Chapter 1 Sources of History
Textbook Questions and Answers
1. Complete the names of the following sources of history:
Question 1.
l _ _ _ _ d
Answer:
legend
Question 2.
t _ _ _ _ h
Answer:
tarikh
Question 3.
b _ _ _ _ r
Answer:
bakhar
Question 4.
p _ _ _ _a
Answer:
Powada
Question 5.
i _ _ _ _ i _ _ i _ n
Answer:
inscription
Question 6.
m _ _ u _ _ _ t
Answer:
monument
2. Let’s write:
Question 1.
What do monuments include?
Answer:
Monuments include samadhis, graves and veergalas and buildings.
Question 2.
What is a Tarikh?
Answer:
Tarikh or Tavarikh means the sequence of events.
Question 3.
What qualities of the author are important in the writing of history?
Answer:
The author’s integrity, impartiality and neutrality are very important in writing history.
3. Find the odd man out:
Question 1.
Material sources, written sources, unwritten sources, oral sources.
Answer:
unwritten sources
Question 2.
Monuments, coins, cave sculptures, stories.
Answer:
stories
Question 3.
Bhurjapatra, temples, treatises, paintings.
Answer:
temples
Question 4.
Owis, tarikhs, folk tales, myths.
Answer:
tarikhs
4. Explain the following concepts:
Question 1.
Material sources
Answer:
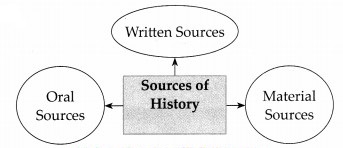
Those authentic material evidences or proofs of the ancient period which support our study of historical events are called material sources of history, e.g. memorials, buildings, cave sculptures, inscription, coins, copper, plates, forts, etc.
Question 2.
Written sources
Answer:
Those authentic evidences or proof of the ancient period which are in written form are called written sources of history, e.g. Documents of proceedings in Courts of kings, genealogies, Shakavali, correspondence, dispatches, treatises, biographies, travelogues, chronicles, Tavarikh, etc.
Question 3.
Oral sources
Answer:
We understand various aspects of folk life through folk literature traditionally passed from generation to generation and they are known as oral sources of history, e.g. Myths, Folk songs, Gatha, Shlokas, Abhangas, Powadas Proverbs, Legends, etc.
5. Is it necessary to evaluate sources of history ? Give your opinion.
Answer:
(i) Yes, it is necessary to evaluate the sources of history.
(ii) Just because a source is old does not mean it is reliable or true. We should examine their authenticity and see which sources are genuine and which are fake.
(iii) We must evaluate its quality with the help of different methods and through critical analysis.
(iv) It is necessary to determine the integrity, impartiality and neutrality of the authors by knowing their personal interests, the period during which they lived and political pressures on them.
6. Write why in your words:
Question 1.
A stone inscription is considered to be an authentic source of history.
Answer:
A stone inscription, i.e. a carving on the stone is a very authentic source of history as it throws light on different features of the ancient time like the language of communication which existed, script used and the social, political and economic life of a period, etc.
Question 2.
Oral sources reveal various aspects of people’s lives.
Answer:
(i) Various aspects of folk life through folk literature passed on to us by our ancestors.
(ii) They are pearls of wisdom and they hold a wealth of knowledge about the past.
(iii) It throws light on the rich cultural life of the past and different art forms which were practised in those times.
Activity:
Visit any museum that is nearby. Gather information about the sources of history from the period that you are studying and record it in your activity book.
In Text Questions and Answers
Formative Evaluation
Can you tell?
Question 1.
How do coins narrate history?
Answer:
(i) The coins made by different rulers using metals like gold, silver, copper are important sources of history.
(ii) From these coins we learn about the rulers, the period they ruled in, governance, religious ideas, personal details and use of language in that period.
(iii) Similarly, we also learn about the financial transactions and economic conditions, the advancement in metallurgy prevailing at that time.
(iv) From the images of Ram-Sita on the coins of Emperor Akbar or Shiva Parvati on the coins of Hyder Ali we see religious co-ordination of those days.
Speak your thoughts:
Question 1.
Suggest measures for preserving sources of history.
Answer:
(i) Written documents can be digitized and at the same time the original source should be preserved.
(ii) Controlling moisture by storing artefacts in an encasement which is oxygen free can help in their preservation.
(iii) Museums and other institutions must put in place steps and measures to preserve material sources of history in a scientific manner.
(iv) Handling, storage and display of artefacts must be done with care.
(v) Artefacts and other sources must be kept locked and continuous monitoring must be ensured to avoid any loss.
If any artefacts show signs of deterioration, conservationist must be called in for restoration of the same.
Additional Important Questions and Answers
Complete the sentence by choosing the appropriate words from the options given below:
Question 1.
The period from the ninth century CE till the end of the eighteenth century is considered to be the _____ period of Indian history. (Ancient, Medieval, Modern)
Answer:
Medieval
Question 2.
History gives us a chronological, scientific and systematic account of ______ events. (past, present, future)
Answer:
past
Question 3.
Historical sources should be used judiciously and only after a ______. (thorough reading, indepth study, critical analysis)
Answer:
critical analysis
Question 4.
Veergala is a ________. (fort, monument, palace)
Answer:
monument
Question 5.
The Peshwas used the _______ language on their coins. (Arabic or Persian, Hindi or Sanskrit, Pali)
Answer:
Arabic or Persian
Question 6.
Travellers of other countries who came to India have written ______ or accounts of their travels, (biography, autobiography, travelogues)
Answer:
travelogues
Question 7.
Tavarikh or Tarikh means the ______. (information about past, sequence of events, dates)
Answer:
sequence of events
Question 8.
The author’s ______ is very important in writing history. (viexvpoint, perspective, impartiality and neu trality)
Answer:
impartiality and neutrality
Question 9.
An, _____ is a carving on a stone, or a wall. (metal plate, inscription, edict)
Answer:
inscription
Question 10.
______ is a type of chronicle that originated in Maharashtra. (Bakhar, Myths, Travelogues)
Answer:
Bakhar
Find the odd man out:
Question 1.
Genealogies, Travelogue, Chronicles, Inscription.
Answer:
Inscription
Question 2.
Churches, Temples, Mosques, Myths
Answer:
Myths
Name the following:
Question 1.
The subject which gives us a chronological, scientific and systematic account of past events.
Answer:
History.
Question 2.
Any two metals used by different rulers in the past to make coins.
Answer:
Gold, Silver
Question 3.
One place in Tanjavur where inscriptions are found.
Answer:
Brihadishwara temple premises.
Question 4.
Two things inscribed on copper plates.
Answer:
(a) Royal edicts
(b) Verdicts
Question 5.
Any two scripts used in the Medieval period.
Answer:
(a) Devanagari
(b) Arabic
Question 6.
Written accounts of the travels by the travellers from other countries.
Answer:
Travelogues.
Question 7.
Any two travellers who visited India in the Medieval period.
Answer:
(a) A1 Biruni
(b) Ibn Batuta
Question 8.
Sanskrit biography of Shivaji Maharaj was composed by this poet.
Answer:
Paramanand.
Question 9.
A source of history which means the sequence of events.
Answer:
Tavarikh or Tarikh.
Question 10.
Two people who compiled Tavarikh.
Answer:
(a) A1 Biruni
(b) Ziauddin Barani.
Question 11.
A type of chronicle that originated in Maharashtra.
Answer:
Bakhar.
Question 12.
Any two chronicles written in Marathi.
Answer:
(a) Mahikavatichi Bakhar
(b) Sabhasad Bakhar
Question 13.
Any two contemporary western historians.
Answer:
(a) Robert Arm
(b) Grant Duff
Question 14.
Any two oral sources of history.
Answer:
(a) Owis
(b) Folk songs
Answer in one sentence:
Question 1.
What information does history give us?
Answer:
History gives us a chronological and systematic account of past events.
Question 2.
What must history be based on?
Answer:
History must be based on authentic evidence or proofs which are known as sources of history.
Question 3.
What are the different sources of history?
Answer:
Material sources, written sources and oral sources are the three different sources of history.
Question 4.
How should we use different sources of history?
Answer:
We have to use the different sources of history judiciously and only after critical analysis.
Question 5.
What do we learn when we look at forts and monuments built in the past?
Answer:
When we look at the forts and monuments we come to know about the development of architecture, the economic conditions, the quality of art, style of the building construction and people’s standard of living in that particular period.
Question 6.
Why is an inscription considered to be a very important and reliable source of history?
Answer:
An inscription is considered to be a very important and reliable source of history because it helps us to understand features like the language, script, social life of a period etc.
Question 7.
What are known as copper plates?
Answer:
Inscriptions carved on sheets of copper are known as ‘copper plates’.
Question 8.
How do we understand various aspects of folk life?
Answer:
We understand various aspects of folk life through folk literature traditionally passed from generation to generation.
Explain the following terms:
Question 1.
History
Answer:
History is a chronological, scientific and systematic account of past events.
Question 2.
An inscription
Answer:
An inscription is a carving on a stone or a wall.
Question 3.
Tavarikh or Tarikh
Answer:
Tavarikh or Tarikh means the sequence of events.
Question 4.
Bakhar
Answer:
Bakhar is a type of chronicle that originated in Maharashtra.
Question 5.
Chronicles
Answer:
Chronicles are written sources of history which help in understanding aspects like the contemporary political happenings, linguistic transaction, cultural life, social conditions, etc.
Classify the following into Material sources, Written sources and Oral sources of history:
Question 1.
Ornaments, Fort, Owis, Myths, Utensils, Folk songs, Weapons, Travelogue, Well, Biographies, Clothing, Powada, Copper plate, Folk tales, Coins, Shloka, Temples, Books
Answer:
Written Sources | Material Sources | Oral Sources |
Books, Travelogue, Copper plate, Coins, Temples | Ornaments, Forts, Utensils, Weapons, Well, Clothing | Owis, Myths, Folk songs, Hearsays, Powada, Folk tales, Shloka |
Complete the following diagrams:
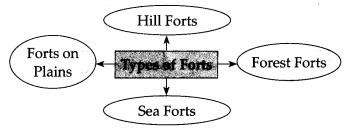
Question 1.

Answer:
Question 2.
Answer:
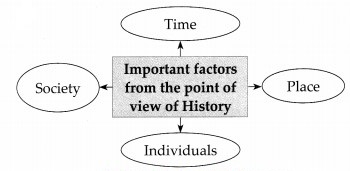
Question 3.
Answer: