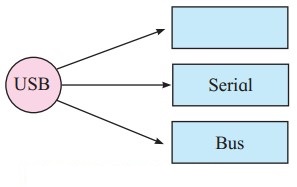
Answer:
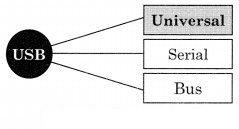
Question 4.
Tick the appropriate box.
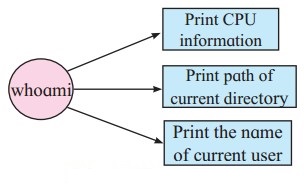
Answer:
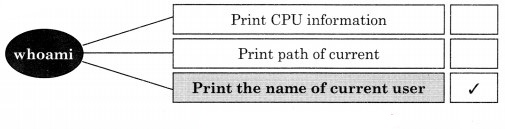
Question 5.
Answer:
2. Divide the following list of devices into appropriate categories.
Question 1.
Monitor, Barcode reader, Printer, Keyboard. Optical character reader, Speaker
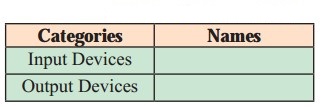
Answer:
Categories | Names |
Input Devices | Barcode reader, Keyboard, Optical Character reader |
Output Devices | Monitor, Printer, Speaker |
3. Multiple choice two correct answers.
Question 1.
The primary memory consists of ____________ and ____________
(a) Pendrive
(b) Hard Disk
(c) RAM
(d) Scanner
(e) ROM
Answer:
(c) RAM, (e) ROM
Question 2.
The network architectures which are widely used are ____________
(a) Server
(b) Client
(c) Peer to peer
(d) Client-server
(e) Internet
Answer:
(c) Peer to peer, (d) Client-server
4. Match the following.
Question 1.
1. IS | (a) change directory |
2. FTP | (b) Translates Network Address |
3. CD | (c) List of Directory |
4. DNS | (d) To transfer file on interent |
Answer:
1. IS | (c) List of Directory |
2. FTP | (d) To transfer file on interent |
3. CD | (a) change directory |
4. DNS | (b) Translates Network Address |
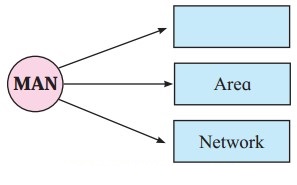
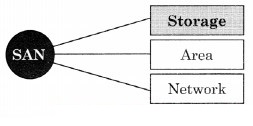
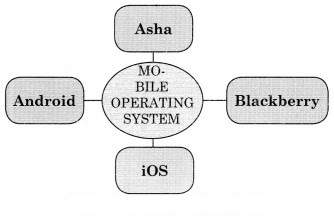
5. Name the following and complete the diagram.
Question 1.
Answer:
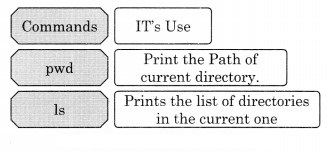
6. Complete the following with Linux commands with their use.
Question 1.
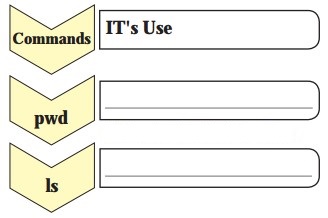
Answer:
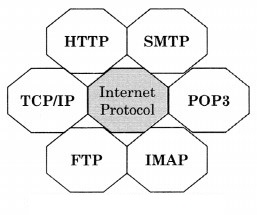
7. Complete the list of the following protocols.
Question 1.
Answer:
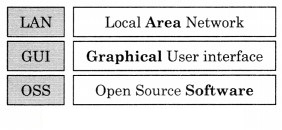
8. Complete the following Long form.
Question 1.
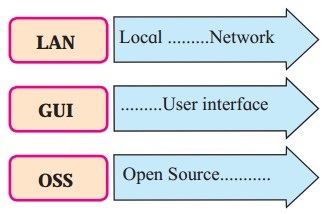
Answer:
9. Identify the following activity.
Question 1.
You are typing a letter using a computer and suddenly there is a power failure.
Which type of Memory does this activity deal with?
Answer:
Random Access Memory
10. Answer the following.
Question 1.
What are Data and Information? Give examples of data and information.
Answer:
Data can be any character, text, word, number, or raw facts.
Example of Data:
Mumbai, 1234, Aditya, MG Road, Maharashtra, 9444444441, 411004
Information is data formatted in a manner that allows it to be utilized by human beings in some significant way.
Example of Information:
Aditya, 1234, MG Road, Mumbai 400004, Maharashtra, 944444444114.
Question 2.
Explain functional units of a computer system.
Answer:
The computer system has the following three basic components:
Input Unit:
An input device is any hardware device that sends data to a computer, allowing you to interacts with and controls it. Data can be in the form of words, symbols, numbers, etc. The function of the input device is to direct commands and data into the computer.
For example keyboard, mouse, scanners, digital cameras, joysticks, and microphones.
Central Processing Unit:
After receiving data and commands from the user, a computer system has to process the instructions provided using Central Processing Unit (CPU). It has three elements:
(a) Arithmetic and Logic Unit: An arithmetic logic unit (ALU) is a major component of the central processing unit of a computer system. It does all processes related to arithmetic and logic operations like add, subtract, multiply, etc.
(b) Control Unit: The control unit (CU) is a component of a computer’s central processing unit (CPU) that directs the operation of the processor. It tells the computer’s memory, arithmetic, and logic unit, and input and output devices how to respond to the instructions that have been sent to the processor.
(c) Memory Unit: A memory unit is the amount of data that can be stored in the storage unit. Once the data has been entered using input devices, the system stores the data in the memory unit.
Types of Memory: Primary Memory & Secondary Memory.
- Primary Memory: It has 18 internal memory of the computer also known as main memory. It is of two types RAM and ROM.
- RAM (Random Access Memory): RAM stands for Random Access Memory also known as reading/write memory. Information stored in this memory is lost as the power supply to the computer is switched off; it is also called “Volatile Memory”.
- ROM(Read Only Memory): ROM stands for Read-Only Memory. ROM is a permanent type of memory. The contents are not lost as the power supply to the computer is switched off. ROM cannot be overwritten by the computer. It is also called “Non Volatile Memory”.
- Secondary Memory: It is the external memory of the computer which is used to store a large amount of data. The secondary storage devices are a Hard disk, Pen drive, CD, DVD, etc.
Output Unit:
An output device is any device used to send data from a computer to another device or user. Most computer data output that is ‘meant for humans is in the form of audio or video. Thus, most output devices used by humans are in these categories. Examples include monitors, projectors, speakers.
Question 3.
What is a storage unit? Explain types of primary memory storage.
Answer:
When a user enters data using input devices, the computer system stores this data in a memory unit i.e. storage unit. The storage unit uses a set of pre-programmed instructions to further transmit this data to other parts of the CPU. There are two types of memory
- Primary Memory
- Secondary Memory
RAM: It stands for Random Access Memory. RAM is known as reading/write memory. It is the main memory of the computer system. The information stored in this memory is lost as the power supply to the computer is switched off, so it is also called as “Volatile Memory”.
ROM: It stands for Read-Only Memory. ROM is permanent memory. The content is not lost when the power supply is switched off. ROM cannot be overwritten by the computer, so it is also called “Non-Volatile Memory”.
Question 4.
Explain how Linux is different from Windows.
Answer:
- Linux is open sources system whereas the window operating system is commercial.
- Linux has access to source code and alters the code as per user need whereas a window does not have access to source code.
- Linux distribution doesn’t collect user data” whereas Windows collects all the user details which leads to privacy concerns.
- As the software is open to the public, it constantly updates, improves, and expands as more people can work on its improvement.
Question 5.
Write down the difference between LAN, MAN, and WAN.
Answer:
LAN (Local Area Network) | MAN (Metropolitan Area Network) | WAN (Wide Area Network) |
LAN Stands for Local Area Network. | MAN stands for Metropolitan Area Network. | WAN stands for Wide Area Network. |
A LAN is a network of connected devices that exist within a specific location. | A public or private network is used to connect various locations including suburbs in metropolitan cities. | A WAN is any network that crosses metropolitan, regional, or national boundaries. |
LANs may be found in homes, offices, educational institutions, or other areas. | A MAN is a network, which covers an entire city, but uses LAN topology. | Most networking professionals define a WAN as any network that uses routers and public network links (e.g. Telephone lines). |
LAN is easy to set up. | MANs are formed by connecting multiple LANs. | Due to long-distance transmission, the noise and errors are more in WAN. |
Data transmits at a very fast rate. | Examples of a MAN are the cable TV network in a city. | The best example of WAN is the Internet. |