Chapter 10 Human Occupations
Textbook Questions and Answers
A. Select the correct option:
Question 1.
Serving as a ______ is a tertiary type of occupation.(bus conductor, veterinary doctor, brick kiln worker)
Answer:
bus conductor
Question 2.
In the tropical areas, we mainly see ________ occupations. (primary; secondary, tertiary)
Answer:
primary
Question 3.
Amol’s Granny sells papads and pickles. This is a _______ occupation. (primary, secondary, tertiary)
Answer:
secondary
B. Give reasons:
Question 1.
The type of occupation determines a person’s
income.
Answer:
(i) Occupation is a job, a person’s role in society wherein a regular activity is carried out for income.
(ii) Certain occupations bring greater economic benefits to the society and the nation at large while certain occupations bring relatively less economic benefits.
(iii) Similarly some occupations require higher level of knowledge and skill while some can be carried out with little or no skill or expertise. Person’s income is proportionate to the economic benefit his occupation brings with it and the land of his knowledge and skill. So the type of occupation determines a person’s income.
Question 2.
Primary occupations are associated with developing countries while tertiary, with developed countries.
Answer:
(i) Countries which are developing have low income as they are in a state of development and their main source of income comes from production carried out in primary sector.
(ii) Developed countries are rich with high income and so they practice tertiary occupation. They have enough money to invest in business which creates tertiary occupations which requires huge investment.
Question 3.
Quaternary occupations are not commonly seen.
Answer:
Quaternary occupations are occupations which require special knowledge, skills and expertise. This sectorevolves in well-developed countries and requires skilled workforce apart from sufficient money to invest in fields like IT, research and development, quality testing, etc.
Activity:
- Visit a secondary occupation in your area.
- Gather information related to that occupation
- using the following points and note it down.
- Name of the occupation
- Raw material used
- Source of raw material
- Finished product
- Market for finished product
- Tertiary occupations required in it.
In Text Questions and Answers
Look at the figure and answer the following questions:

Question 1.
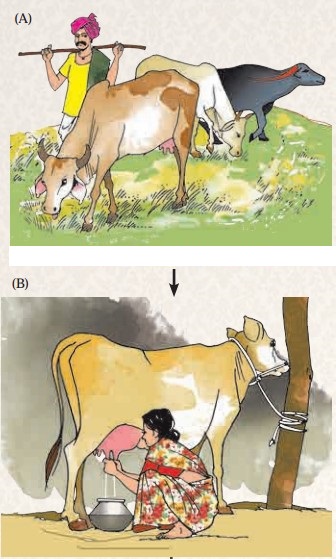
What are the cows and buffaloes in picture A doing?
Answer:
The animals, cows and buffaloes are grazing in the pasture, i.e. land covered with grass and other low plants.
Question 2.
What is being obtained in picture B?
Answer:
Milk is being obtained in picture B.
Question 3.
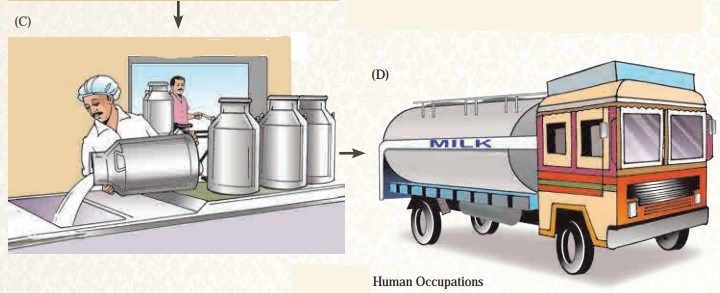
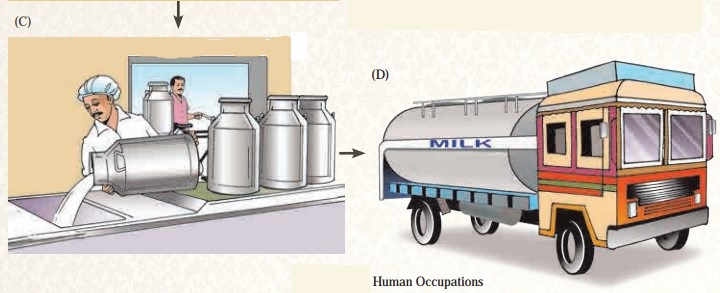
What is happening at the Milk Collection Centre in picture C?
Answer:
Milk is being filled for storage and sold at the milk collection centre.
Question 4.
In picture D, what is being transported? Where could the tanker be going?
Answer:
Milk is being transported to the milk processing centre. The tanker is on the truck
Question 5.
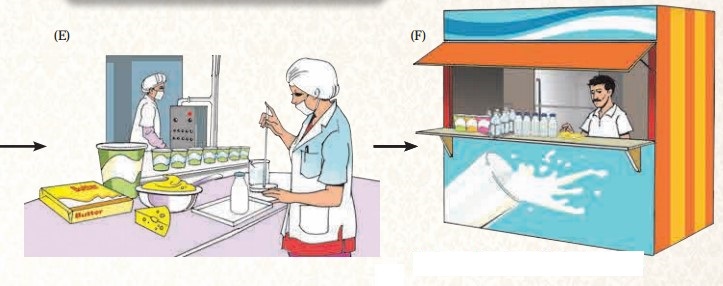
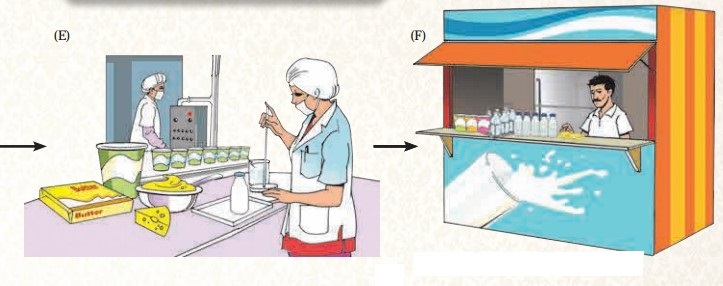
Which products are seen in picture E? From what have these products been made?
Answer:
Curd, ghee, butter, cheese and shrikhand are the products seen in picture E and these products have been made from milk.
Question 6.
What else is happening in picture E?
Answer:
In picture E, person is testing the quality of the prepared milk products.
Question 7.
Out of the products shown in picture F, which products do you use?
Answer:
I use all the products shown in picture F as milk products are high on nutrients and good for health.
Question 8.
What would be main difference between milk and milk products?
Answer:
Milk is a beverage obtained from nature, directly from different animals. While milk products are obtained by processing milk into different products.
Question 9.
Do these products perish quickly like milk?
Answer:
No, they have a longer life unlike milk.
Look at the figure and answer the following questions:
Question 1.
Which of these activities is undertaken to obtain a product from nature?
Answer:
Obtaining milk from the cow is the activity undertaken to obtain a product from nature.
Question 2.
How long does this product last?
Answer:
If refrigerated it will last for about five days to one week.
Question 3.
In which picture is the product obtained from nature being collected?
Answer:
In picture C, the product obtained from nature is being collected.
Question 4.
Which service did the milk producer get through this activity?
Answer:
Transport and unloading of milk, a tertiary service is the service which the milk producer received.
Question 5.
Where is milk being taken? What happens to the milk thereafter?
Answer:
The milk is being taken to the milk processing centre for processing milk to make milk products.
Question 6.
What milk products are seen in the picture?
Answer:
Ghee, butter, cheese, shrikhand are the products seen in the picture.
Question 7.
Who inspects these products?
Answer:
A food inspector, a person with special skill and expertise inspects these products.
Question 8.
What does the shopkeeper do with these products?
Answer:
The shopkeeper sells these products to the consumer.
Question 9.
Which of these products are perishable and which are non- perishable?
Answer:
All are the products, even after proper storage will deteriorate and perish over a period of time.
Question 10
Will the price and weight of these products be same as that of the milk?
Answer:
The price and weight of these products will be higher after processing. These products will be more durable and its quality too will be enhanced and so their price will be also higher.
Use your brainpower!
Question 1.
Milk is available at ₹ 40 per litre while dahi at ₹ 60 per kg and paneer at ₹ 200 per kg. If both are obtained from milk, why is there so much difference in their prices?
Answer:
Milk is being processed, obtained from nature and made it into different products. These products are more durable. Their quality its enhanced and therefore their price is higher.
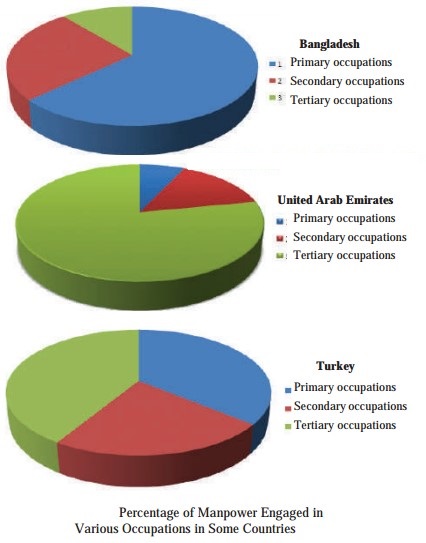
Answer the following questions based on the pie charts:
Question 1.
Which country has more manpower engaged in primary occupation?
Answer:
Bangladesh.
Question 2.
Which country has more manpower engaged in secondary occupation?
Answer:
Turkey.
Question 3.
Which country has more manpower engaged in tertiary occupations?
Answer:
United Arab Emirates.
Question 4.
Which country has almost equal manpower engaged in all the occupations?
Answer:
Turkey.
Think a little!
Who am I?
Question 1.
Who examines us when we fall ill?
Answer:
Doctor
Question 2.
Who checks our examination papers?
Answer:
Teacher
Question 3.
Who prepares the designs of buildings?
Answer:
Architect
Question 4.
Who produces machines and looks after their maintenance and repairs?
Answer:
Engineer
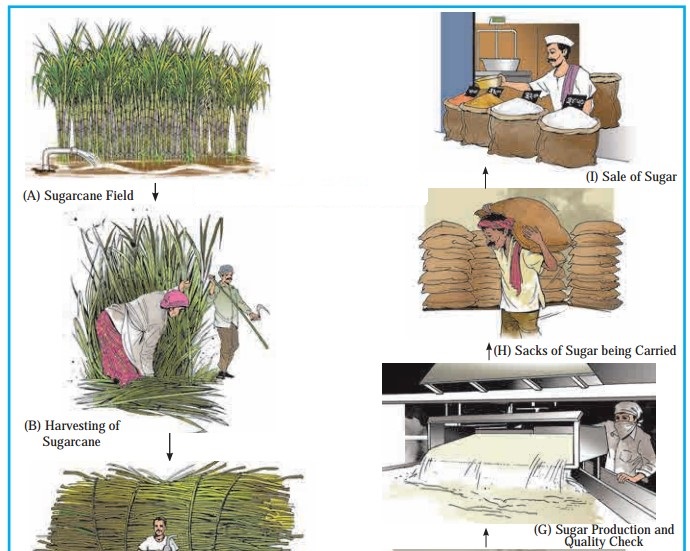
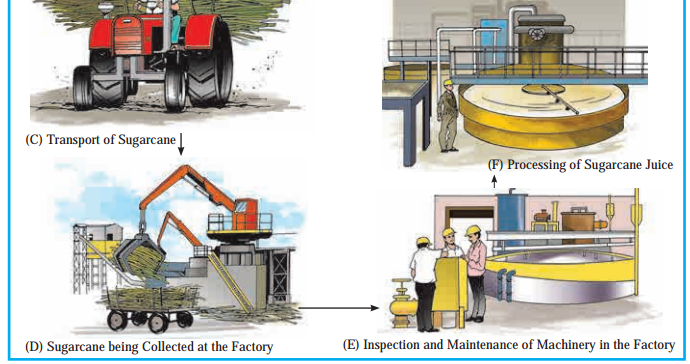
Observe figure and answer the questions related to sugar production:
Question 1.
Classify the occupations from primary to quaternary
Answer:
Primary | Secondary | Tertiary | Quaternary |
Harvesting of sugarcane | Sugarcane being collected at factory | Transport of sugarcane | Quality check |
Processing of sugarcane juice | Sacks of sugar being canned |
Inspection and
| |
Sugar production | Sale of goods |
Question 2.
Which raw material is used in the secondary occupation?
Answer:
Sugarcane is the raw material used in the secondary occupation.
Question 3.
Which is the finished product obtained in the secondary occupation?
Answer:
Sugar is the finished product obtained in the secondary occupation.
Question 4.
What are the services in tertiary occupations?
Answer:
Transport of sugarcane, sacks of sugar being carried and sales of goods are the services in tertiary occupations.
Question 5.
Which picture is related to a quaternary occupation? Can you name the occupation?
Answer:
Picture G is related to a quaternary occupation. The occupation is quality testing.
Think and discuss:
What effect does nature have on our occupations? Think a little. Give a thought to the following issues. Discuss them in the class. Write two paragraphs about it.
- There have been no rain at all (drought).
- A storm strikes
- There was an earthquake.
- Untimely rains
- Good rains
- Excessive rains and floods
- All of a sudden, a volcano erupts
- A tsunami hits.
Answer:
Primary occupations like agriculture can be totally disrupted if there are no rains or excessive rains while good rains will usher with good agricultural output. When we receive good agricultural yield it will have a positive input on all secondary occupations which rely on agriculture. It will bring about all-round growth in both agricultural and industrial sector.
Natural calamities like storms, earthquake, volcanoes and tsunami can have adverse impact on various occupations. It can bring all the primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary occupations to a standstill. Occupations related to production, storage, distribution, etc. will be greatly affected as rescue and rehabilitation of the people and reconstruction of the damaged caused, becomes a priority.
Do it yourself!
Question 1.
Which occupations are found in your area?
Answer:
I live in Maharashtra and occupations like textile manufacture, manufacture of sugar, pharmaceutical, petrochemicals, electronics, automobiles, engineering services, food processing, etc. are practised here.
Question 2.
Which occupation is practised on a large scale?
Answer:
Sugar manufacturing is an occupation which is practised on a large scale.
Question 3.
Find the reason behind it.
Answer:
Advantageous location of Maharashtra, progressive government policies, availability of raw material, i.e. sugarcane, good infrastructure and above all the ownership given to farmers in sugar factories are the reasons why this occupation is practised on a large scale.
Question 4.
Both human and natural factors affect occupations. Can you find those factors?
Answer:
Development of industries, availability of technical know-how and skilled manpower, existing labour laws and government policies pertaining to occupations development of infrastructure are the human factors that affect occupations.
Climate, terrain of a region, fertility of soil, susceptibility to natural calamities, availability of raw materials, etc. are the natural factors which affect occupations.
Question 5.
Obtain information about the damage caused to the environment through different occupations.
Answer:
Pollution of the environment in all its form – air, water, soil and land, deforestation, soil erosion, depletion of the ozone layer, etc. are some of the damages caused due to different occupations practised.
While practising occupations we should be careful not be cause of hazardous air emissions, land contamination leading to soil pollution, marine and coastal pollution caused due to untreated waste water, etc. Sustainable development, let us remember should be the need of the hour.
Visit a secondary occupation in your area gather information related to that occupation using the following points and note it down:
Answer:
Name of the occupation | Pharmaceutical manufacturing. |
Raw material used | Animal extracts, herbal extracts, additives like glaze, talc, etc. and chemical substances. |
Sources of raw material | From different parts of India, some raw materials are imported from other countries. |
Finished products | Medicine and other pharma products. |
Market of finished products | National and international markets including US, UK, Australia, Russia, Germany, etc. |
Tertiary occupations | Transport of goods, loading and unloading of goods and sale of goods. |
Additional Important Questions and Answers
Complete the following statements by choosing the correct options:
Question 1.
Occupations which are dependent on nature are called _______ occupations. (secondary, primary, tertiary)
Answer:
primary
Question 2.
Processed products are ________.(non-perishable, more durable, less durable)
Answer:
more durable
Question 3.
Occupations dependent on primary occupations are called ______ occupations. (primary, secondary, quaternary)
Answer:
secondary
Question 4.
The occupations which provide complimentary services to the other two occupations are called _________ occupations. (tertiary, secondary, primary)
Answer:
tertiary
Question 5.
Countries which have more manpower engaged in _______ activities are considered to be developed countries. (primary , secondary, tertiary)
Answer:
tertiary
Question 6.
Countries which have more manpower engaged in primary activities are considered to be _____ countries. (developed, developing, under developed)
Answer:
developing
Question 7.
transactions decide the country’s ______.(production, occupation, manpower)
Answer:
primary
Arrange the following in proper order:
- Selling milk products in the market.
- Obtaining milk and selling milk.
- Processing milk at milk processing centres.
- Rearing of domestic animals.
- Making ghee, butter, cheese, shrikhand, paneer, milk powder, etc.
Answer:
- Rearing of domestic animals.
- Obtaining milk and selling milk.
- Processing milk at milk processing centre.
- Making ghee, butter, cheese, shrikhand, paneer, milk powder, etc.
- Selling milk products in the market.
Match the pairs correctly:
Question 1.
Column A | Column B |
(1) Animal husbandry and fishing | (a) secondary occupation |
(2) Processing of milk | (b) tertiary occupation |
(3) Transport of goods | (c) quaternary occupation |
(4) Quality testing of product | (d) primary occupation |
(5) Transaction of the country | (e) economic transactions |
(f) production |
Answer:
1 – d
2 – a
3 – b
4 – c
5 – f
Name the following:
Question 1.
Any two products obtained after processing milk at milk processing centre:
Answer:
- Butter
- Cheese
Question 2.
Any two animals domesticated by man:
Answer:
- Cow
- Buffalo
Question 3.
Occupation which is directly dependent on nature:
Answer:
Primary occupations.
Question 4.
Occupations dependent on primary occupations:
Answer:
Secondary occupations.
Question 5.
Occupations which provide complementary services to primary and secondary occupations:
Answer:
Tertiary occupations.
Question 6.
Occupations like sale of goods
Answer:
Tertiary occupations or service occupations
Question 7.
Occupations which requires special expertise:
Answer:
Quaternary occupations.
Question 8.
Countries which have more manpower engaged in tertiary activities:
Answer:
Developed countries.
Question 9.
Countries which have more manpower engaged in primary activities:
Answer:
Developing countries.
Complete the table:
Occupations | Definition | Examples |
Primary | ||
Secondary | ||
Tertiary | ||
Quaternary |
Answer:
Occupations | Definition | Examples |
Primary | Occupation which directly depend on nature are called primary occupations. | Farming, animal husbandry, mining, foresting, fishing. |
Secondary | Occupations dependent on primary occupations are called secondary occupations. | Food processing, manufacturing, construction. |
Tertiary | Occupations which provide complementary services to primary and secondary occupations are called tertiary occupations. | Transport of goods, commercial services, loading and unloading goods, sale of goods. |
Quaternary | The occupations which requires special expertise and special skills are called quaternary occupations. | Quality testing of food products, inspection and maintenance., IT. |
Answer the following questions in one sentence each:
Question 1.
Why does man undertake various activities?
Answer:
Man undertakes various activities to satisfy his need.
Question 2.
How are activities undertaken by man classified?
Answer:
Activities undertaken by man are classified on the basis of their nature and the products they yield.
Question 3.
Where are raw materials supplied to the industries often obtained from?
Answer:
Raw materials supplied to the industries are often obtained from nature.
Question 4.
Which occupations require special skills and expertise?
Answer:
Quaternary occupations requires special skills and expertise.
Answer the following questions in short:
Question 1.
Why are the prices of processed milk products higher?
Answer:
- Milk obtained from nature is processed and made into different products which involves high cost.
- These products are more durable.
- Their quality too is enhanced.
- Therefore their price is also higher.
Question 2.
Explain the term “Service occupation”.
Answer:
- The occupations which provide complementary services to the other two occupations, i.e., primary and secondary occupations are tertiary occupations.
- These occupations are complementary i.e., supportive to all other occupations.
- These occupations are called as service occupation e.g., transport of goods, loading and unloading of goods and sale of goods, etc.
Question 3.
A person testing the quality of a product is practising a quaternary occupation. Elaborate.
Answer:
- To test the quality of a product, a person must have some special skills.
- This service is not an ordinary one but the one which requires special expertise.
- Such services which requires special skills and expertise are called quaternary occupations.
Question 4.
How can we decide the extent of the country’s development?
Answer:
- Different occupations are practised in different countries of the world.
- Through these occupations, economic transactions occur within a country and between various countries.
- These transactions decide the country’s production of various goods and their national income.
- This, in turn, is used to decide the extent of a country’s development.
Question 5.
What decides the country’s annual income?
Answer:
Different occupations are practised in different countries of the world through which economic transactions occur within country and various countries which decide the country’s production of various goods and their annual income.
I can do this!
Question 1.
Answer:
Name different occupations |
|
Differences |
|
Question 2.
Classify the occupations from primary to quaternary.
Answer:
Primary occupations | Secondary occupations | Tertiary occupations | Quaternary occupations |
Farming, mining, forestry, animal husbandry, fishing | Manufacturing, construction, food processing | Commercial services, transport of goods, loading and unloading of goods, sale of goods | Research and development, IT, quality assurance, inspection and maintenance |