Chapter 1 Psychology: A Scientific Discipline
Chapter 1 Psychology: A Scientific Discipline
1. Choose the correct option and complete the following statements.
Question 1.
Till 1879, psychology was a branch of ……….
(a) physics
(b) philosophy
(c) physiology
Answer:
(b) philosophy
Question 2.
Psychology is a science.
(a) natural
(b) social
(c) biological
Answer:
(b) social
Question 3.
…………………. is considered as founder of Psychoanalysis.
(a) Wilhelm Wundt
(b) Carl Rogers
(c) Sigmund Freud
Answer:
(c) Sigmund Freud
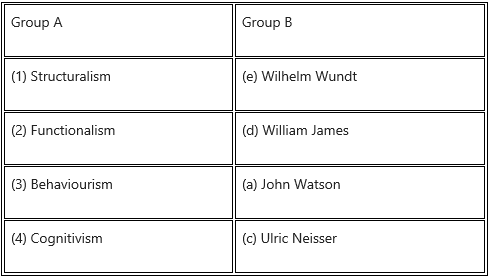
2. Match the pair
Answer:
3. State whether the following statements are true or false.
Question 1.
Psychology is a study of mental processes.
Answer:
True
Question 2.
Case study method is quite often used by clinical psychologists.
Answer:
True
Question 3.
An experimenter is a person on whom the experiment is conducted.
Answer:
False
4. Answer the following in one sentence each.
Question 1.
In which year was the first psychology laboratory established?
Answer:
The first psychology laboratory was established in 1879 by Wilhelm Wundt, at the University of Leipzig in Germany.
Question 2.
Who is considered as the ‘Father of American Psychology’?
Answer:
William James, founder of Functionalism school of thought of psychology is considered ‘Father of American Psychology’.
Question 3.
What is meant by an experimenter?
Answer:
The person who conducts the experiment is called the experimenter.
5. Define / Explain the concepts in 25 – 30 words each.
Question 1.
Replicability
Answer:
Replicability is one of the key features of science. Scientific knowledge can be replicated under the same circumstances as the original experiment. This ensures reliability of results towards establishing a scientific theory.
Question 2.
Correlation coefficient.
Answer:
Correlation coefficient is the measurement of the correlation between two or more variables. Its value extends between -1.00 to +1.00. The concept was first introduced by Sir Francis Galton. The Pearson product-moment correlation coefficient is the most commonly used type of correlation coefficient.
6. Write short notes on the following in 50 – 60 words each.
Question 1.
Observation method
Answer:
Observation method is a research method that is employed in conditions where experiments may not be possible or even necessary. Observation is used by child psychologists and social psychologists. It may be carried out in a natural setting, for e.g., observing candidates waiting their turn for an interview. It may also be carried out in controlled conditions.
The following factors should be kept in mind while carrying out the observation
- it should be done systematically.
- a comprehensive list of behaviours to be observed must be prepared.
- the persons should not be aware of being observed.
The disadvantages of observation are:
- it is a time consuming method.
- objectivity is difficult to maintain during observation.
- it is difficult to establish cause-effect relationships.
Question 2.
Survey method
Answer:
A survey is a research method used to collect data from a pre-determined group of respondents, i.e., a sample. It is used to obtain information about the preferences, opinions, etc., of the ‘sample’ population. It makes use of tools like questionnaire, checklist, interviews, etc. Survey method is employed by social psychologists, industrial psychologists, etc. The researcher must ensure that-
- sample of respondents is representative of the population.
- questions should not be ambiguous.
The disadvantages of survey method are:
- it is a very subjective method,
- it lacks reliability.
Question 3.
Case study method
Answer:
Case study method is a qualitative research method employed by clinical psychologists. It provides intensive, descriptive information about an individual from multiple sources such as family, peers, school, academic and health records, etc. This helps to assess the person’s level of psychological and social functioning. Researchers may employ techniques like observation, interview, psychological tests, etc. Psychologist such as Sigmund Freud and Jean Piaget made extensive use of case study method. However, this method is very time consuming and subjective.
Question 4.
Importance of rationality
Answer:
Rationality implies being agreeable to reason. According to Stanovich, “Rationality involves adaptive reasoning, good judgement and good decision making.”
According to Dr. Albert Ellis, rationality helps a person to successfully attain goals and be happy. He proposed Rational Emotive Behavioural Therapy (REBT), which is a popular intervention method in counselling psychology.
Rationality is important because:
- It allows us to make decisions in new or unfamiliar situations by helping us to gather and process relevant information.
- It enables the person to exhibit tolerance and flexibility.
- A rational person accepts oneself unconditionally and assumes responsibility for their own behaviour.
- Rationality helps to understand and respect the views and interests of others.
7. Define / Explain the concepts in 25 – 30 words each.
Question 1.
Science
Answer:
The word science is derived from the Latin word ‘Scientia’ which means ‘knowledge’. Science is the pursuit and application of knowledge and understanding of the natural and social world, following a systematic methodology based on evidence. The key features of science are empirical evidence, objectivity, scientific causality, systematic exploration and replication.
Question 2.
Objectivity
Answer:
Objectivity is one of the key features of science. It refers to the ability to observe and accept facts as they exist setting aside all sources of expectations, values, prejudices, etc. Science objectively studies some particular phenomenon.
8. Answer the following questions in detail.
Question 1.
Explain the types of correlation.
Answer:
A correlation refers to a statistical tool used to measure the relationship between two or more variables.
If the change in one variable is accompanied by a change in the other variable, this interdependence is called correlation. It is measured by correlation coefficient which extends between -1.00 to + 1.00.
The types of correlation are:
(i) Positive correlation – Both variables either increase or decrease at the same time, for e.g., extent of rehearsal (revision)↑ and recall score↑.
The value of positive correlation from 0.00 to + 1.00. It is represented as: variable 1 variable 2

(ii) Negative correlation – An increase in one variable is associated with a decrease in the other and vice-versa. The value of the correlation is between 0.00 to -1.00, for e.g., bunking of lectures (↑) and score in exams (↓).

(iii) Zero correlation – A change in one variable leads to no significant change in the other variable, for e.g., height and intelligence.
Question 2.
Explain some of the challenges in establishing psychology as a science.
Answer:
Many criticisms of psychology as a science have been made on practical, philosophical and ethical grounds. The challenges in establishing psychology as a science are:
(i) It is in preparadigmatic state – According to American philosopher, Thomas Kuhn, psychology is still in a preparadigmatic state as it has not succeeded in producing a cumulative body of knowledge that has a clear conceptual cove.
(ii) Issues related to objectivity and validity – Methods used in psychology such as introspection, surveys and questionnaires are subjective. Due to this, psychology lacks two criteria of science, i.e., objectivity and validity.
(iii) Issues related to predictability and replicability – In psychology it is difficult to make exact predictions as people respond differently in different situations. Test result are more varied and hence difficult to replicate.
(iv) Objectifying humans – According to some psychologists, subjecting human behaviour to experimentation amounts to objectifying individuals.
Question 3.
Explain the key features of science.
Answer:
The word science is derived from the Latin word ‘Scientia’ which means ‘knowledge’. Science is the pursuit and application of knowledge and understanding of the natural and social world, following a systematic methodology based on evidence.
They key features of science are:
- Empirical evidence – It refers to acquiring information through direct observation or experiments. Scientific knowledge is based on verifiable evidence.
- Objectivity – This refers to the ability to observe and accept facts as they exist, setting aside all sources of expectations, values, prejudices, etc.
- Scientific causality – Science aims to establish a cause-effect relationship between the variables under consideration, i.e., the effect of the Independent Variable on the Dependent Variable.
- Systematic exploration – Science adopts a sequential procedure for studying various phenomena. It includes scientific steps like formulating a hypothesis, collection of facts, scientific generalisation etc.
- Replication – Scientific knowledge can be replicated under the same circumstances as the original experiment. This ensures reliability of results towards establishing a scientific theory.
- Predictability – Science involves describing and explaining phenomena as well as to make predictions accordingly.
Question 4.
Write detailed information of the experimental method in psychology.
Answer:
The systematic observation about a certain problem under controlled laboratory conditions is called an experiment.
For example, Albert Bandura conducted experiment to investigate if social behaviours i.e., aggression can be acquired by observation and imitation. The steps involved in an experiment are:
- identifying the problem
- formulation a hypothesis
- selecting an experimental design
- conducting the experiment and data collection
- data analysis
- drawing conclusions
The key terms of experimental method with examples are:
- Problem: To study the effect of music on the level of blood Pressure.
- Hypothesis: The music will help in regulating the level of blood pressure.
- Independent variable: Music.
- Dependent variable: Level of blood pressure.
- Intervening variables: Age, gender, all other sounds other than music, etc.
- Experimenter : A person who will be conducting this experiment. (May be you or your psychology teacher.)
- Participant : A person on whom this experiment will be conducted. (May be your family member/ friend.)
The two variables in an experiment are:
- Independent Variable (I.V.) – It is the variable that the experimenter manipulates or changes systematically to study it’s effect on the D.V. (Cause).
- Dependent Variable (D.V.) – the variable that may change due to manipulation of the I.V. (effect).
The features of the method are:
- it is the most objective and scientific method of studying behaviour
- it helps to establish cause-effect relationship between two or more variables
- the findings of an experiment are verifiable
The limitations of the method are:
- it may not be possible to control all intervening variables
- it has a limited scope, i.e., there may be ethical constraints or risk factors
- experimenter’s expectations or participant attitude may influence the conclusions
Question 5.
Explain the characteristics of a rational individual.
Answer:
One of the significant aims of individuals is attainment of happiness. However, in the pursuit of happiness, one should not be driven by irrational influences or compromise on social norms and ethics. Psychology helps to improving life quality by applying the concept of rationality in daily life. According to Stanovich, “Rationality involves adaptive reasoning, good judgement and good decision making.”
According to Dr. Albert Ellis, rationality helps a person to successfully attain goals and be happy. He proposed Rational Emotive Behavioural Therapy (REBT), which is a popular intervention method in counselling Psychology.
According to Ellis, rational people possess characteristics such as:
- Understanding both self-interest and social interest – Rational people understand what choices help them to grow and take responsibility for their actions. They are also careful not to violate other’s rights.
- Self-direction – The person does not demand excessive attention or support from others as he/she assumes the responsibility for his/her own life.
- Tolerance – It is the willingness to accept beliefs and behaviour patterns of others that may differ from our own way of thinking.
- Flexibility – Rational people tend to be flexible and unbiased in their thoughts and actions.
- Self-acceptance and self-responsibility – A rational person accepts him/herself unconditionally as well as responsibility for his/her thoughts, emotions and behaviour.
The concept of rationality can be explained as:

How Rational Am I?
Question 1.
Identify the strongest and the weakest characteristics in you from those explained by Dr. Albert Ellis.
Answer:
Rational people are psychologically healthy and show adaptive reasoning and good decision making.
According to Dr. Albert Ellis, some characteristics of rational persons are:
- Understanding self-interest and social interest
- Self-direction
- Tolerance
- Flexibility
- Self-acceptance and self-responsibility.
The strongest characteristic in me is self-direction. The weakest characteristic in me is flexibility.
Question 2.
How will you work on your weakest characteristic? Write two strategies.
Answer:
Two strategies that I can use to improve the flexibility in my life is:
- Adopt an unbiased perspective and non-judgmental thinking
- Practicing meditation and mindfulness.
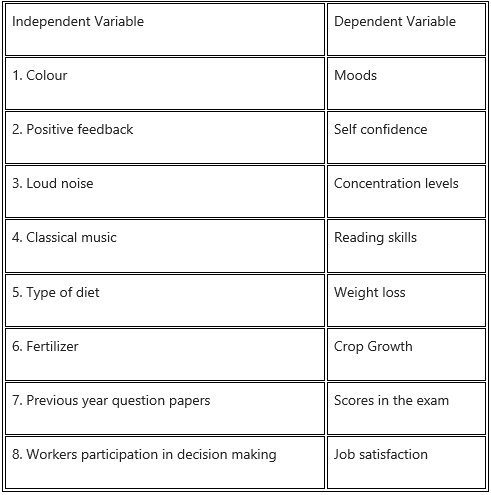
(A) Identify the Independent Variable and Dependent Variable.
- To study the effect of colour on moods.
- To study the effect of positive feedback on self-confidence.
- To study the effect of loud noise on concentration levels.
- To study the effect of exposure to classical music on reading skills.
- To study the effect of a type of diet on weight loss.
- To study the effect of a fertilizer on crop growth.
- To study the effect of solving previous years exam papers on scores in the exam.
- To study the effect of worker’s participation in decision making on job satisfaction.
Answer:
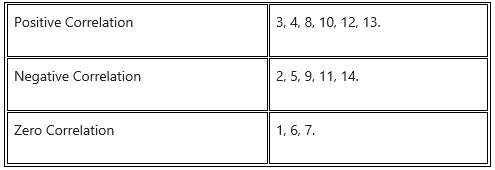
(B) Identify the type of correlation.
- Gender and Intelligence.
- Cold weather and sales of air conditioners.
- Low income and standard of living.
- Consuming foods with antioxidants and immune system.
- Speed and time taken to cover a distance.
- Heads/tails, on flipping a coin and result when you flip another time.
- Colour of the hair and learning a dance form.
- Average temperature in a city and ice cream sales in it.
- Chain smoking and lifespan.
- Intelligence and language development.
- Increasing age after 60 years and physical agility.
- Level of water in a fish tank and area of fish habitat.
- Large number of trees felled and probability of soil erosion.
- More hours spent at work and available leisure time.
Answer:
ACTIVITIES (Textbook Page. No. 1)
Activity 1
Read the following statements. Think and discuss whether the given statements are facts or myths and misconceptions about psychology:
(i) Psychology is just common sense and not a real science.
(ii) Psychology is simply a pseudoscience.
(iii) Psychologists are simply mind readers or the face readers.
(iv) Psychology is related only to the study of crazy people who are in need of therapy.
(v) Psychologists, psychiatrists and counsellors have the same professional qualifications and their jobs are almost of the same nature.
(vi) Anyone with a degree in psychology can provide counselling to a need person. Answer:
Answer:
All the statements are misconceptions.
Statement 1, 2 are misconceptions because Psychology is a social science that fulfils the criteria of a science, e.g., it employs the scientific method.
Statement 3 is a misconception. Psychologists are trained professionals in some field of psychology, e.g., counselling psychology. They employ tools like observation, case study, experiments, etc.
Statement 4 is a misconception. There are numerous branches of psychology such as Social Psychology, Developmental Psychology, Abnormal Psychology, Environmental Psychology, etc.
Statement 5 is a misconception. Psychiatrists are trained medical doctors and focus on medication management. Psychologists employ psychotherapy such as CBT, REBT, etc.
Statement 6 is a misconception. A counsellor is a person who has academic qualifications as well as professional training in counselling techniques.
Activity 2 (Textbook Page. No. 3)
Read the following statements and discuss about the same in the classroom:
(i) Psychology is a science because it fulfils many conditions of science.
(ii) Psychology is not an exact science like physics or chemistry.
(iii) Psychology is a social science that studies human (and animal) behaviour and mental processes.
(iv) Psychology uses some objective research methods, it examines cause-and-effect relationships to produce laws governing human behaviour and its findings can be verified.
(v) Psychology can be distinguished from pseudoscience and folk wisdom as psychology has evidence against its theories.
(vi) The subject matter of psychology is complex as human behaviour is dynamic and the mental processes are abstract. Therefore, the theories of psychology are not as universal, exact and precise as those in physics and chemistry.
Answer:
- Psychology fulfils conditions of science such as acquiring empirical evidence, objectivity, predictability, scientific causality, etc.
- Psychology is a social science which deals with human beings. It is not a physical science.
- Psychology is defined as the scientific study of human behaviour and mental processes.
- Psychology uses objective methods like controlled laboratory experiments and aims to establish scientific causality and verifiable theories.
- Psychology is not based on folk wisdom, pseudo knowledge or myths. It is based on systematic exploration and acquisition of empirical evidence.
- Psychology is a social science so its theories cannot be universal or exact as in the physical science. Human behaviour is constantly evolving and unpredictable.
Activity 3 (Textbook Page. No. 4)
Visit the website given below and collect information about various schools of thought of psychology: https://www. verywellmind.com/psychology-schools-of-thought-2795247
Answer:
- Structuralism – Focused on breaking down mental processes into the basic elements using techniques like introspection.
- Functionalism – Focused on the mind’s functions and adaptations.
- Gestalt school – Focused on looking at the ‘whole’ rather than individual elements.
- Behavioural school – Focused on study of observable behaviour.
- Psychoanalytic school – Emphasized the influence of the ‘unconscious’ on behaviour.
- Humanistic school – It developed as a response to psychoanalysis and behaviourism. It focused on individual free will, personal growth and concept of self-actualization (achieving one’s full potential).
- Cognitive school (Cognitivism) – Focused on the study of mental processes like learning, perception, memory etc.
In recent times, Behavioural school, Cognitive school and Humanistic school remain influential. Most psychologists adopt an eclectic approach drawing upon different perspectives.
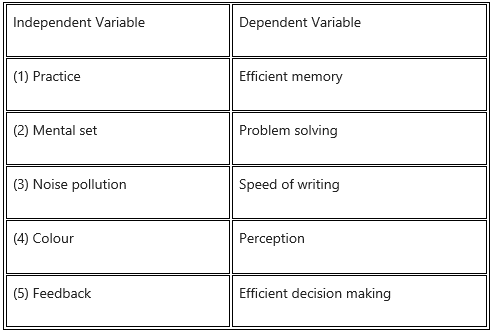
Activity 5 (Textbook Page. No. 5)
Find out the Independent Variable and Dependent Variable from the experiment ideas given below:
(i) To study the effect of practice on memory.
(ii) To study the effect of mental set on problem solving.
(iii) To study the effect of noise pollution on the speed of writing.
(iv) To study the effect of colour on perception.
(v) To study the effect of feedback on decision making.
Answer:
Activity 6 (Textbook Page. No. 8)
Discuss about the following topics that can be studied using correlation study method:
(i) Bunking lectures and score in exams
(ii) Weight and intelligence
(iii) Amount of salary and level of job satisfaction
(iv) Rehearsal and forgetting
(v) Height and aptitude in music
(vi) Urbanization and pollution
(vii) Speed of vehicles and road accidents
Answer:
(a) Positive correlation
- Urbanization and pollution
- Speed of vehicles and road accidents
(b) Negative correlation
- Bunking lectures and score in exams
- Rehearsal and forgetting
(c) Zero correlation
- Weight and intelligence
- Height and aptitude in music