Chapter 13 Fulfillment of Struggle for Independence
Textbook Questions and Answers
1. Rewrite the statements by choosing the appropriate options:
Question 1.
There were more than six hundred small and big …………….. in India.
(a) states
(b) villages
(c) princely states
(d) cities
Answer:
(c) princely states
Question 2.
All the princely states merged with India except the states of Junagad, ……………. and Kashmir.
(a) Aundh
(b) Jhansi
(c) Vadodara
(d) Hyderabad
Answer:
(d) Hyderabad
2. Explain the following statements with reasons :
Question 1.
Junagad merged with India.
Answer:
- Junagad was a princely state in Saurashtra.
- The Nawab of Junagad wanted to merge the state with Pakistan.
- It was opposed by the people vigorously as they wanted the merger with India.
- Due to this, the Nawab fled to Pakistan and Junagad was merged with India in February, 1948.
Question 2.
The Indian government started police action against the Nizam.
Answer:
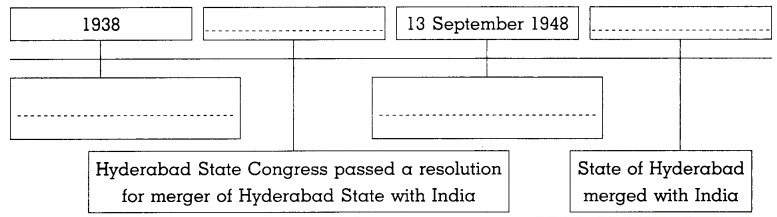
- Hyderabad State Congress passed a resolution for a merger of Hyderabad state with India in July 1947.
- The Nizam took an anti-India stand and tried for a merger with Pakistan.
- The Razakar organisation of Kasim Rizvi committed atrocities on Hindus as well as Muslims who supported the democratic movement.
- The Nizam did not respond to the appeal of the Government of India for peaceful negotiations.
- At last, the Government of India started police action on 13 September, 1948 and the state of Hyderabad was merged with India.
Question 3.
Hari Singh signed the Instrument of Accession with India.
Answer:
- Hari Singh the ruler of Kashmir, had decided to retain the independence of Kashmir.
- Pakistan was keen to secure the merger of Kashmir with itself.
- So, Pakistan began to put pressure on Hari Singh for this purpose.
- At the instigation of Pakistan, the armed intruders attacked Kashmir in October, 1947.
Therefore, Hari Singh signed the ‘Instrument of Accession’ with India.
3. Answer the following in Brief:
Question 1.
Explain the contribution of Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel in the integration of the Princely States in India.
Answer:
- The problem of the merger of the princely states was very tactfully handled by Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel, the then Home Minister of India.
- He convinced the Princes that the merger of their states with India was in their interest.
- He prepared the ‘Instrument of Accession’, acceptable to all.
- The Princes accepted the proposal and all the states except Junagad, Kashmir and Hyderabad were merged with India.
- These three states, too, were merged with India subsequently.
- Thus, he took a firm stand and solved the issue of merger of princely states.
Question 2.
Explain the contribution of Swami Ramananda Tirth in the struggle for liberation of Hyderabad.
Answer:
- Hyderabad was the largest princely state in India.
- The autocratic ruler, Nizam had denied civil and political rights to the people.?
- In 1938, Swami Ramananda Tirth formed Hyderabad State Congress.
- As Nizam banned his organisation, a struggle began for getting recognition to Hyderabad State Congress and democratic rights.
- In July, 1947 a resolution was passed by the Hyderabad State Congress for its merger with India.
- Swami Ramananda Tirth was assisted by Narayan Reddy and Siraj-ul-Hasan Tirmiji in his efforts.
Project:
Gather information and pictures related to the struggle for liberation of Hyderabad. Organise a Poster Exhibition based on it in the history department.
Additional Important Questions and Answers
Rewrite the statements by choosing the appropriate options:
Question 1.
Due to the influence of …………….., there was beginning of political awakening among the princely states.
(a) Champaranya Satyagraha
(b) Civil Disobedience Movement
(c) Non-Co-operation Movement
(d) Quit India Movement
Answer:
(c) Non-Co-operation Movement
Question 2.
Junagadh was a princely state in ……………… .
(a) Kutch
(b) Saurashtra
(c) South Gujarat
(d) East Gujarat
Answer:
(b) Saurashtra
Question 3.
Through ‘Vande Mataram’ movement ……………… participated in the struggle for liberation of Hyderabad.
(a) farmers
(b) workers
(c) students
(d) Nizam’s army
Answer:
(c) students
Question 4.
……………… is celebrated as ‘Marathwada Mukti Din’.
(a) 13 September
(b) 19 December
(c) 2 August
(d) 17 September
Answer:
(d) 17 September
Question 5.
There was significant contribution of ……………… Samaj in the Hyderabad Mukti Sangram.
(a) Arya
(b) Satyashodhak
(c) Brahmo
(d) Prarthana
Answer:
(a) Arya
Question 6.
The youth of Azad Gomantak Dal made an armed attack and liberated the territories of ……………… from Portuguese rule.
(a) Diu and Daman
(b) Goa
(c) Dadra and Nagar Haveli
(d) Chandianagai and Mahe
Answer:
(c) Dadra and Nagar Haveli
Question 7.
In 1949, France held a plebiscite in ………………
(a) Mahe
(b) Karaikal
(c) Puducheri
(d) Chandranagar
Answer:
(d) Chandranaga
Question 8.
……………… was an aggressive leader in this struggle for liberation of Goa.
(a) Swami Ramananda Tilth
(b) Govindbhai Shioff
(c) Mohan Ranade
(d) Babasaheb Paianjpe
Answer:
(c) Mohan Ranade
Name the following:
Question 1.
Founder of ‘Razakar’ in Princely state of Hyderabad.
Answer:
Kasim Rizvi
Question 2.
Founder of Hyderabad State Congress.
Answer:
Swami Ramananda Tirth
Question 3
Founder of Goa Congress Committee.
Answer:
Dr. T.B. Cunha
Question 4.
Took a firm stand in solving the issue of Princely States.
Answer:
Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel.
Answer the following questions in one sentence :
Question 1.
Which European powers had control over some parts of India after Independence?
Answer:
The Portuguese and French powers had control over some parts of India after Independence.
Question 2.
What are Praja Mandals?
Answer:
People formed organisations like Prajamandals which worked for people’s interests in the princely states and for securing political rights for them.
Question 3.
Which languages were spoken in the princely state of Hyderabad?
Answer:
Telugu, Kannada and Marathi were the languages spoken in the princely state of Hyderabad.
Question 4.
What is ‘Operation Polo’?
Answer:
Indian government started the police action against the Nizam to merge the princely state of Hyderabad with India. It was symbolically called ‘Operation Polo’.
Question 5.
Which organisations were formed by people to secure civil and political rights in princely state of Hyderabad?
Answer:
To secure civil and political rights in Hyderabad princely state, people formed organisations such as Andhra Parishad in Telangana region, Maharashtra Parishad in the Marathwada region and Karnataka Parishad in the Karnataka region.
Do as Directed :
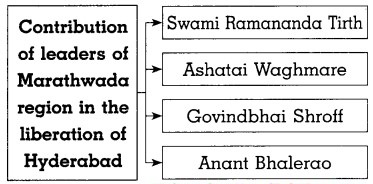
Complete the concept map :
Question 1.
Answer:
Question 2.
Answer:
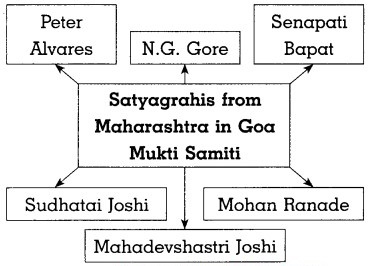
Show the events during merger of Hyderabad princely states on timeline:
Question 1.
Answer:

Answer the following in Brief :
Question 1.
Write about contribution of Marathwada in the struggle for liberation of Hyderabad.
Answer:
The contribution of Marathwada in the liberation of Hyderabad is as follows :
- To secure civil and political rights of the people in the region, MaharashtraParishad was formed.
- Many eminent leaders like Ved Prakash, Govind Pansare, etc. from Marathwada led the Hyderabad liberation struggle.
- Through ‘Vande Mataram’ Movement many students participated in the movement.
- Many sacrificed their lives in this historical struggle.
- The people and leaders of Marathwada had a lion’s share in Hyderabad liberation struggle.
Question 2.
Why was the struggle for independence not over in spite of India gaining independence?
Answer:
- When India got independence, there were more than six hundred princely states.
- The French and Portuguese powers too controlled some parts of India.
- It was essential to merge these regions with India.
Therefore, the struggle for independence continued in spite of India gaining independence.
Question 3.
Write about the contribution of Dr. T. B. Kunha for the liberation of Goa.
Answer:
- Dr. T. B. Kunha was in the forefront of the struggle to liberate Goa from the Portuguese rule.
- He worked to bring about awakening among the people against the Portuguese Government.
- With an objective of carrying out the struggle, he founded the Goa Congress Committee.
- He founded the Goa Youth League in Mumbai in 1945.
- He entered Goa in 1946 and was sentenced to eight years imprisonment for the violation of the ban on public speeches.
Explain the following statements with reasons :
Question 1.
Merger of the Princely States was essential.
Answer:
- When India got independence there were more than six hundred princely states in India.
- If the princely states had remained independent, India would have been split into hundreds of territorial fragments.
- The dream of Indian National Congress of undivided India would have remained incomplete.
- Moreover, the organisations in the princely states had started movements to secure rights.
- It was necessary to free the people from the autocratic rule in the princely states.
- Some princely states started carrying out movements for merging with Pakistan.
Question 2.
All India States People’s Conference was formed in 1927.
Answer:
- There was political awakening among the people of princely states due to influence of non-co-operation movement.
- Praja Mandals were formed to secure the political rights for the people in the Princely states and to work for their interest.
- All the Praja Mandals came together and formed an “All India States People’s Conference, in 1927 which gave an impetus to the freedom movement.
Question 3.
Many organisations were formed in the Hyderabad Princely State.
Answer:
- There were Telugu, Kannada and Marathi speaking regions in princely state of Hyderabad.
- There was absence of civil and political rights under the autocratic rule of the Nizam.
- To secure these rights organisations were formed in the princely states of Hyderabad.
Answer the following in detail:
Question 1.
Give information about Goa Liberation Movement.
Answer:
- Portuguese refused to hand over territories under its possession to India.
- Dr. T. B. Kunha was in the forefront to lead the struggle.
- He formed the organisation like ‘Goa Congress Committee’ and ‘Goa Youth League’.
- He worked to bring about an awakening of the people against the Portuguese government.
- He was arrested and imprisoned in 1946 for violating a ban on public speeches.
- Dr. Ram Manohar Lohia started a Satyagraha for liberation of Goa.
- He was deported by the Portuguese as he violated a ban and delivered a public speech at Madgaon in Goa in 1946.
- The youths of the Azad Gomantak Dal liberated Dadra and Nagar Haveli from the Portuguese rule on 2 August, 1954.
- The Portuguese rulers committed unlimited tyranny and atrocities on the Satyagrahis sent by Goa Mukti Samiti from Maharashtra in 1954.
- As the negotiations between the Government and the Portuguese did not succeed, the Indian government unwillingly took the decision of using military force.
- On 19 December, 1961, Goa was finally liberated from the dominion of the Portuguese.
Question 2.
How was the integration of the French occupied territories brought about?
Answer:
- Even after the independence of India, the regions of Chandranagar, Puduchcheri, Karaikal, Mahe and Yaman were in the possession of the French.
- People were keen to merge with India.
- The Indian Government demanded that these territories should be handed over to it.
- In 1949, the French-occupied territory of Chandranagar was transferred to India in view of the result of the plebiscite undertaken there.
- Thereafter, the remaining territories in the French possession were also handed over to India without any problem.
Question 3.
What would have happened if the Princely States would not have merged with India?
Answer:
Had the Princely States remained independent, the following could have been the result :
- The people in the princely states would never have got freedom and they would have faced injustice.
- The feeling of unity would have never developed among Indians due to the independent princely states.
- They would have created trouble in the development of India.
- Even the boundaries of India would not have remained safe.
- Injustice on the population, encroachment by the princely states and many other issues would have risen.
- Thus, It would have threatened the peace and security of India.