Chapter 1 Story of Psychology
1A. Complete the following statements.
Question 1.
Psychology is a study of ______________
(A) mind
(B) behaviour
(C) soul
Answer:
(B) behaviour
Question 2.
processes include thinking, memory, emotions, etc.
(A) Mental
(B) Cognitive
(C) Spiritual
Answer:
(B) Cognitive
1B. Match the following pairs.
Question 1.
A | B |
1. Tri-Doshas | a. First laboratory of Psychology |
2. Tri-Gunas | b. Study of unconscious |
3. Wilhelm Wundt | c. Perception, thinking, memory, etc. |
4. Sigmund Freud | d. Sattva, Rajas, Tamas |
5. Cognitive processes | e. Ashtanga Yog |
6. Patanjali | f. Kapha, Vata and Pitta |
Answer:
1 – f, 2 – d, 3 – a, 4 – b, 5 – c, 6 – e
1C. State whether the following statements are true or false.
Question 1.
Psychology is a study of the mind.
Answer:
False
Question 2.
The first mental hospital in India was established in Mumbai.
Answer:
False
Question 3.
There was no study of mental processes in India till the formal discipline of Psychology was recognized as a science.
Answer:
False
Question 4.
Dr. Sigmund Freud proposed the concept of the unconscious.
Answer:
True
Question 5.
Control is one of the objectives of Psychology.
Answer:
True
1D. Identify the odd item from the following and give reasons for the same.
Question 1.
Soul, Mind, Feeling, Consciousness, Behaviour.
Answer:
Feeling
Reason: Rest is the term used in the definition of Psychology.
Question 2.
Walking, dancing, playing, thinking, eating.
Answer:
Thinking
Reason: The rest are overt behaviours.
Question 3.
Yam, Niyam, Karya, Aasana, Pratyahar.
Answer:
Karya
Reason: The rest are the aspects of Ashtanga Yoga.
Question 4.
Feeling, memory, attention, perception
Answer:
Feeling
Reason: The rest are the processes in the study of cognition.
1E. Complete the following table.
Question 1.
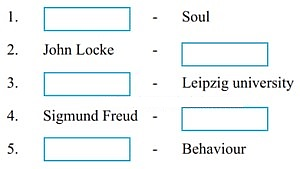
Answer:
1. Greek word: Psyche – Soul
2. John Locke – Empty slate
3. First Psychological Laboratory
4. Sigmund Freud – Founder of Psychoanalysis
5. John Watson OR Organism’s response to stimuli – Behaviour
2. Explain the following concepts.
Question 1.
Psychology
Answer:
The word Psychology is derived from Greek words – ‘Psyche’ and ‘Logos’. It is denoted by the Greek Alphabet “Psi” and the symbol is 4L Wilhelm Wundt defined it as “the study of consciousness”. Dr. Sigmund Freud defined it as “the study of unconsciousness”. John B. Watson defined it as “the science of human behaviour”. The latest definition of Psychology is ‘The study of human behaviour and mental processes.
For your understanding
- Conscious mind: It is the level of mind that someone is aware of at any particular point in time.
- Unconscious mind: It contains thoughts, memories, and desires that are buried deep in us. Although we are not aware of their existence, they exert great influence on our behaviour.
Question 2.
Behaviour
Answer:
In general, behaviour is an organism’s response to various internal and external stimuli.
John Watson defined behaviour as ‘anything that can be observed, recorded and studied in human beings and animals.’ Behaviour is either overt (seen) or covert (hidden).
Question 3.
Overt behaviour
Answer:
Overt behaviour is that behaviour that is directly noticeable or observable. It includes responses such as walking, talking, dancing.
Question 4.
Covert behaviour
Answer:
Covert behaviour is that which is not directly noticeable but can be inferred from behaviour like thinking, feeling. It basically includes mental processes.
Question 5.
Stimulus
Answer:
Stimulus is defined as any physical event or condition that gives rise to a reaction. It can be external or internal.
In simple words, it is an object or event that elicits a sensory or behavioural response in an organism.
Question 6.
Response
Answer:
A response is defined as a reaction of the organism to a given stimulus. All organisms respond differently to the same stimulus.
Example:
Stimulus (S): A teacher asks students to prepare a presentation.
Organism (O): All students present in class.
Response (R):
- Some students actively participate in presentations.
- Some students remain silent as they are scared to talk in front of the entire class.
3. Answer the following questions in 35-40 words.
Question 1.
Psychology is a science: explain why?
Answer:
- Psychology is the scientific study of human behaviour and mental processes.
- Through experiments and observations, Psychologists try to analyze and predict human behaviour. This shows the empirical nature of Psychology.
- Wilhelm Wundt used scientific methods to study fundamental psychological processes. John Watson also conducted scientific research on animal behaviour and child-rearing.
Question 2.
Explain the S-O-R model, with your own experience.
Answer:
-
The S-O-R model explains how organisms respond differently to the same stimulus. It can be explained as follows:

- Example: Suppose Neha is an excellent orator while her friend Seema is afraid of public speaking.
- Stimulus: The teacher asks Neha and Seema to give speeches.
- Organism: Neha and Seema.
-
Response: Neha will confidently give her speech.
Seema is likely to get cold feet and become nervous.
- This shows that different organisms (Neha and Seema) react differently to the same situation.
Question 3.
Explain the goals of Psychology.
Answer:
- Describe
- To precisely identify and classify behaviours and mental processes
- Involves recording behaviour using various tools
- Explain
- To understand the causes of behaviour through meaningful explanation of facts
- Involves the use of standardized tests
- Behaviour observed in most people can be generalized
- iii. Predict
- To predict how given conditions will lead to a particular behaviour and mental processes.
- b. Involves knowledge of possible outcomes
- Control
- To mould behaviour in a particular direction
- Involves the use of psychological principles and psychotherapeutic techniques
4. Give a historical account of the emergence of Psychology as a science.
Answer:
- Psychology is a vast field studying behavioural aspects of mankind and it started as a branch of Philosophy. It evolved as a separate branch in the 19th century.
- The first attempt to define Psychology was made based on the terminology. The word ‘Psychology’ is derived from two Greek words: ‘Psyche’ (soul or mind) and ‘Logos’ (science or branch of knowledge).
- Rational sciences establish facts based on observation and experimentation. However, neither soul nor mind can be observed. Hence, the definition of Psychology changed over time.
- In the late 19th century, Wilhelm Wundt established the first psychological laboratory at Leipzig University. He defined Psychology as the study of consciousness.
- Sigmund Freud defined Psychology as the study of the unconscious while John Watson defined it as ‘Science of human behaviour’.
- The latest definition of Psychology is the ‘Study of human behaviour and processes.’
- Psychology as a discipline evolved over time.
5. Describe the goals of Psychology.
Answer:
- Describe
- To precisely identify and classify behaviours and mental processes
- Involves recording behaviour using various tools
- Explain
- To understand the causes of behaviour through meaningful explanation of facts
- Involves the use of standardized tests
- Behaviour observed in most people can be generalized
- Predict
- To predict how given conditions will lead to a particular behaviour and mental processes.
- Involves knowledge of possible outcomes
- Control
- To mould behaviour in a particular direction
- Involves the use of psychological principles and psychotherapeutic techniques
Activities
Activity 2. (Textbook Page No. 3)
Do you agree with the definition of Psychology as the Science which deals with the soul? If yes why? If no, why?
Answer:
- No, I don’t agree with this definition since the soul refers to the spiritual part of a person; which is believed to exist in some form even after death.
- Psychology is not a spiritual science. Since it studies the mental activities and behaviour of living beings, this definition seems to be incorrect.
Activity 3 (Textbook Page No. 3)
Collect information about Bahinabai Chaudhari: Mana (description of Mind)
Answer:
- Bahinabai Chaudhari (11 Aug 1880 – 3 Dec 1951) was an illiterate cotton farmer from the Jalgaon district in Maharashtra.
- She was a famous Marathi poet. Her poems captured the essence of her life, reflect the culture of the village and farming life, and present her wisdom.
- She has beautifully compared the mind with different aspects of nature such as wind, waves, butterflies, small particles, etc. The poet stressed that the mind is a unique creation of God and nothing in this world compares to it.
Activity 5 (Textbook Page No. 4)
Do you agree with the definition that Psychology is the study of the unconscious? What could be the limitations of this definition?
Answer:
I agree with the above definition because Psychology studies unconscious behaviour. A person himself may not be aware of unconscious aspects of his personality even when it may have a significant impact on his thoughts and behaviour. Psychology enables us to understand this unconscious side of human beings and hence, I agree with this definition. However, the limitation of the definition is the unconscious mind. It can’t be observed directly and hence is difficult to study it. Furthermore, Psychology is also concerned with the study of the conscious mind.
Activity 6 (Textbook Page No. 5)
Make a note of how your friends react to the same stimulus in a different way. Example: examination.
Answer:
- Nisha and Seema are two of my friends. During the examination, Seema gets extremely tensed. She is not able to concentrate. She even fails to sleep and eat peacefully.
- She needs the constant emotional support of her parents and friends to overcome her fear.
- Conversely, Nisha views the exam as a challenge. She does not get worked up.
- Instead, her moderate tension motivates her to study sincerely.
- She also knows that failure is a part and parcel of life and tries to learn from each mistake.
- Hence, she remains calm and confident even during the exam period.
Activity 8 (Textbook Page No. 6)
Find out more attributes of Vata, Kapha, and Pitta.
Answer:
Vata:
- Elements: Air + Space
- Body Type: Slim, lean
- Properties: Energetic, Moody, Creative
Kapha:
- Elements: Earth + Water
- Body Type: Average build, moderate weight
- Properties: Strong build, Affectionate, Cool
Pitta:
- Elements: Fire + Water
- Body Type: Large frame, heavy
- Properties: Smart, Fiery nature
Activity 9 (Textbook Page No. 6)
Find out different characteristics of Rajas, Tamas, and Sattva Guna.
Answer:
Rajas represent passion, action, energy, and motion. Tamas manifests itself as impurity, laziness, and darkness. Sattva manifests itself as purity, knowledge, and harmony.
Activity 10 (Textbook Page No. 7)
Look at the statements given below. Analyze each one of them and come up with goats of Psychology or the role that Psychology plays in real life.
Question 1.
A group of Psychologists observed 1000 individuals and recorded their behaviour and reactions.
Answer:
The goal of description (What): Describing what happens in a particular situation
Question 2.
After analyzing their responses, they tried to understand the reasons behind their behaviours.
Answer:
The goal of explanation (Why): Explaining why a particular instance happened
Question 3.
These observations can be generalized to the entire population. Therefore behaviour of an individual under stressful situations can be predicted.
Answer:
The goal of prediction (Anticipate): Predicting how people will behave under a given situation
Question 4.
The Psychologists came up with some conclusions so that people can change their responses to stressful situations for the better.
Answer:
The goal of control (Modify): Controlling actions of human beings with the help of psychological techniques.
Activity 11 (Textbook Page No. 8)
Find more examples of each of the above goals of Psychology. They could be real examples that you know or you have read about or they could be fictional examples.
Answer:
Goal | Example | Explanation |
i. Describe | Recording how different students behave during exam period | Neha is confident while Reena gets anxious. |
ii. Explain | Analyzing why different students behave in different ways during exam | Neha has always done well in exams while Reena gets tensed due to over-expectations from her parents. |
iii. Predict | Anticipating how students will react in other stressful situations | Neha is likely to handle stressful situations calmly than Reena |
iv. Control | Enabling anxious students to control their anxiety level during exams and other stressful situations | Reena could take counselling to improve her abilities to deal with examinations and other stressful situations. |
