Chapter 4 Business Services
Chapter 4 Business Services
1. (A) Select the correct option and rewrite the sentence.
Question 1.
Door to door service is provided by …………….. transport.
(a) railway
(b) road
(c) air
Answer:
(b) road
Question 2.
…………….. creates time utility.
(a) Warehouse
(b) Transport
(c) Communication
Answer:
(a) Warehouse
Question 3.
…………….. warehouses provide facilities for perishable commodities.
(a) Bonded
(b) Cold storage
(c) Government
Answer:
(b) Cold storage
Question 4.
……………. policy covers all types of risks of a vessel while it is anchored at the port for a particular period of time.
(a) Port risk
(b) Voyage
(c) Floating
Answer:
(a) Port risk
Question 5.
Principle of …………….. is not applicable to life insurance.
(a) insurable interest
(b) utmost good faith
(c) indemnity
Answer:
(c) indemnity
1. (B) Match the pairs.
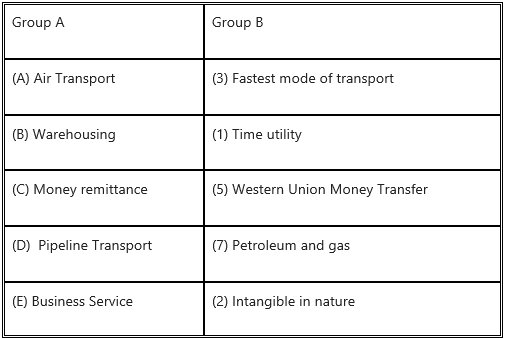
Question 1.
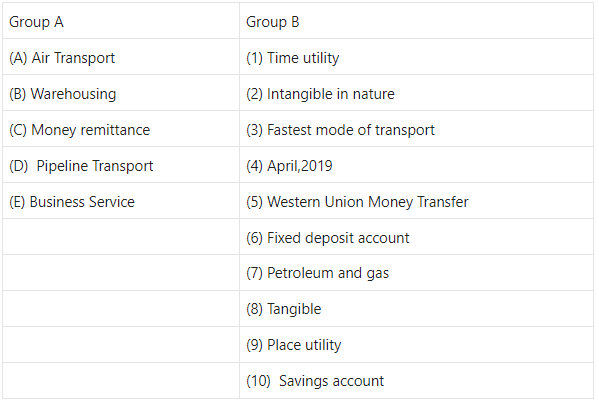
Answer:
1. (C) Give one word/phrase/term for the following sentence.
Question 1.
These warehouses are owned, managed and controlled by central and state governments or public authorities.
Answer:
government warehouse
Question 2.
An art of exchanging ideas, facts, information etc. from one person or entity to another.
Answer:
Communication
Question 3.
A rail system in which the track consists of a single rail or a beam.
Answer:
monorail
Question 4.
A transport system used to carry petroleum and gases.
Answer:
pipeline transport
Question 5.
A ministry who looks after development of surface transport throughout country.
Answer:
Ministry of Road Transport and Highways
1. (D) State whether following statements are true or false.
Question 1.
Business services are important for the growth of business.
Answer:
True
Question 2.
Current Account is opened by salaried persons.
Answer:
False
Question 3.
NEFT stands for National Electric Fund Transfer.
Answer:
False
Question 4.
Air transport is cheapest mode of transport.
Answer:
False
Question 5.
The Internet is the global system of interconnected computer networks that use the internet protocol suite to link devices worldwide.
Answer:
True
1. (E) Find the odd one.
Question 1.
Primary credit co-operative society, state co-operative bank, district co-operative bank, exchange bank.
Answer:
exchange bank
Question 2.
NABARD, RBI, SIDBI, EXIM.
Answer:
RBI
Question 3.
Direct mail, Logistics post, Business post, Parcel
Answer:
Parcel
Question 4.
Endowment policy, Whole life policy, Money back policy, Blanket policy.
Answer:
Blanket policy.
1. (F) Complete the sentence.
Question 1.
The term bank comes from the French word …………….. .
Answer:
Banco
Question 2.
…………….. warehouses provide facilities for perishable commodities
Answer:
Cold storage
Question 3.
In ……………… policy, several ships belonging to one owner are insured under the same policy.
Answer:
fleet
Question 4.
…………….. banking refers to the use of banking services with the help of mobile phones.
Answer:
Mobile
1. (G) Select the correct option and complete the following table.
(RTGS, SIDBI, apex financial institution in banking industry of country, recurring deposit, long term loans)
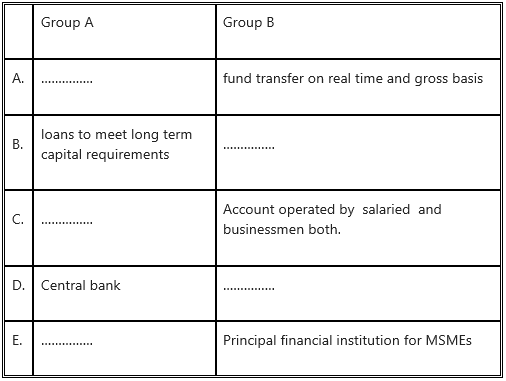
Answer:

1. (H) Answer in one sentence
Question 1.
What is debit card?
Answer:
A debit card is a card which is used by the cardholders to make purchases and avail of services at different places without making cash payment but payment is deducted from or debited to the account of the debit cardholders immediately.
Question 2.
What is ‘subject matter’ In insurance?
Answer:
‘Subject matter’ In Insurance refers to life, property, cargo or ship, etc. which is Insured against whose insurance policy Is taken.
Question 3.
What is government warehouse?
Answer:
The warehouses which are owned. managed and controlled by the Central and State Governments or public authorities to assist small farmers, businessmen, traders in storing goods at nominal charges are called government Warehouses.
Question 4.
What is air transport?
Answer:
The mode of transport which is operated above the surface of the earth and carries goods and passengers through airways by using different aircrafts Is called air transport.
Question 5.
What is communication?
Answer:
The term ‘communication’ means any exchange of Ideas, facts, information, messages. feelings and emotions among two or more persons in a way that they share common understanding about it.
1. (I) Correct the underlined word and rewrite the following sentences.
Question 1.
Overdraft facility is available for savings bank account holder.
Answer:
Current
Question 2.
Services are tangible in nature.
Answer:
Intangible
Question 3.
Insurance helps to maximize the risks in the business.
Answer:
Minimise
Question 4.
The foreign bank is the apex financial institution in banking industry in the country.
Answer:
Centrals
Question 5.
RTGS stands for Reasonable Time Gross Settlement.
Answer:
real
1. (J) Arrange in proper order.
Question 1.
Claim, Accident, Taking the policy, Compensation.
Answer:
Taking the policy, Accident, Claim, Compensation
Question 2.
Email, Inland letter, Courier
Answer:
Inland letter, Courier, E-mail
2. Explain the following terms/concepts.
Question 1.
Transport
Answer:
(1) Service or facility which creates physical movement of men, materials, goods. animals. etc. from one place (location) to another is called transport. Transportation can be defined as a means of carrying or transferring goods. people, animals, material. etc. from one place to another.
(2) Usually transportation is carried through various modes like land transport (i.e Railways and Roadways), water transport and air transport. It brings mobility both to human resources and physical resources. Transport plays key role in nations economy and economic development. After 1991, in India. development of infrastructure within the country has made progress at rapid rate and today there are different modes of transport operated in India. Transport helps in production. expands market, create place utility in goods and services, brings stability to prices, creates employment opportunities, improves standard of living of the people, provides help during emergency and facilitates economic development.
Question 2.
Communication
Answer:
(1) The term ‘communication’ means any interchange of ideas, messages, facts, information, feelings and emotions among two or more persons In a way that they share common understanding about it. It Is a process of giving away or passing on any information by any person to some other person with the help of some medium. Thus, receiver after receiving the message understands it in the desired form and acts accordingly.
(2) Means of communication consist of magazines, newspaper, post and telegraphs. telephone. Internet, e-mail, television, etc. Communication facilitates transmit business Information more quickly among the businessmen. The difficulty of distance is effectively solved by various means of communication. Effective communication facilitates the development and growth of domestic and international markets which bring prosperity to the country.
Question 3.
Banking
Answer:
(1) The term ‘Bank’ Is derived from the French word ‘Banco’ which means a ‘bench’. In olden days, moneylenders used to display coins and currencies on the tables or benches for the purpose of lending or exchanging. An organisation which is dealing with money is called bank. An institution offering certain financial services such as the safe keeping of money and lending money to needy people is called Bank.
(2) According to the Indian Banking Regulation Act, 1949, bankIng company means “any company which transacts the business of banking in India.” The word banking has defined further as “acceptingfor the purpose of lending or investment of deposits of money from the public repayable on demand or otherwise and withdrawable by cheques. drafts, order or otherwise.” Bank accepts deposits repayable on demand by cheques or drafts and lends or invests the surplus money as a part of normal business. It makes a profit by accepting deposits at a lower rate of Interest and lending money at a higher rate of Interest.
Question 4.
Insurance
Answer:
(1) Business involves various risks like accident, fire, theft, flood, cyclone, etc. It is very difficult for a trader to bear risks of loss. Similarly, human life is subject to various risks such as death by accident, premature death, etc. The specialised agency called insurance company has emerged to provide financial protection against the possible loss due to the happening of such events. Insurance company gives financial protection by charging certain amount as a premium. It. is a risk management, primarily meant to hedge or for compensating against the risk of a contingent or uncertain loss.
(2) Insurance is a contract between two parties whereby one of them (the insurer) agrees in return for a premium to indemnify the other (the insured) against a monetary loss that may be suffered by the other on the happening of some specified event. According to Insurance Act of 1938, “Insurance Is defined as, “A provision which a prudent man makes against inevitable contingencies”.
Question 5.
Warehousing
Answer:
(1) Warehousing means storing of goods in a godown to hold them in stock from the time of production or purchase till the time of their sale. It is generally used to denote all those activities which are concerned with the storage of goods in a godown or warehouse. One of the marketing processes or a group activity is to hold the goods in stock from the time of production till the time of consumption. When storage of goods is required to be arranged on a large scale In a specified manner, it is called warchousing’. Warehouse means a building in which especially retail goods are stored.
(2) Warehousing is defined as “an establishment for the storage of or accumulation of goocis.’ Warehousing gives protection to goods and helps businessmen to raise finance. It facilitates and provides space for grading. branding and processing. It creates time utility and help in price stabilisation of goods. Thus, warehousing implies a group of activities connected with the storing and preserving of stored goods from the time of their production or purchase till the Urne of their sale or consumption.
3. Study the following case/situation and express your opinion.
Question 1.
Ms. Harshali has started new business two years ago. Her customers are located in different parts of the country and hence they are directly depositing bill amount in her business account. At the same time she used to pay various payments from this account only.
(i) Identify Type of account maintained by Ms. Harshali.
(ii) Suggest any one modern way of money transfer to Ms.Harshali.
(iii) State any one facility she gets on her bank account?
Answer:
(i) Ms. Harshali is a businesswoman and hence she has maintained current account to suit the needs of her business.
(ii) NEFT which stands for National Electronic Funds Transfer is the one of the modern ways of transferring fund (money) from one branch to another branch or from one bank to another bank safely can be suggested to Ms. Harshall to transfer money.
(iii) Ms. Harshali gets overdraft facility on her current account.
Question 2.
Mr. Jagan is a salaried person. He wants to take policy for his two children which assures them protection as well as completes their financial needs once they become major by age.
(i) Suggest him a policy which can satisfy requirements of his children.
(ii) Who are beneficiaries of policy?
(iii) In above case which principle is involved?
Answer:
(i) Mr. Jagan. a salaried person should take “Child Insurance Policy” to satisfy the financial requirements of his children.
(ii) In child insurance policy, children of the insured person are the beneficiaries.
(iii) In the above case, principle of Insurable interest is involved.
Question 3.
Mr. Sharan is successful manufacturer. He is having production units at various locations. He is having multiple production units, he has large stock of raw material and finished goods. He is worried about safeguarding goods from any unwanted financial loss. He also requires to transfer raw material and finished goods from one unit to other but does not have any facility for that. He also requires funds for expansion.
(i) Name the service which will help him to safeguard goods from any damage?
(ii) Which service will help him to remove difficulty of place?
(iii) From which service sector will he get financial support?
Answer:
(i) Warehousing’ is the service that helps Mr. Sharan to safeguard his goods from any damage.
(ii) Transport service will help Mr. Sharan to remove the difficulty of place.
(iii) Mr. Sharan will get financial support from Banking sector.
Question 4.
Mr. Amit is a businessman. He has his own factories in Pune and Nashik. He lives in Pune with his wife and 2 daughters aged 5 and 8 years.
(i) Can Mr. Amit take a life insurance policy for his wife and 2 children?
(ii) Can Mr. Amit take a marine insurance policy for his factories?
(iii) Which type of insurance should Mr. Amit take for protecting his factories from loss due to fire?
Answer:
(i) Mr. Amit can take whole life policy or term insurance policy for his wife and child insurance policy or money back policy for his daughters.
(ii) Mr. Amit cannot take marine insurance policy for his factories.
(iii) Mr. Amit can take Floating Fire Insurance Policy for protecting his factories at Pune and Nashik.
4. Distinguish between.
Question 1.
Duty Paid Warehouse and Bonded Warehouse
Answer:
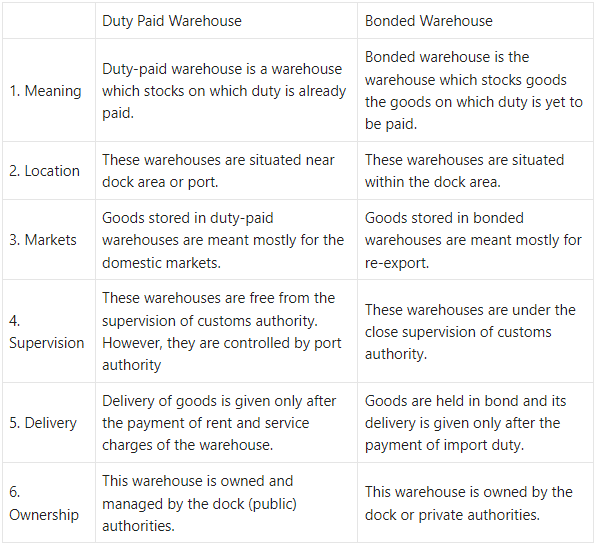
Question 2.
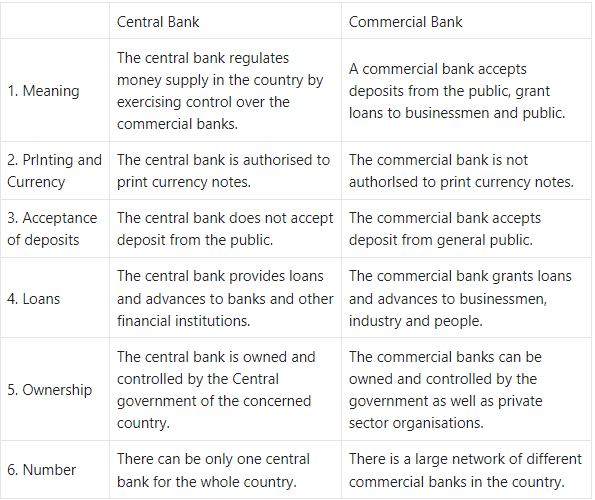
Central Bank and Commercial Bank
Answer:
Question 3.
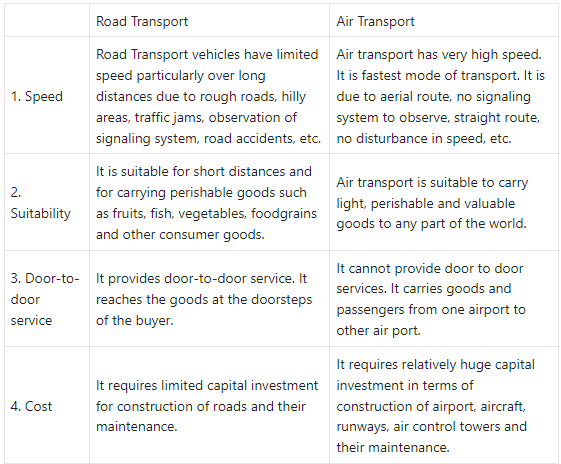
Road Transport and Air Transport
Answer:

Question 4.
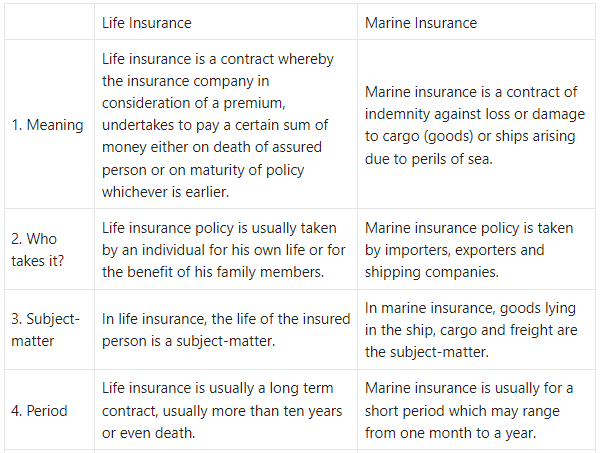
Life Insurance and Marine Insurance
Answer:

Question 5.
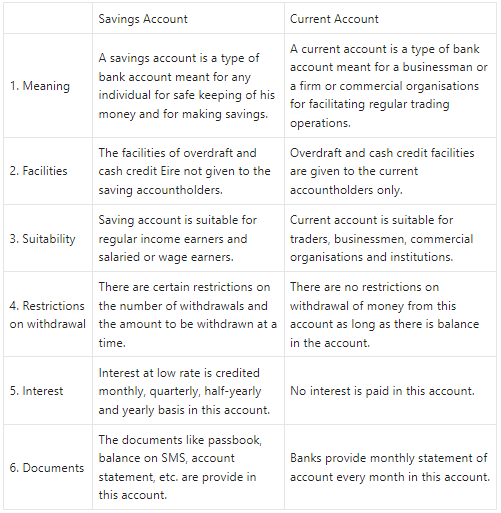
Savings Account and Current Account
Answer:
Question 6.
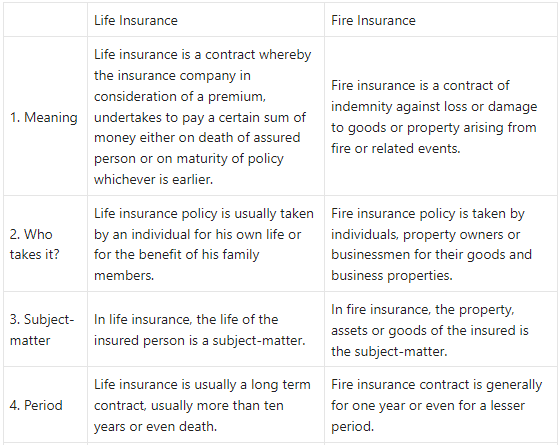
Life Insurance and Fire Insurance
Answer:

Question 7.
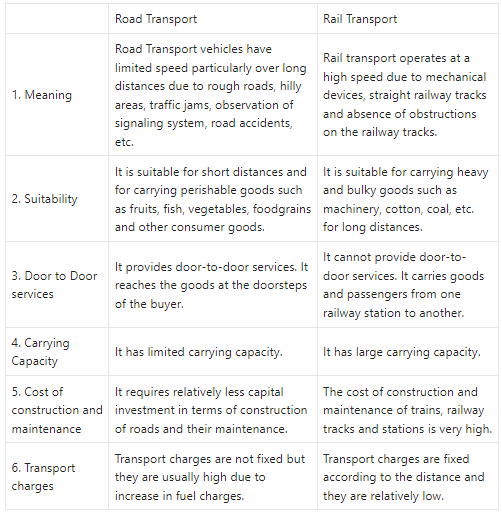
Road Transport and Rail Transport
Answer:
Question 8.
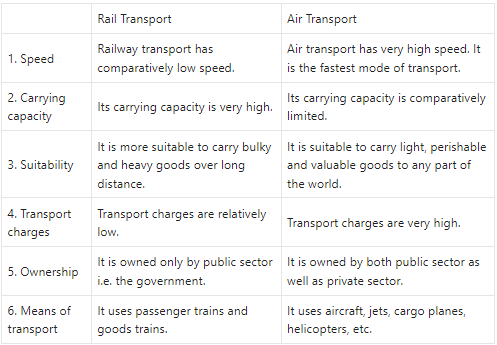
Rail Transport and Air Transport
Answer:
Question 9.
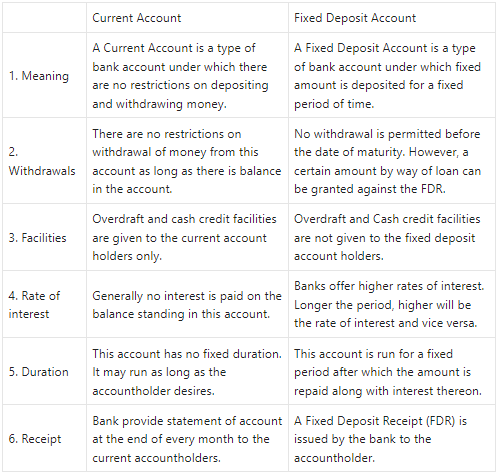
Current Account and Fixed Deposit Account
Answer:
5. Answer in brief.
Question 1.
State four types of deposits.
Answer:
The different types of deposits are explained below:
(1) Fixed Deposits : Fixed deposit is a type bank account in which certain fixed amount is deposited and kept in the bank for certain fixed period of time bearing fixed interest rate. The rate of interest paid on fixed deposit is higher than the rate of interest paid on other types of deposits. This rate of interest varies with the deposit period. Interest may also be paid periodically or annually. On Premature withdrawal of deposit before maturity date lower rate of interest is given. The deposit holder gets Fixed Deposit Receipt (FDR) issued by the bank. Loan can be obtained against this FDR.
(2) Recurring deposit : Recurring deposit is an account where depositor is required to deposit certain fixed amount at regular interval say monthly for certain fixed period. On the date of maturity, depositor gets the total amount deposited and interest accrued on such deposit amount. Rate of interest paid is higher and varies according to period of time. The depositor is given pass j book to record the entries of deposits, ft is taken by salaried people and businessmen who have regular income.
(3) Demand deposit: The demand deposit is one in which deposited amount is repaid to the accountholder as and when demanded. The amount of money can be withdrawn by the accountholder from the bank by using withdrawal slips, cheques, ATM cards, online transfer, etc.
(4) Savings deposit : A bank account designed for the personal savings is called savings account. The main aim of this deposit account is to inculcate the regular habit of savings among the common people. This account is suitable for those people who have fixed and regular income like salaries, wages, etc. Although there is no restriction on the depositing of money but frequent withdrawals are not permitted by the bank. Interest on balance amount is credited in this account quarterly or half yearly. Pass book, cheque book, balance on SMS, account statement, etc. are provided to the accountholders to know the position of account.
Some banks provide to their accountholders flexi deposit facility which combines the advantages of savings account and fixed deposit account. In case of multiple option deposit account, the excess amount above certain predetermined limit gets automatically transferred from Savings Account to fixed deposit account. Under this type of account, if adequate fund is not available in savings account to honour the cheques, then the funds get transferred automatically from fixed deposit account to savings deposit account.
Question 2.
State four modes of transport.
Answer:
The four modes of transport are explained as follows:
(1) Road transport : Road transport is the oldest mode of transport. It means and includes various means of transport which move on the surface of the earth without the use of railway tracks. Roads are the means which connect people and places on the surface of the land. It provides connectivity on any terrain (land) in comparison to other modes of transport. The different types of vehicles plying on the road include bullock carts, cycles, motor-cycles, autorickshaws, cars, tempos, trucks, buses, etc. They are called means of road transport.
(2) Rail transport : The mode of transport which moves on the surface of the earth with the help of parallel railway tracks is called rail transport. In other words, transportation of goods and passengers over long distances on rail lines through trains is called rail transport. It is an important land transport system of our country. The services of railways are provided by Ministry of Railways. Indian Railways operate different types of trains such as passenger trains, mails, express and cargo or goods trains. Some popular trains run by Indian Railways are Rajdhani Express, Duronto Express, Shatabdi Express, Intercity Express, Vande Bharat Express, holiday special trains, etc. Some luxury trains like Palace on Wheels, Deccan Odyssey, Ramayana Express, Maharaja Express, etc. are run to promote domestic tourism business.
(3) Air transport: The mode of transport which is operated above the surface of the earth i.e., in the sky through airways is called air transport. It has recent origin. Air transport uses different air crafts such as passenger air crafts, cargo aircraft, helicopters, etc. to carry the goods and passengers through airways at distant places. As compared to other modes of transport, air transport has fastest speed. It does not provide door to door services. Air transport is convenient mode in hilly or mountainous areas where other modes of transport cannot reach. It is also suitable mode of transport in emergency situations like war, natural calamities, etc. Air transport is classified into domestic and international air transport. The different national and international private and public sector airways companies are giving services.
(4) Water transport: The mode of transport which is carried out on the surface of water is called water transport. It represents transport facilities in water. It is the cheapest mode of transport. Water transport carries passengers and goods to different places on water ways by using various means like boats, steamers, launches, ships, etc. Water transport can be sub-divided into two categories viz. inland water transport which carries goods and passengers within the country and ocean transport which carries goods and passengers on ocean, sea route. In India, the Ministry of Shipping takes care of development of ocean transport.
Question 3.
State four life insurance policies.
Answer:
The different types of life insurance policies are explained as follows:
(1) Whole Life Policy : Under this policy, whole life of a person is insured and that he is required to pay premium up to his death. The policy holder (assured) cannot get any benefits i.e. money from insurance policy till he is alive. After his death, the amount of the policy is paid to his nominee or to the legal heir. Such a policy is meant for making a provision for the dependents of the assured. The rate of premium is usually low.
(2) Endowment Insurance Policy : An endowment insurance policy is for a specific period and the amount of such a policy along with bonus is paid after the maturity to the assured himself or on the death of the assured to the nominee or his dependents whichever is earlier.
(3) Term Insurance Policy : This type of policy is issued for a specific period. Premium is very low, fixed and remains unchanged during the term of the policy. In case of untimely death of assured, the nominee or dependents are paid the benefit amount mentioned in the insurance policy.
(4) Annuity Policy : Under this policy, insured has to pay the premium in lump sum or in instalments over certain number of years. After that, a certain amount is paid to the assured ; regularly on monthly basis for fix period or up to his death. It is similar to pension payment scheme.
(5) Money back Policy : Under this policy, the policyholder is paid regular or pre-determined percentage of the sum assured after every 10 years or 5 years during life time of policy and also provided the benefit of full sum assured to the nominee or dependents in the event of untimely death of the assured. Usually money back policy is available for 12 years, 15 years, 20 years, 25 years, etc.
Question 4.
State any four features of business services.
Answer:
The features of business services are explained as follows:
(1) Intangibility : Business services are intangible in nature. This is because business services cannot be seen, touched and smelt. They are not physical or material product. For instance, the building of the insurance company can be seen but insurance services offered by such company cannot be seen. People can avail of the benefits of insurance services although they are intangible in nature. On account of intangibility, services cannot be demonstrated as like goods. Hence services providers have to provide quality services to create good impression on the customers.
(2) Inseparability: One of the important features of business service is that the service and service provider cannot be separated from each other. At the time of rendering the services to the customers, the presence of service provider is must, e.g. medical treatment given by doctor to patient. In the case of services, production and its use (consumption) take place simultaneously.
(3) Inconsistency : Business services are heterogeneous i.e. they are not identical or exactly similar in all cases. They may differ from one person to another and from one place to another although service provider remains same. In fact, business services are heterogeneous, e.g. the services of a salesman in a Mall may have good impact on one customer and may not be liked by another customer.
(4) Perishability : Business services are perishable in nature. Hence, they cannot be stocked. The production and consumption (use) of services cannot be separated because services cannot be stored for future consumption. Since business services are intangible and perishable, there can never be inventory of services. Unlike products services cannot be stored for future sale, e.g. vacant seats of a morning bus from Mumbai to Pune cannot be utilised for evening trip of the same bus.
(5) Non-transferability : Business services are non-transferable in nature. The ownership of business services cannot be exchanged. We can exchange the ownership of products but not of services. A lady goes to a beauty parlour and hires services of the beautician by paying the fees. The lady cannot buy the ownership as its ownership remains with the beautician. If she needs such services again, she has to go to the beauty parlour and pay the beautician again for her services.
(6) Consumer participation : The participation of consumer is important for services. The seller or service provider will not be able to provide its services in absence of a consumer and vice versa. So, the presence or participation of both is necessary.
Question 5.
State money remittance services of postal department.
Answer:
Money remittance services : The money remittance services are explained as follows:
(i) Electronic Money Transfer (eMO) : A money order is the most convenient method of remitting money to distant places. It is an order issued by one post office to another to pay a certain amount of money to a person specified therein. The person to whom money is to be paid is called ‘Payee’. Under this service of the post office, money is delivered at the house or the place of stay of the receiver.
(ii) Instant Money Order (iMO) : Instant Money Order (iMO) is an instant web based money transfer service by which minimum Rs 1000 and maximum Rs 50,000 can be transferred to distant places from designated iMO post offices. It is the instant on-line money transfer service which is safe, convenient, reliable and affordable. The money can be sent to close relative residing at distant place in India. It is simple, quick and economical to send and receive money.
(iii) International Money Transfer : International Money Transfer is the most convenient, quick and easy way of transferring personal remittances from foreign country to family members or other beneficiaries in India. Now this service is made available in all post offices in India by Department of Post, Government of India with the help of Western Union Financial Services. The remittances of money are permitted from around 195 countries to India.
6. Justify the following statements.
Question 1.
Air transport is fastest mode of transport.
Answer:
(1) The mode of transport which is operated above the surface of the earth i.e. in the sky through airways is called air transport. For carrying passengers and goods, air transport uses different aircrafts such as passengers aircrafts, cargo aircraft, helicopters, etc.
(2) Among the means of transport available at present, air transport is the fastest and the quickest means of transport. It uses natural ways and no separate construction of routes is required. It is also due to use of modern and advanced technology and highly qualified and professional technicians. Thick forests, high mountains, vast deserts and oceans cannot obstruct its speed and air routes.
(3) Air transport adopt shortest route to reach destination. It has faster speed without any disturbance of observing signal system speed. Air transport is useful to provide valuable services in hilly and mountainous areas, in situations like war and areas affected by natural calamities such as floods, cyclones, earthquakes, etc.
Question 2.
Communication is essential for growth of business.
Answer:
(1) Exchange of ideas, facts, information etc. from one person to another is called communication. It is a process of transfer of information from one place to another or from one person to another with the help of some medium. Means of communication comprise magazines, newspapers, post and telegraphs, radio and television, telephone, internet, e-mail, etc. Communication is essential for growth of business, which include industry, commerce, trade, etc.
(2) The difficulty of distance is effectively solved by various means of communication. Communication helps to transmit business information more quickly among the businessmen. Effective communication facilitates carrying required raw materials and other requirements from the place of their origin or market to the place of their production to facilitate large scale production. The communication also helps to carry finished products from the place of production to the places of consumption as well as market.
(3) Communication helps to make goods and services available wherever they are demanded. It helps to widen the market. Effective communications facilitates the development and growth of domestic and international market and bring prosperity to the country.
(4) Effective communication facilitates the reduction in the cost of production and distribution of goods at low prices which increase their demand and widen market. Increase in demand in turn leads to large scale production and supply. Thus, communication is essential for growth of business.
Question 3.
Principle of subrogation is applicable to all contracts of indemnity.
Answer:
(1) The principle of subrogation is a colliery to the principle of indemnity. According to the principle of subrogation, after the insured is fully compensated for the total loss of the property or goods insured by him, all the rights in such property or goods pass on to the insurer.
(2) Insured person cannot claim any right in the property saved from the damage or loss, once he is fully compensated by the insurer. This is necessary because, if part of the goods or property saved from the fire, accident, damage, floods or cyclone, etc. could fetch any price, the same cannot be retained by the policyholder or insured. In that case he would realise more than the actual loss, which is against the principle of indemnity.
(3) As like the principle of indemnity, the principle of subrogation is applicable to all insurance policies except life insurance policies. In life insurance contracts, the question of indemnity and subrogation does not arise. The insurer cannot indemnify the insured because the loss due to death cannot be determined exactly in terms of money.
(4) In all insurance contracts, except life insurance contract, principle of indemnity and principle of subrogation are applicable. On indemnifying the insured, the insurer can sell the remains of the property damaged and reduce his loss. However, this principle is applicable only if the damaged property has any value after the happening of the event.
Question 4.
Warehousing is important.
Answer:
(1) The term ‘warehousing’ is generally used to denote all those activities which are concerned with the storage of goods in a godown or warehouse. In modern days, these is a time gap between production of goods and their distribution. Warehousing is essential to hold the stock of goods till they have suitable demand.
(2) Agricultural goods such as rice, wheat, sugar, spices, etc. are produced seasonally but consumed throughout the year. It is necessary to store them in large quantity. Some goods may be required to be stored for conditioning, canning or processing, e.g. oil seeds, fish, fruits, etc. Some perishable goods such as eggs, meat, butter, fruits, vegetables, medicines, etc. are preserved in cold storage so that their quality remains as it is.
(3) Warehousing plays an important role in price stabilisation. It helps to protect the goods from theft, deterioration, i.e. future risks. Warehouses nowadays provide facilities like packing, processing, grading, etc. Warehousing is necessary to facilitate dispersion of goods from production centres to different markets.
Question 5.
Cash can be withdrawn from ATM at any time.
Answer:
(1) ATM is the abbreviation of Automated Teller Machine. It is popularly known as All Time Money or Any Time Money. ATM is an electronic cash dispensing machine. It is free standing self service terminal. There is no specific time limit for withdrawals of cash from ATM.
(2) ATM is one of important facilities provided by the bank to its savings accountholder. To avail of this facility, bank installs ATM terminals at the places of public utility such as railway stations, shopping malls, airports, post offices, busy streets, etc.
(3) For withdrawal of cash from ATM, every accountholder is given specific code number. By operating this system, the accountholder can withdraw the cash up to a specific limit or the quantum of amount available in the account whichever is less. ATM also provides other information like cash deposits, withdrawals, balance in the account, etc.
(4) Under this system, the accountholder has cent per cent liquidity of banking funds. ATM avails twenty four hours service. Hence, the accountholder can withdraw cash any time, i.e. even after banking hours, on holidays, Sundays or in the case of emergency by operating ATM. This facility is available in different parts of the country as well as outside the country.
7. Attempt the following.
Question 1.
Explain money remittance services of post department.
Answer:
Money remittance services : The money remittance services are explained as follows:
(i) Electronic Money Transfer (eMO) : A money order is the most convenient method of remitting money to distant places. It is an order issued by one post office to another to pay a certain amount of money to a person specified therein. The person to whom money is to be paid is called ‘Payee’. Under this service of the post office, money is delivered at the house or the place of stay of the receiver.
(ii) Instant Money Order (iMO) : Instant Money Order (iMO) is an instant web based money transfer service by which minimum Rs 1000 and maximum Rs 50,000 can be transferred to distant places from designated iMO post offices. It is the instant on-line money transfer service which is safe, convenient, reliable and affordable. The money can be sent to close relative residing at distant place in India. It is simple, quick and economical to send and receive money.
(iii) International Money Transfer : International Money Transfer is the most convenient, quick and easy way of transferring personal remittances from foreign country to family members or other beneficiaries in India. Now this service is made available in all post offices in India by Department of Post, Government of India with the help of Western Union Financial Services. The remittances of money are permitted from around 195 countries to India.
Question 2.
Explain marine insurance policies.
Answer:
The different types of marine policies are:
(1) Voyage Policy : Under the Voyage Policy, the cargo is insured for a specified voyage, from one port to another, irrespective of the time taken. For instance, the voyage may be from Mumbai to Tokyo. In this type of policy, risk begins as soon as ship starts from Mumbai and ends when it reaches Tokyo.
(2) Time Policy : Under the Time Policy, the subject-matter is insured for a specific period of time. It covers risks of the voyage undertaken during the specified period. Time policy cannot be issued for a period more than 1 year but may contain continuation clause which explains that if voyage is not completed within the specified time, the risk shall be covered until voyage is completed.
(3) Mixed Policy : This policy is the combination of the two policies, viz. time policy and voyage policy. It insures the cargo (i.e. goods loaded on a ship, etc.) on a particular voyage for a specific period of time. For instance, the policy may contain the clause ‘Mumbai to Singapore, for one month starting from 25th February, 2020 to 25th March, 2020’.
(4) Valued Policy : The valued policy is a policy in which the value of the subject-matter is agreed upon between the insurer and the insured at the time of taking out the insurance policy. Agreed amount of policy becomes payable by the insurance company to the insured i.e. policyholder in the event of loss. It facilitates easy settlement of claim, where it is difficult to find out real market value S of the cargo.
(5) Blanket Policy: Under this policy, the maximum limit of the needed amount of protection is estimated and premium is paid in advance. This policy gives information of nature of goods insured, ports and places of voyages, specific route and risks covered. This policy covers multiple 1 risks on one property or it may cover different properties under one policy.
(6) Port Risk Policy : This policy is taken by the shipowner. It undertakes to indemnify the shipowner for any loss that may occur to the ship while it is anchored at a port. This policy is held applicable till the departure of the vessel from the port.
(7) Composite Policy : This policy is purchased from many insurance companies when the amount of insurance is very high. However, the liability of each insurance company to pay the amount of j claim is separate and distinct.
(8) Single vessel policy : The small shipowner having only one ship in different fleets, usually purchases single vessel policy to cover the risk of loss. This policy covers the risk of one vessel of the insured.
(9) Fleet policy and Block policy : The marine policy which insures several ships belonging to one owner is called Fleet Policy. The Block Policy is another marine policy under which the cargo owner is given protection against the loss or damage of cargo in all modes of transport i.e. rail, road and sea.
Question 3.
Explain types of warehouses.
Answer:
The different types of warehouses are:
(1) Private warehouses : The warehouses owned and operated by the big manufacturers and wholesalers for storing their own goods are called private warehouses. Big companies which need large storage capacity on a regular basis, can afford to construct and maintain their own warehouses. Many public sector organisations also have their own private warehouses, e.g. the Food Corporation of India (FCI) has constructed warehouses in different parts of the country for its own use. Usually these warehouses are constructed near to ones business factory or industry for convenience. They have network of warehouses in different parts of the country.
(2) Public warehouses : Warehouses which are established to provide storage facilities to the general public, small manufacturers and traders on rental basis are called public warehouses. These warehouses are owned and managed by an individual or co-operative societies. These warehouses are located near railway junctions, highways, waterways, airport, seaport, etc. They are well guarded and specially designed to protect goods from several types of risks. These warehouses have to obtain licence from the government. They provide warehousing facilities at low cost. Many marketing facilities such as standardisation, grading, labelling, packing, branding, etc. are provided in these warehouses.
(3) Bonded warehouses : Warehouses which are licensed by the government to accept and store imported goods till the customs duties are not paid on such goods are called bonded warehouses. These warehouses are managed and controlled by customs authorities. These warehouses are located near the ports. The importers cannot take possession of goods from such warehouses unless and until the duty on the goods is paid. The warehouse-keeper is required to give undertaking or ‘Bond’ that without the consent of the customs authorities goods will not be removed from the warehouse. Hence, such warehouses are called ‘Bonded Warehouses’. If an importer is unwilling or unable to pay customs duty immediately, he can withdraw them in instalments and pay customs duty proportionately.
(4) Duty-paid warehouses : The duty-paid warehouses provide the facility of storing the imported goods but not yet sold or transported to importers’ place or godown. These warehouses are owned and managed by the dock authorities only and hence they are also known as public warehouses. These warehouses are located near port and dock areas. They are more useful to importers who re-export the imported goods. The concerned authorities take all the due and reasonable care to ensure their safety. Processing of imported goods such as sorting, re-packing is done in these warehouses.
(5) Government warehouses : Warehouses which are owned, managed and controlled by the Central and State Governments or public authorities are called Government warehouses. These warehouses offer storage facilities to small traders, farmers, businessmen, etc. who are in need of the same on payment of reasonable rent. Central Warehousing Corporation of India (CWC), State Warehousing Corporation (SWC) and Food Corporation of India (FCI) own warehouses for keeping stock of foodgrains and other goods In different states and countries.
(6) Co-operative warehouses : These are warehouses owned, run, managed and controlled by co-operative societies to provide warehousing facilities to the members who are farmers in rural areas. These warehouses are similar to private warehouses but they run on the principle of co-operation. They are used for storing agricultural commodities, consumer goods, raw materials, etc. Farmers, small producers and traders are benefited by such warehouses as they charge at economical rates.
(7) Cold storage warehouses : Cold storage warehouses are largely used to store and preserve perishable goods such as flowers, fish, eggs, meat, vegetables, fruits, medicines, dairy products, etc. These products are kept in cold storage warehouses at very low temperature so that their quality and freshness would remain intact. These warehouses ensure continuous supply of seasonal and perishable products throughout the year. International trade for seasonal and perishable goods such as green peas, mangoes, etc., becomes possible only because of cold storage facilities.
Question 4.
Explain utility function of banks.
Answer:
The utility functions of the commercial bank are explained as follows:
(1) Issue of drafts and cheques : The Bank draft/cheque is an order issued by the bank upon the other branch of the same bank or other bank to pay money to the person whose name is specified thereon. The bank issues bank drafts to its accountholders or non-account holders. However, cheque are issued by the bank only to its account holders. For issuing the bank draft, bank charges some commission.
(2) Locker facility: The bank provides safe deposit vaults to the customers for keeping their valuables like gold ornaments, jewels, securities, valuables, documents, etc. in safe custody. Safe deposit vaults/lockers are made available to the customers on rental basis.
(3) Project reports : As per the request of the clients, bank prepare project report and feasibility study (i.e. a study designed to determine practicability of a system or plan) on their behalf. This helps the business organisation to get funds from the market and clearance from the government authorities.
(4) Gift cheques : The commercial banks also issue gift cheques and gold coins to the customers as well as to the general public by charging nominal charges. It is more popular and has wider acceptance in India. Instead of giving gifts in cash, one can give gift cheques as a present on various occasions such as birthdays, weddings, marriage anniversaries, etc.
(5) Underwriting Services : Underwriting services are given by the banks to the companies in which the bank gives guarantee to the issuing company to purchase unsubscribed portion of the shares, debentures, bonds and other securities if the public demand is not enough to fulfil the minimum subscription amount. For this services bank charges underwriting commission.
(6) Gold related services : Nowadays, many commercial banks offer gold related services to its customers. The banks on commercial basis buy and sell gold and gold ornaments to the customers on large scale basis. Some banks even gives advisory services to its customers in regard to gold funds, gold Exchange Traded Fund (ETF) etc.
Question 5.
Explain modes of traditional communication.
Answer:
(I) Postal Services : The postal services in India are provided by the Department of Post which comes under Ministry of Communication and Information Technology. India has the largest postal network in the world with 1,54,965 post offices of which 1,49,067 are in the rural areas. The different types of postal services are explained below:
(1) Mail Services : The different types of mail services are described below:
(i) Inland letters : The inland letter is one of the cheapest means of conveying written message. It contains a blank sheet of paper of prescribed size and folding for writing messages. It is folded and sealed. Only names and addresses of the receiver and sender can be seen from outside. So, it ensures complete secrecy. Inland letters are used for transmission of messages within India only.
(ii) Envelopes : A postal envelope is a small size paper cover with postage stamps affixed on it having one side open to put in papers, written messages and enclosures like cheques, photos, resumes, etc. It ensures maximum secrecy. On the front outside space name and address of receiver are written and on the backside space name and address of sender are written.
(iii) Parcel : Parcels help to send small articles from one place to the other by post. Parcel post provides economical and reliable parcel delivery service. Parcels of specified weight and size can be sent at different places within the country as well as outside the country Anything except those items which are banned can be sent. Parcel can be insured by paying extra charges for insurance. In case of insured parcel is lost in transit post office pays insured amount.
(iv) Book post : Printed materials such as publications, newspapers, printed books, wedding, cards, greeting cards, periodicals, legal documents, etc. can be mailed as book post. The book post packets should simply be closed and should not be sealed. The words ‘Book Post’ should be written on the face of the cover.
(2) Specialised Postal Services : The following specialised postal services are provided by the post offices:
(i) Business Post : Business post arranges complete mailing services right from preparation of mail to delivery of mail. It is most suitable for small business and large companies. As per requirement, customers can select from a range of cost effective and professional mailing services which include printing, collating (comparing or examining), inserting, sealing and addressing. Indian post has established Business Post centres in major cities to handle business post consignment.
(ii) Logistics Post : Logistics post provides its business customers a cost-effective and timely solution that manages the entire value chain from collection to storage to transmission to distribution throughout the country.
(iii) Bill Mail Service : Communications in the nature of financial statements, bills, monthly account statements or any such other items of similar nature are sent by service providers to the customers by using bill mail service of post office. This service is used at least once in 90 days. Under this service, at a time minimum 5000 articles can be posted. The bill mail service does not include communication in the nature of letter mail or having personal communication or exclusive commercial publicity material. The mail is to be received at specified location provided. Bill mail is to be sorted pin code wide and bundled delivery post office wise.
(3) Money remittance services : The money remittance services are explained as follows:
(i) Electronic Money Transfer (eMO) : A money order is the most convenient method of remitting money to distant places. It is an order issued by one post office to another to pay a certain amount of money to a person specified therein. The person to whom money is to be paid is called ‘Payee’. Under this service of the post office, money is delivered at the house or the place of stay of the receiver.
(ii) Instant Money Order (iMO) : Instant Money Order (iMO) is an instant web based money transfer service by which minimum Rs 1000 and maximum Rs 50,000 can be transferred to distant places from designated iMO post offices. It is the instant on-line money transfer service which is safe, convenient, reliable and affordable. The money can be sent to close relative residing at distant place in India. It is simple, quick and economical to send and receive money.
(iii) International Money Transfer : International Money Transfer is the most convenient, quick and easy way of transferring personal remittances from foreign country to family members or other beneficiaries in India. Now this service is made available in all post offices in India by Department of Post, Government of India with the help of Western Union Financial Services. The remittances of money are permitted from around 195 countries to India.
(4) Retail services : The retail services are explained as follows:
(i) Retail post : Under retail post service, the department of post offers services to general public by making available some products and services of third party available in their areas through selected post offices. Under this, post offices offer a range of services including the collection of electricity bills, telephone bills, insurance premia, collection of taxes and fee for the government, etc. The post office also sells application form.
(ii) e-post : Recently, the department of posts has introduced e-post services, e-post service is service under which printed messages of customers are scanned and transmissed as email through internet. At the destination place or offices, these messages are printed, enveloped and delivered at the postal address. Thus, it is the combination of electronic transmission and physical delivery. Through e-post customers can send their messages to any address in India through network of more than 1,55,000 post offices. Corporate customers get special e-post rates and value additions.
Question 6.
Explain disadvantages of air transport.
Answer:
The disadvantages of air transport are as below:
- Costliest mode : In comparison to all other modes of transport air transport is most expensive.
- Affected by adverse weather conditions : It is exposed to the vagaries of weather changes, heavy rains, snow, storm, etc.
- Unsuitability : Air transport is not suitable for short distances. It is also not suitable for carriage of bulky and heavy goods.
- Huge capital investments : As compared to other modes of transport, air transport requires huge capital investment costs like construction of airports, aircrafts, runways, air traffic control tower, etc. Huge capital investment increases freight and fare charges.
- International restrictions : Air transport is required to observe international restrictions such as aeroplane of some nations are not permitted to fly over other countries.
- Limited carrying capacity : In comparison to other means of transport, the carrying capacity of air transport is very limited. It is not suitable to carry heavy and bulky goods.
Question 7.
Describe the role of transport.
Answer:
The role of transport are explained as follows:
(1) Helps in production : Transport carries raw materials and other requirements from the place of their origin or market to the place of their production to facilitate large scale production. It also carries labour from their residence to place of factory. It carries finished products from the place of production to the places of consumption or markets.
(2) Expanding markets : Producers and consumers are separated by geographical distance. Transport bridges this gap and facilitates distribution. It makes goods available wherever they are demanded. This helps to widen the market. With the development and growth of transport, the domestic and international markets for both agricultural and industrial products expand, bringing the prosperity to the country.
(3) Creates place utility : Transport is a public utility service which creates time and place utilities. Transport mainly creates place utility by carrying goods from the place of plenty to places where they are in more demand but not available, e.g. Apples which are produced on large quantity in Himachal Pradesh are brought over to Mumbai and other places throughout the country by transport to get high prices.
(4) Stability of prices : Transport carries goods from the areas of plenty to the areas of scarcity. It helps to regulate and balance the supply of goods and services in relation to demand and thereby helps to stabilise the prices of goods. The shortage of goods at any place can be easily removed by efficient transport system.
(5) Creates employment : Transport creates job opportunities directly for transport owners, drivers, conductors, cleaners, mechanics, helpers, etc. It helps to move labour and goods from the place of abundance to the place of scarcity. This movement of goods and labour creates indirect employment. Transport an industry by itself has provided job opportunities to millions of people all over the world.
(6) Improves standard of living : By generating employment, transport leads to increase purchasing power with people. Further, it makes products of their choice from different regions available in local markets. This results in higher standard of living.
(7) Cost reduction : Efficient, cheap and quick means of transport facilitate the reduction in the cost of production and distribution of goods. On account of low cost of production, the goods can be sold at low prices which increase their demand and widen market. Increase in demand again leads to large scale production of goods and supply.
(8) Provides help during emergency : The life of the people is badly affected during natural calamities such as floods, earthquakes, landslides, droughts, etc. and also during man-made disasters such as bomb blasts, riots, accidents, etc. In such circumstances, urgent and timely help in the form of food, water, medicines, clothes and other provisions, etc. can be provided quickly with the help of transport to save the lives of affected people. Rescue operations are possible only with the help of helicopters, fire brigades, railways, etc.
(9) Economic development : An efficient transportation system contributes to the rapid development of commerce and industry. Transport also helps to develop agriculture of a country. New industries are established and rapidly developed due to efficient network of transport. Further, a country can make progress in international trade and thereby earn foreign exchange only through efficient transport services.
Question 8.
What are the functions of warehouses?
Answer:
Functions : The functions of warehouses are explained as follows:
Function of Warehouses
- Storage
- Price Stabilisation
- Risk-Bearing
- Financing
- Grading and Packing
- Transportation
- Time and Place Utility
- Processing
1. Storage : Storage of goods is the basic function of warehousing. Warehouses provide space for storage of goods in large quantity and in good condition. The commodities which are not required immediately are stored in the warehouses. Stored goods are supplied as and when they are required by the customers.
2. Price stabilisation : Warehousing facilitates price stabilisation by maintaining proper balance between demand for and supply of commodities. It is achieved by creation of time utility by warehousing. Usually, large stock of goods is kept in the warehouse. Wherever, there is shortage of goods in the market, goods are released from the warehouse which increases supply and facilitates price stabilisation. Thus, it helps to avoid any rise in prices.
3. Risk-bearing : While the goods are stored in the warehouse, the warehouse-keeper takes reasonable care to protect the goods from risks of loss or damage due to heat, cold, moisture, dryness, insects, fire and thefts. This is because he has to return the goods in the same condition. For any loss or damage of goods during storage, warehouse-keeper will be held liable to the owner of the goods. Thus, the risk is transferred from the owner to the warehouse-keeper.
4. Financing : On the basis of goods stored in the warehouse, loans can be raised from the financial institutions or warehouse-keeper. The goods act as a security for financial institution. This loan can be used to meet other operations of business by the owners of goods.
5. Grading and Packing : Warehousing provides enough space for undertaking various marketing functions like grading, processing and packing of goods. Goods can be packed in suitable sizes as per the instructions of the owner. Thus, services of warehousing are very useful to manufacturers, wholesalers and the importers of goods.
6. Transportation : Some warehouses also provide transport facility to the traders who store large quantity of goods in the warehouse. It brings the goods from the places of production and also sends them to the places of delivery on behalf of depositors.
7. Time and Place Utility: Warehousing creates time utility by storing goods and releasing the same at the time when they are demanded. It also creates place utility by transporting goods at the far away places, where they are required.
8. Processing : For certain commodities processing is necessary to make them consumable or useable. This is because those commodities cannot be consumed in the form they are produced in the nature, e.g. paddy, raw fruits, etc. The activities such as polishing the paddy, ripening the fruits, etc. are undertaken by the warehouses on behalf of the owners.
8. Answer the following.
Question 1.
What is insurance ? Explain principles of insurance.
Answer:
[A] Meaning : The term insurance refers to the method (means) of protection from financial loss which may occur due to happening of specific uncertain events. It is a type of risk management primarily used to compensate against the risk of a contingent loss. Insurance is a contract between two parties whereby one of them (the insurer) agrees in return for a consideration (premium) to indemnify (compensate) the other (the insured) against a monetary loss that may be suffered by the other on the happening of some specified event.
According to Insurance Act of 1938, Insurance is defined as, “A provision which a prudent man makes against inevitable contingencies”.
[B] Principles of insurance : The different principles of insurance are:
- Principle of Utmost Good Faith
- Principle of Insurable Interest
- Principle of Indemnity
- Principle of Subrogation
- Principle of Contribution
- Principle of Mitigation of Loss
- Principle of Causa-Proxima
1. Principle of Utmost Good Faith : The principle of utmost good faith is applicable to all types of insurance. According to this principle, both the parties in an insurance contract are under am obligation to make the fullest disclosure of all material facts relating to the insurance contract clearly, correctly and completely. Insured must provide correct and complete information of the subject-matter of the insurance whereas insurer must provide correct and complete information about the terms and conditions of the insurance contract. Failure to provide correct, complete information on the part of insured may lead to non-settlement of claim by the insurer.
For example, Mr. Hari has not given information about his kidney ailment to the insurance company while taking policy. So, if the insurance company discovers it after his death, then his family will not get compensation.
2. Principle of Insurable Interest : No person can enter into a valid insurance contract unless he has insurable interest in the object insured. Insurable interest of an insured is said to have in the subject matter if the existence of it provides financial benefit to the insured and non-existence of that subject matter put the insured to financial loss. Principle of insurable interest is applicable to all contracts of insurance. In the case of life insurance it is enough if the insurable interest s exists at the time of entering into the contract. In the case of marine and fire insurance interest the insurable must exist both at the time of the contract as well as at the time of the happening of the event.
A person has insurable interest in his own life and his property. A businessman has insurable interest in the goods he trades and in his property. Similarly, a wife has insurable interest in the life of her husband and vice versa.
3. Principle of Indemnity : Indemnity refers to a guarantee or assurance given by the insurer to place the insured in same financial position in which he was before the happening of the uncertain event. Principle of indemnity is applicable to marine, fire and general insurance as in such cases actual loss can be measured in terms of 1 money. Under this principle, the insurer undertakes to indemnify the policyholder or insured to the extent of the policy amount or the actual monetary loss suffered, whichever is lower, e.g. if a property owner has insured his property for Rs 5 lakh and it is destroyed by fire and incurred a loss of Rs 2 lakh, then the property owner will be paid only Rs 2 lakh i.e. the actual loss. This principle prevents a policyholder from making a profit out of his actual loss. However, in case of death of the insured, insurance company pays the actual sum assured to the nominee of the insured.
4. Principle of Subrogation : The principle of subrogation is a corollary to the principle of indemnity and is applicable to all contracts of j indemnity. According to it, after the insured is fully compensated for the total loss of the property or goods insured by him, all the remaining rights in such property or goods pass on to the insurer. Suppose a car owner has insured his car for Rs 2,00,000 against risk of loss due to accidents. If his car meets with an accident and is completely damaged, the insurance company pays Rs 2,00,000, the policy amount, to the car owner. On indemnifying the insured, the insurer can sell the remains of the car in scrap and reduce his loss.
5. Principle of Contribution : The principle of contribution is applicable to all contracts of indemnity. A person can insure his property with two or more insurance companies. It is done mainly to have better security, i.e. if one insurer fails to pay the claim, it can be recovered from another insurer. In the case of loss, the insured cannot recover compensation from both the insurance companies. All the insurers will jointly compensate the total amount of loss. According to the principle of contribution, each insurance company will contribute to the loss in proportion to the amount of policy undertaken from each company. If the insured chooses to collect the amount of compensation from one particular insurer, the insurer can in turn recover proportionate amount from the other insurers.
For instance, Dr, Ashok has insured his property of Rs 2,00,000 with two insurance companies viz. with X insurance company for Rs 1,20,000 (i.e. 60% of property value) and with Y insurance company for Rs 80,000 (i.e. 40% of property value).
If Dr. Ashok’s property is destroyed and he incurred a loss of Rs 1,50,000, then both the insurance companies will contribute towards actual loss of Rs 1,50,000. Here X insurance company will pay Rs 90,000 (i.e. 60% of Rs 1,50,000) and Y insurance company will pay Rs 60,000 (i.e. 40% of Rs 1,50,000).
6. Principle of Mitigation of Loss : Under this principle, the insured is required to take all possible steps to minimise the loss to the insured property on the happening of the event. He should not remain indifferent merely because the property which is getting damaged is insured. For example, Mr. Kishor’s house is on fire due to short circuit. In this case Mr. Kishor, must take necessary steps to put off the fire and to save the insured property as much as possible.
7. Principle of Causa-Proxima : The term ‘Causa-Proxima’ means a proximate, i.e. nearest or immediate cause or reason. Accordingly, when loss is occurred due to more than one cause, then proximate or nearest cause of loss is taken into consideration to fix the liability of insurer. If proximate cause is one of the causes from list of insured causes, then insurer is liable to pay compensation. In other words, the insurance company will indemnify the insured only if it is definitely established that the said loss is caused directly by the occurrence of the event covered by the policy.
Question 2.
Define bank. Explain. Different types of banks.
Answer:
[A] Definition : Bank is a dealer in money and credit. It is a financial institution whose basic activities are to accept deposits and advance, lend money and provide other related services, According to The Indian Banking Regulation Act, 1949, “any company which transacts the business of banking in India.” The term banking is further defined as, “accepting for the purpose of lending or investment of deposits from the public, repayable on demand or otherwise and withdrawable by cheque, draft and order or otherwise.”
Types of Bank:
- Central Bank
- Commercial Bank
- Co-operative Bank
- Industrial Development Bank
- Exchange Bank
- Regional Rural Bank
- Savings Bank
- Investment Bank
- Specialised Bank
The different types of banks are explained below:
1. Central Bank: The central bank in a country is the financial institution at the top (apex) of all the banking institutions operating in the country. In India, The Reserve Bank of India was established in 1945 under a special statute called the Reserve Bank of India Act, 1944. It performs the functions like framing monetary policy, issuing currency notes, acting as a banker to the Government and acting as the banker’s bank to commercial and other banks in India.
2. Commercial Bank : The Commercial bank plays key role in the economic, industrial and social development of a country. It performs broadly two functions such as (i) Primary functions which include accepting deposits and lending money in different forms and (ii) Secondary function which include agency functions and utility functions. The different types of commercial banks in India are as follows:
(i) Public Sector Banks : The banks in which majority of the share capital or stake (interest) is held by the Government of India are called Public Sector Bank, e.g. State Bank of India, Bank of India, etc.
(ii) Private Sector Banks : The banks in which majority of the share capital or stake is held by private individuals are called Private Sector Banks, e.g. Axis Bank, HDFC Bank, etc.
(iii) Foreign Banks : The banks which are registered and have their headquarters in foreign country but operate in different countries including India through their branches established there, are called Foreign banks e.g. Standard Chartered Bank, American Express Bank, HSBC, etc.
3. Co-operative Banks : Co-operative banks are formed, registered and organised under the Indian Co-operative Societies Act and regulated under Banking Regulation Act. These banks are more popular in rural and semi-urban areas. These banks are primarily meant for catering to the financial needs of economically backward people, farmers and small scale units. They operate at three different levels:
(a) Primary Credit Societies : The primary credit societies work at village level. These credit societies collect the savings and surplus money in the form of deposits from members and common people. They are also financed by the State Co¬operative Banks and District Co-operative Banks for the purpose of lending to needy people for productive purpose.
(b) District Central Co-operative Banks : The District Central Co-operative Banks operating at district level and financed by the State Co-operative Bank for the purpose of providing finance to primary credit societies.
(c) State Co-operative Banks : The State Co-, operative Banks Eire working at state level. These banks provide funds to District Central Co-operative Banks and Primary Credit Societies to enable them to provide finance to rural and semi urban areas. Apart from this, they also supervise the working of district banks and credit co-operative societies.
4. Industrial Development Banks : The banks which provide medium and long term equipment, latest technology, expansion and modernisation of business, etc. are called Industrial Development Banks. Industrial Finance Corporation of India (IFCI), State Financial Corporations (SFCs), Maharashtra State Finance Corporation (MSFC), etc. are the examples of Industrial Development Banks. These banks perform the following functions:
- Provide medium and long term finance to business organisations for expansion and modernisation.
- Underwriting i.e. giving guarantee to buy shares issued by public limited companies.
- Purchase debentures and bonds.
5. Exchange Banks : An exchange bank specialises in financing import and export trade and in foreign exchange transactions. The American Express Bank, Bank of Tokyo, Barclays Bank, etc. are the examples of Exchange Banks functioning in India. The Exchange Banks perform the following functions:
- Finance foreign trade transactions,
- Issue letter of credit on behalf of importer,
- Discount foreign bills of exchange,
- Remit dividend, interests and profits.
6. Regional Rural Banks : These banks were constituted (established) in 1975 and are sponsored by large public sector banks. 50%, 35% and 15% of the capital of these banks are provided by the Central Government, sponsored banks and State Government respectively. These banks collect (mobilise) funds in the form of deposits from rural and semi-urban areas. They provide loans and advances to small and marginal farmers, agricultural workers, rural artisans for productive purpose.
7. Savings Bank : A savings bank is one which has the main object of inculcating the habit of saving among the community. It collects scattered savings of the community especially from rural areas and invests the same in good securities. In India, Postal Savings Bank is an example of such a bank. Commercial Banks and Co-operative Banks act as savings banks as they have separate savings accounts departments.
8. Investment Bank : Investment banks offer financial and advisory assistance to their customers which usually include business firms and government organisations. These banks provide advice on investment decisions and facilitate mergers and acquisitions by undertaking research. These Banks do not directly deal with the common people.
9. Specialised Banks: The banks which make available to the requirements of the business and provide possible support to set up business activities in specific area are called Specialised Banks. The different types of specialised banks are:
(a) Export Import Bank of India (EXIM Bank) : These banks provide the needed financial assistance and support to the exporters and importers in setting up business for exporting and importing products respectively. They work to expand and promote country’s international trade.
(b) Small Industries Development Bank of India (SIDBI) : SIDBI was established on 2nd April, 1990 under the Act of Parliament of India. Its main function is to act as the main institution for financing, promoting and developing the Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) as well as co-ordinator of the institutions engaged in similar activities.
(c) National Bank for Agricultural and Rural Development (NABARD) : NABARD has been established to work as an apex institution to finance agricultural and rural sector. It provides long term and short term loans through regional rural banks. It provides loans to financial institutions and not individuals. It is also concerned with the function of policy planning and operations relating to agricultural credit and credit for other activities in rural areas.
Question 3.
What is warehouse? Explain its different functions.
Answer:
[A] Meaning : A warehouse can be defined as, “an establishment for the storage or accumulation of goods.” The term ‘warehousing’ is generally used to denote storage of goods and consists of all those activities which are connected with the storage and preservation of goods in a godown or warehouse. One of the group activity or functions is to hold the goods in stock from the time of production till the time of consumption is called storage of goods. When storage of goods is required to be arranged on a large scale in a specified manner, it is called ‘warehousing’.
[B] Functions : The functions of warehouses are explained as follows :
Function of Warehouses
- Storage
- Price Stabilisation
- Risk-Bearing
- Financing
- Grading and Packing
- Transportation
- Time and Place Utility
- Processing
1. Storage : Storage of goods is the basic function of warehousing. Warehouses provide space for storage of goods in large quantity and in good condition. The commodities which are not required immediately are stored in the warehouses. Stored goods are supplied as and when they are required by the customers.
2. Price stabilisation : Warehousing facilitates price stabilisation by maintaining proper balance between demand for and supply of commodities. It is achieved by creation of time utility by warehousing. Usually, large stock of goods is kept in the warehouse. Wherever, there is shortage of goods in the market, goods are released from the warehouse which increases supply and facilitates price stabilisation. Thus, it helps to avoid any rise in prices.
3. Risk-bearing : While the goods are stored in the warehouse, the warehouse-keeper takes reasonable care to protect the goods from risks of loss or damage due to heat, cold, moisture, dryness, insects, fire and thefts. This is because he has to return the goods in the same condition. For any loss or damage of goods during storage, warehouse-keeper will be held liable to the owner of the goods. Thus, the risk is transferred from the owner to the warehouse-keeper.
4. Financing : On the basis of goods stored in the warehouse, loans can be raised from the financial institutions or warehouse-keeper. The goods act as a security for financial institution. This loan can be used to meet other operations of business by the owners of goods.
5. Grading and Packing : Warehousing provides enough space for undertaking various marketing functions like grading, processing and packing of goods. Goods can be packed in suitable sizes as per the instructions of the owner. Thus, services of warehousing are very useful to manufacturers, wholesalers and the importers of goods.
6. Transportation : Some warehouses also provide transport facility to the traders who store large quantity of goods in the warehouse. It brings the goods from the places of production and also sends them to the places of delivery on behalf of depositors.
7. Time and Place Utility: Warehousing creates time utility by storing goods and releasing the same at the time when they are demanded. It also creates place utility by transporting goods at the far away places, where they are required.
8. Processing : For certain commodities processing is necessary to make them consumable or useable. This is because those commodities cannot be consumed in the form they are produced in the nature, e.g. paddy, raw fruits, etc. The activities such as polishing the paddy, ripening the fruits, etc. are undertaken by the warehouses on behalf of the owners.
Question 4.
What is Services? Explain in detail different business services.
Answer:
[A] Meaning : A service is an act of performance that one party offer to another for certain consideration. Service is essentially intangible i.e. cannot be touched, seen and felt. Services are neither manufactured nor stocked or transported. They are produced and consumed simultaneously. So, Services are intangible, heterogeneous, inseparable, inconsistent, instantly perishable in nature, not transferable and require consumer participation. Services which help in successful running of a business are called business services.
Business cannot be run without business services. These services are provided to the customers which fulfil their needs. Banking, insurance, transport, warehousing, communication, etc. are the examples of business services. According to American Marketing Association, services implies, “Activities, benefits or satisfaction which are offered for sale or provided in connection with the sale of goods.”
[B] Types : The different types of services are shown:
- Banking
- Insurance services
- Transport services
- Warehousing
- Communication
The different types of business services are explained as follows:
1. Banking : As the production has to take place on a large scale, adequate finance is required. Further, there must be facilities for the exchange of goods. Banks provide necessary finance and to facilitate exchange issue different types of facilities such as cheques, drafts, debit card, credit card, net banking, mobile banking, etc. The banks also provide loans to the business and industry to buy properties and to pay for routine expenses.
2. Insurance services : There are several business risks involved during the period from the stage of production to the stage of consumption. Insurance company in consideration of a definite fees called premium, undertakes all such risks through fire, marine, life and other insurance contracts. Insurance is a service contract in which insurance company in consideration of specific premium amount promises to pay a fixed amount to insured person either on the expiry of pre-determined fixed period or in case of happening of any unlucky accident whichever is earlier. Thus, by protecting the traders against the risks, an
insurance company enables the traders to concentrate on their day-to-day business activities.
3. Transport services : Transport is a service or facility which creates place utility by carrying essential products, raw materials and human resources from one place to another. It plays an important role in the development of all sectors of the economy. Transport helps to widen the market for agriculture and manufactured goods. The efficient transport network facilitates development of commercial activities. It facilitates movement of labour and capital assets from different areas to developed areas.
4. Warehousing : Warehouse is a place or a room or a building where goods are stored prior to their use, distribution or sale. Warehousing creates time utility. It solves the problem of holding the stock of goods during the time-gap between production and consumption. It also provides enough place to perform certain marketing services like grading, weighing, packing, branding, labelling, etc. Warehousing also equalises demand for and supply of goods in the market and helps to stabilise the prices of goods.
5. Communication : George Terry defines communication as, ‘the process of transmitting and interchanging ideas, facts and actions’. It is a main aid to trade. Communication services such as post, telegraph, telephone, cell phones, telex, fax, courier, e-mail, internet, etc. help to transmit and communicate business information quickly among the businessmen
Question 5.
What is communication? Explain in detail various types of communication.
Answer:
[A] Meaning : The term ‘communication’ means any interchange of ideas, messages, facts, information, feelings and emotions among two or more persons In a way that they share common understanding about it. It Is a process of giving away or passing on any information by any person to some other person with the help of some medium. Thus, receiver after receiving the message understands it in the desired form and acts accordingly.
[B] Types of Communication : The different types of communication are shown in the following diagram:
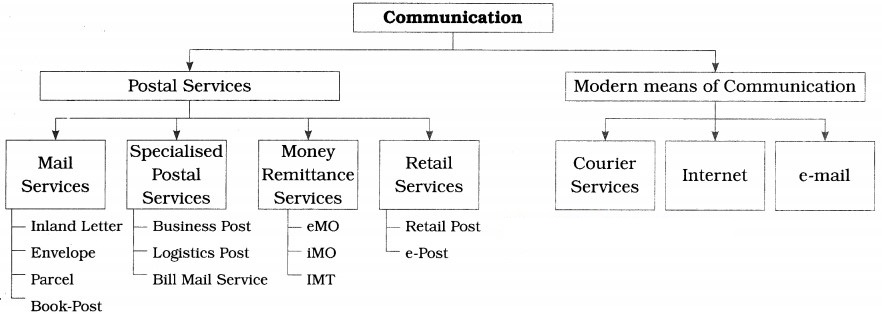
The different types of communication are explained below:
(I) Postal Services : The postal services in India are provided by the Department of Post which comes under Ministry of Communication and Information Technology. India has the largest postal network in the world with 1,54,965 post offices of which 1,49,067 are in the rural areas. The different types of postal services are explained below:
(1) Mail Services : The different types of mail services are described below:
(i) Inland letters : The inland letter is one of the cheapest means of conveying written message. It contains a blank sheet of paper of prescribed size and folding for writing messages. It is folded and sealed. Only names and addresses of the receiver and sender can be seen from outside. So, it ensures complete secrecy. Inland letters are used for transmission of messages within India only.
(ii) Envelopes : A postal envelope is a small size paper cover with postage stamps affixed on it having one side open to put in papers, written messages and enclosures like cheques, photos, resumes, etc. It ensures maximum secrecy. On the front outside space name and address of receiver are written and on the backside space name and address of sender are written.
(iii) Parcel : Parcels help to send small articles from one place to the other by post. Parcel post provides economical and reliable parcel delivery service. Parcels of specified weight and size can be sent at different places within the country as well as outside the country Anything except those items which are banned can be sent. Parcel can be insured by paying extra charges for insurance. In case of insured parcel is lost in transit post office pays insured amount.
(iv) Book post : Printed materials such as publications, newspapers, printed books, wedding, cards, greeting cards, periodicals, legal documents, etc. can be mailed as book post. The book post packets should simply be closed and should not be sealed. The words ‘Book Post’ should be written on the face of the cover.
(2) Specialised Postal Services : The following specialised postal services are provided by the post offices:
(i) Business Post : Business post arranges complete mailing services right from preparation of mail to delivery of mail. It is most suitable for small business and large companies. As per requirement, customers can select from a range of cost effective and professional mailing services ! which include printing, collating (comparing or examining), inserting, sealing and addressing. Indian post has established Business Post centres in major cities to handle business post consignment.
(ii) Logistics Post : Logistics post provides its business customers a cost-effective and timely solution that manages the entire value chain from collection to storage to transmission to distribution throughout the country.
(iii) Bill Mail Service : Communications in the nature of financial statements, bills, monthly account statements or any such other items of similar nature are sent by service providers to the customers by using bill mail service of post office. This service is used at least once in 90 days. Under this service, at a time minimum 5000 articles can be posted. The bill mail service does not include communication in the nature of letter mail or having personal communication or exclusive commercial publicity material. The mail is to be received at specified location provided. Bill mail is to be sorted pin code wide and bundled delivery post office wise.
(3) Money remittance services : The money remittance services are explained as follows:
(i) Electronic Money Transfer (eMO) : A money order is the most convenient method of remitting money to distant places. It is an order issued by one post office to another to pay a certain amount of money to a person specified therein. The person to whom money is to be paid is called ‘Payee’. Under this service of the post office, money is delivered at the house or the place of stay of the receiver.
(ii) Instant Money Order (iMO) : Instant Money Order (iMO) is an instant web based money transfer service by which minimum Rs 1000 and maximum Rs 50,000 can be transferred to distant places from designated iMO post offices. It is the instant on-line money transfer service which is safe, convenient, reliable and affordable. The money can be sent to close relative residing at distant place in India. It is simple, quick and economical to send and receive money.
(iii) International Money Transfer : International Money Transfer is the most convenient, quick and easy way of transferring personal remittances from foreign country to family members or other beneficiaries in India. Now this service is made available in all post offices in India by Department of Post, Government of India with the help of Western Union Financial Services. The remittances of money are permitted from around 195 countries to India.
(4) Retail services : The retail services are explained as follows:
(i) Retail post : Under retail post service, the department of post offers services to general public by making available some products and services of third party available in their areas through selected post offices. Under this, post offices offer a range of services including the collection of electricity bills, telephone bills, insurance premia, collection of taxes and fee for the government, etc. The post office also sells application form.
(ii) e-post : Recently, the department of posts has introduced e-post services, e-post service is service under which printed messages of customers are scanned and transmissed as email through internet. At the destination place or offices, these messages are printed, enveloped and delivered at the postal address. Thus, it is the combination of electronic transmission and physical delivery. Through e-post customers can send their messages to any address in India through network of more than 1,55,000 post offices. Corporate customers get special e-post rates and value additions.
(II) Modern means of communications : The modern means of communication are explained as follows:
(i) Courier Service : A courier service is a service that allows someone to send a parcel or consignment from one place to some other distant place. Usually, courier services are provided by a company and charge flat rates to the parties using the courier service regularly. Courier services differ from ordinary mail services in respect to speed, security, tracking, signature, delivery time, etc. Usually, premium courier services are more expensive as compared to ordinary mail services. DHL, DTDC, etc. are the examples of courier services.
(ii) Internet : The internet is one, in which users at one computer can, if it has permission, get information from other computer. It is a networking infrastructure. It connects millions of computers together globally, framing a network in which any computer can communicate with any other computer as long as they are both connected to internet. It is a network of networks that include of private, public, academic, business and government networks of local to global scope linked by a broad array of electronic, wireless and services such as world wide web, etc.
(iii) E-mail : E-mail stands for Electronic mail. E-mail refers to the transmission of information, from one computer terminal to another. It is a method of exchanging mail between the users of electronic devices. E-mail servers accept, forward, deliver and store messages. Users are not required to be online simultaneously. They are required to connect to a mail server briefly for as long as it takes to send or receive messages.
Question 6.
What is road transport. Explain its advantages and disadvantages.
Answer:
[A] Meaning : Road transport is the oldest mode of transport. It means and includes various means of transport which move on the surface of the earth without the use of railway tracks. Roads are the means which connect people and places on the surface of the land. It provides connectivity on any terrain (land) in comparison to other modes of transport. The different types of vehicles plying on the road include bullock carts, cycles, motor-cycles, autorickshaws, cars, tempos, trucks, buses, etc. They are called means of road transport.
[B] Advantages : The advantages of road transport are explained as follows:
(1) Cheaper mode of transport : As compared to other modes of transport, road transport is relatively cheaper mode of transport. Its operational cost is relatively low.
(2) Useful for perishable goods : Road transport is suitable and more useful to carry and deliver perishable goods such as milk, vegetable, fish, mutton, fruits, flowers, eggs, etc., over a short distance and that too at a faster speed.
(3) Flexible mode of transport : Road transport is flexible mode of transport because loading and unloading of goods are possible at any destination. Similarly, it is more flexible because of the choice of different routes, timings and types of vehicles.
(4) Door-to-Door service : Road transport facilitates door-to-door delivery of goods. It carries the goods and passengers directly to the godowns, factories and places of residence, i.e. user.
(5) Good reach : Roads constructed in plain areas and also in hilly areas can be used by different road vehicles such as trucks, tempos, motor cars and even carts driven by animals for carrying goods and passengers from one place to another. Wherever any other mode of transport cannot reach, road vehicles can easily reach and thus cover even hilly areas.
(6) Less capital investment : The cost of construction and maintenance of a road system is relatively less than that of railways.
[C] Disadvantages : The disadvantages of road transport are explained as follows:
(1) Not economical for long distance : In comparison to other modes of transport carrying capacity of road transport is very limited. High cost of fuel, tolls, etc. make the road transport uneconomical for long distance transportation.
(2) Not suitable for heavy and bulky goods : Road transport is not suitable for carrying heavy and bulky goods for any distance and involves high cost.
(3) Affected by adverse weather conditions : Road transport is affected more by adverse weather conditions such as fogs often greatly reducing visibility, heavy rain, floods, landslides, storm, etc.
(4) Accidents : The possibility of road accidents is frequent due to poor condition of roads and negligent drivers.
(5) Causes pollution : The vehicles plying on the road release smokes and gases. So, it creates air pollution which affect the health of the people.