Chapter 5 Emotions
Chapter 5 Emotions
1. Choose the correct option and complete the following statements.
Question 1.
…………… is a combination of bodily arousal, expressive behaviour, thoughts, and feelings.
(a) Response
(b) Reaction
(c) Emotions
Answer:
(c) Emotions
Question 2.
According to James Lange we first experience ……………….. then emotions.
(a) physical arousal
(b) feelings
(c) thoughts
Answer:
(a) physical arousal
Question 3.
Emotion is used as a …………….. to control others.
(a) weapon
(b) measure
(c) opportunity
Answer:
(a) weapon
Question 4.
When you allow another person to exploit you, you are a victim of ………….. abuse.
(a) physical
(b) emotional
(c) social
Answer:
(b) emotional
Question 5.
Exercising releases ………………… which makes you feel good as a stress buster.
(a) endorphins
(b) thyroxin
(c) insulin
Answer:
(a) endorphins
2. Identify the odd items from the following and write a suitable reason for your choice
Question 1.
admiration, disgust, acceptance, trust
Question 2.
kicking, ignoring, shoving, screaming
Question 3.
Reassess, React, Respond, Relax
Question 4.
meditation, social work, compassion, engage in hobbies
3. Match the pair.
Question 1.
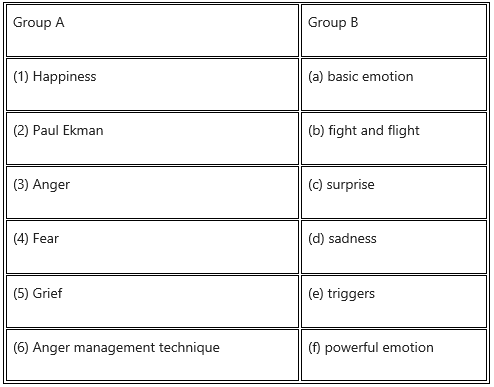
Answer:
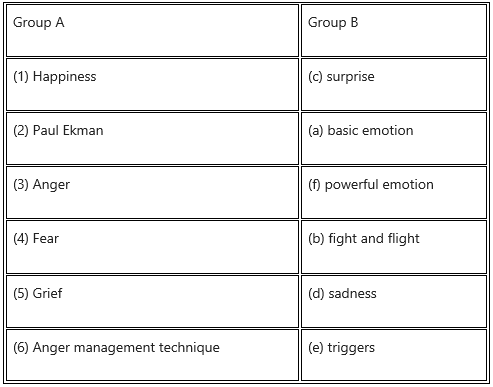
4. State whether the following statements are true or false.
Question 1.
Emotional well-being is not easily observable.
Answer:
True
Question 2.
Positive emotions energise you.
Answer:
True
Question 3.
You should feel guilty for standing up for yourself.
Answer:
false
Question 4.
Anger is a basic negative emotion.
Answer:
True
5. Answer the following questions in 35 – 40 words each.
Question 1.
Explain the term facial feedback hypothesis.
Answer:
According to the facial feedback hypothesis, our facial expressions provide feedback to our brain about our emotions. Facial expressions are not only the result of our emotions, e.g., smiling in happiness, but they are also capable of influencing emotions, e.g. laughter can actually make us feel happier. The same might hold true for other emotions as well. In the 1840’s, William James presented the idea that awareness of our bodily experiences is the basis of emotion.
Question 2.
When does an individual face social rejection?
Answer:
Social rejection occurs when an individual is deliberately excluded from a social relationship or interaction. This can be done by a person or a group. It includes rejection of the person by family/ peers/ colleagues or even in intimate relationships. Rejection may be active, i.e., by ridiculing, bullying, etc., or passive, i.e., ‘silent treatment’. Social rejection may be faced due to individual differences e.g., attractiveness, shyness or due to intergroup exclusion on the basis of prejudice, e.g., in case of Dalits or ethnic minorities.
Question 3.
With the help of an example write the non-verbal triggers of anger.
Answer:
Anger is a common emotion that everybody experiences in life from time to time. Anger is a normal response to some real or perceived threat. It is a protective emotion that help us to defend ourselves against physical or psychological harm.
Triggers of Anger refer to any event that signals the brain to activate the body’s anger system. The triggers of anger may be (i) verbal, for e.g., being blamed, disrespected or abused (ii) non¬verbal, for e.g., being ignored unappreciated or rejected, (iii) physical such as physical threats, sexual/ physical assault, etc.
Non-verbal triggers of anger are feelings of being neglected, disregarded, disappointed, unloved or frequently spurned. It is expressed through gestures such as pointing a finger, shrugging the shoulders; by facial expressions such as sneering, frowning and also by behaviours such as groaning/sighing/whining or speaking in a mocking tone.
There are three factors involved in the experience of anger : A trigger (causes of anger) → individual’s personality → particular interpretation of that situation.
Question 4.
What are the aspects of emotional well-being?
Answer:
Emotional well-being means managing our emotions, both positive and negative ones, so that we can lead a healthy and productive life. It is the absence of negative affect as well as general satisfaction with life. A person who experiences emotional well-being is positively engaged with the world.
The aspects of emotional well-being are at three levels viz. physical, emotional and social.
- Physical level, i.e., well balanced diet, exercise.
- Emotional level, i.e., practise mindfulness, raising levels of motivation and optimism.
- Social level, i.e., engaging in prosocial behaviour, meaningful relationships.
6. Compare and Contrast
Question 1.
Happiness and Sadness
Question 2.
James Lange theory and Cannon Bard’s Theory
7. Write short notes on the following in 50 – 60 words each.
Question 1.
Measures of dealing with Emotional Abuse
Answer:
Emotional abuse is any kind of abuse that is emotional rather than physical in nature. It occurs when one person subjects or exposes another person to intentionally harmful behaviour that may result in anxiety, depression and psychological trauma to the victim.
The types of emotional abuse may be-
- verbal abuse such as blaming, insulting, labeling, threatening, swearing, etc.
- non verbal abuse such as ignoring, rejection, bullying, spying, etc.
The most important technique is to break the silence and stand up for yourself.
- Accept that emotional abuse is not because of you, i.e., don’t justify the actions of the abuser.
- Respond assertively to the abuser but seek distance from him.
- Give yourself time to heal.
- Prioritize your self-care, e.g., eating right, exercise, etc.
- Mobilise support from family and friends. If needed, seek professional help.
Question 2.
Plutchiks’s Model of Emotions
Answer:

Robert Plutchik presented the wheel of emotions,
- there are 8 basic emotions viz. joy, trust, fear, surprise, sadness, anticipation, anger and disgust.
- each primary emotion has its polar opposite such as fear is opposite of anger.
- primary emotions combine to produce complex emotions, for e.g., love (complex) is a combination of joy and trust.
- intensity of emotions increases as we move toward the centre and decreases as we move outward. For e.g., apprehension (weak) → fear (basic) → terror (strongest).
This model is important from the perspective of emotional literacy, i.e., understanding emotional levels, complexity and change as well as appropriate emotional labelling
Question 3.
Anger -A powerful emotion
Answer:
Anger is a common emotion that everybody experiences in life from time to time. Anger is a normal response to some threat. It is a protective emotion that helps us to defend ourselves against physical/ psychological harm. However, anger may also be unwanted, irrational and destructive. When we experience anger, our amygdala goes into action and overrides the cerebral cortex which is in control of thinking and evaluation. Triggers of anger refer to any event that signals the brain to activate the body’s anger system. The triggers may be (i) verbal, for e.g., being blamed, disrespected or abused (ii) non-verbal, for e.g., being ignored unappreciated or rejected, (iii) physical such as physical threats, sexual/ physical assault, etc.
There are three factors involved in the experience of anger: A trigger (causes of anger) → individual’s personality → particular interpretation of that situation. As the experience of anger is subjective, it can be controlled too. If we understand the triggers of anger, we can anticipate potential anger episodes and provide an intentional/ acceptable response such as it may energize us towards solving problems. As anger is a powerful emotion, it must be kept in check to avoid it’s destructive out comes.
Question 4.
Managing Emotions
Answer:
The word emotion is derived from the latin word ‘emovere’, which means to stir up or to move. An emotion refers to an involuntary, aroused state of an organism involving physical, cognitive and behavioural components. It is described as a combination of bodily arousal, e.g., increased heartrate, thoughts and feelings, i.e. emotional tone and expressive behaviour, i.e., facial expression.
Managing of emotions is an important life skill. Managing emotions can be defined as, ‘the ability to be open to feelings and modulate them in oneself and in others, so as to promote personal understanding and growth. It is the ability to be aware and constructively handle both positive and challenging emotions.
Sometimes, our emotions hijack our thinking due to which we act impulsively. This is because the limbic system (emotional section) developed before the prefrontal cortex (thinking part) and is hence, an extremely strong part of the brain. Emotional management is an art as it is a form of expression as well as a science as it is a skill that needs to be learnt and practiced If a person ignores of suppresses his/her emotions it leads to anxiety. The best way of manage emotions is to acknowledge the emotions, find out what is the cause of that emotion in you, chose how to respond in that situation.
Question 5.
Benefits of Emotional Well-being
Answer:
Emotional well-being means managing our emotions, both positive and negative ones, so that we can lead a healthy and productive life.
Persons who have high emotional well-being experience benefits such as- (i) better able to deal with stress (ii) better self-regulation (iii) increased productivity in tasks undertaken (iv) increased creativity (v) life satisfaction due to meaningful activities and relationship.
- Coping with stress – It helps to deal with stress using healthy methods such as exercise, social support, etc.
- Better self-regulation – It enables the person to label how they feel and accept negative emotions life fear, anger, etc.
- Increases productivity in tasks undertaken – The ability to focus is enhanced, the person feels positive and energized.
- Increases creativity – The person indulges in divergent thinking, shows curiosity is open to new experiences.
- Life satisfaction – The individual is able to have meaningful interactions and relationships, show empathy, altruism and engage in activities like volunteer work.
8. Answer the following 50 – 60 words.
Question 1.
Using the 3 R model of Anger Management present a case study of your own experience.
Answer:
Anger management is an intervention programme to prevent anger from turning into a habit or obstacle. It enables the person to create an awareness of and responsibility for his/her emotions. This involves two aspects (i) managing one’s own anger (ii) learning to respond effectively to anger in others.
The 3 R’s in anger management a Relax, Reassess and Respond.
1. Relaxation – Relaxation and connection with the inner self helps to enhance thinking and concentration so that we ‘respond’ rather than ‘react’ impulsively.
2. Reassess – This helps the person to revisit the situation objectively. It involves
- taking complete responsibility for your emotion
- developing empathy for the person you perceive has wronged you
- conduct a reality check e.g., is your anger justified given the facts of what happened.
The feeling’s thermometer helps to focus on the extent of anger we are experiencing and helps in the process of reassessment.

3. Respond – It entails re-engaging with the other person/situation. Responding involves
- consulting a trustworthy person to get another perspective
- engage in talks with the other party in a calm respectful manner with a willingness to sort out the situation.
- active listening and assertive speaking – Allow the person to express their viewpoint. However, we should stand up for our feeling while exhibiting the same for the other person. The right approach is a practical, positive communication style.
- cage your rage i.e. establish boundaries and moderate your anger – We must guard against escalation of our own anger which may lead us to provoke the other person. Moderation of anger and establishing clear boundaries of interaction with each other is essential.
CASE STUDY – 1 was in the passenger seat and my brother was driving the car. Suddenly, a cyclist swerved right in front after he had failed to observe the red light. This led me to get enraged at this uncalled-for action. Using the 3R technique. I tried to breathe for a few seconds to give me recovery time, i.e. Relaxation. I revisited the situation – Is my anger justified? Was it a genuine error? Is the cyclist hurt? Did the incident cause injury to us or damage to the car.? Is the anger worth my time/effort? Reassess. I allowed my elder brother to handle the situation but also assertively cautioned the teenage cyclist about the dangers of riding in a rash manner, i.e. Respond.
Question 2.
How does the brain work when angry?
Answer:
Anger is a common emotion that everybody experiences in life from time to time. Anger is a normal response to some threat. It is a protective emotion that help us to defend ourselves against physical/ psychological harm. However, anger may also be unwanted, irrational and destructive. When we experience anger, our amygdala goes into action and overrides the cerebral cortex which is in control of thinking and evaluation.
Triggers of anger refer to any event that signals the brain to activate the body’s anger system. The triggers may be (i) verbal, for e.g., being blamed, disrespected or abused (ii) non-verbal, for e.g., being ignored unappreciated or rejected, (iii) physical such as physical threats, sexual/ physical assault, etc.
There are three factors involved in the experience of anger: A trigger (causes of anger) → individual’s personality → particular interpretation of that situation. As the experience of anger is subjective, it can be controlled too. If we understand the triggers of anger, we can anticipate potential anger episodes and provide an intentional / acceptable response.
The emotional center of the brain is the Limbic system and is more primitive than the cerebral cortex. It is located in the lower section of the brain. Hence when a person is experiencing and expressing anger, he or she is not using the cortex (thinking section) but primarily functioning from the limbic system. In the limbic system, a small structure called Amygdala which is a storehouse of emotional memories plays an important role in the emotional outbursts. The data coming in from the world around us passes through the amygdala where the decision is made whether to send the data to the limbic or cortex area of the brain.
If the incoming data triggers enough of an emotional charge, the amygdala can override the cortex, which means the data will be sent to the limbic system causing the person to react using the lower part of the brain. During an overriding event, the amygdala goes into action without much regard for the consequences (since this area of the brain is not involved in judging, thinking, or evaluating).
Eg. You are waiting patiently in the queue at the bank, a person comes and cuts the line and moves ahead of you, you scream at them and ask them to go back. On an average, it can take 20 minutes for a person who has experienced an angry state of arousal to calm, to move from functioning from the emotional area to the thinking area of the brain.
Question 3.
After having realised you are emotionally abused by your best friend, write the steps you will take to deal with it.
Answer:
Emotional abuse is any kind of abuse that is emotional rather than physical in nature. It occurs when one person subjects or exposes another person to intentionally harmful behaviour that may result in anxiety, depression and psychological trauma.
The types of emotional abuse may be (i) verbal abuse such as blaming, insulting, labeling, threatening, swearing, etc. (ii) non verbal abuse such as ignoring, rejection, bullying, spying, etc. Some of the techniques to deal with emotional abuse are-
- Accept that emotional abuse is not because of you i.e. don’t justify the actions of the abuser.
- Respond assertively to the abuser but seek distance from him/her.
- Give yourself time to heal.
- Prioritize your self-care, e.g., eating right, exercise, etc.
- Mobilise support from family and friends. If needed, seek professional help.
If I realize that I have been emotionally abused by my good friend I will adopt the following steps-
- Disengage from the friendship and set personal boundaries
- Understand that I am not the cause of abuse and so respond assertively to the abuser
- Practice self care and give myself time to heal
- If necessary seek guidance from other friends or my family / teachers.
9. Analyse the situations presented below and
a. Write the Emotion/s you experience.
b. What will be your response to this situation?
Question 1.
Anish was scolded by his boss. He came home and in a fit of rage hit his son. You are Anish’s friend who witnessed this outburst.
Answer:
I will feel anger as well as disgusted on witnessing this outbust. I will try to calm Anish and make him realise the harm that his anger can cause.
Question 2.
You helped your friend with study notes during his illness. But when your friend got better he did not respond nor show any sense of appreciation.
Answer:
I will feel disappointment as well as sadness. I will meet the friend and tell him that his lack of courtesy has hurt me.
Question 3.
Though you are a good friend of Anushka, she has not invited you to her new year’s party.
Answer:
I will feel disappointed and hurt. I will (if possible) try to find out if the action was deliberate or an oversight.
Question 4.
It’s your Birthday and you wake up that morning to find yourself surrounded with beautiful gifts.
Answer:
I will obviously feel immense happiness.
Question 5.
You have had a hectic day at college when you come home you find the door locked. You forgot your keys at home that day and your parents have not informed you of their plans.
Answer:
I will be angry at my at myself and my parents also. But since I forgot the keys, I will take full responsibility and wait it out some family member returns.
Question 6.
You have planned a surprise day out for your best friend and she tells you she is not interested and has other plans
Answer:
I will be a little sad and disappointed but will accept my friend’s decision sportingly.
ACTIVITIES (Textbook Page. No. 44)
Activity 1
THINK AND ANALYSE
Think of the following situations and note down what will be the experience of each person in that situation.
- It’s Mira’s Std. 12th result today. She comes to know that she has topped in the college.
- Rahul’s mother passed away just few days before his 18th birthday.
- Suchita was ridiculed by her classmate for wearing old fashioned clothes.
- Yash had a fight at home because his parents were not allowing him to go for a late night party.
Answer:
- Mira will experience happiness due to her success.
- Rahul will experience grief and loneliness.
- Suchita will experience a sense of helplessness and shame.
- Yash will be angry with his parents and feel they are doing him an injustice.
Activity 2 (Textbook Page. No. 46)
Observe each figure carefully and write the emotion that corresponds to each in the blank spaces provided below. Can you identify which among these is a positive and negative emotion?
Answer:
(A) = Surprise (positive), (B) = Anger (negative), (C) = Disgust (negative), (D) = Sadness (negative),
(E) = Joy (positive), (F) = Fear (negative).
Activity 3 (Textbook Page. No. 46, 47)
Check whether you can name the emotions accurately from the following examples-
- It’s Riya’s 18th birthday today and her friends have given her a surprise party.
- Rohan recently had a break up with his long time girlfriend with whom he was in love deeply.
- Sameer had a disagreement with his best friend over where to go for a picnic and the situation got heated up.
- Sumi has come to know that she has failed in her exam and she is figuring out how she will convey this to her parents.
- Ashmeet suddenly saw his school best friend across the street after many years.
- Amy opened today’s newspaper and read the news of a 5 year old getting gang raped.
Answer:
- Happiness
- Surprise
- Anger
- Fear
- Surprise
- Disgust
Activity 4 (Textbook Page. No. 48)
THINK, REFLECT, ANALYSE AND DISCUSS
State what will you feel and how will /did you behave in the given following situations:-
- You are crossing the road and suddenly find a car breaking the signal and speeding up towards you.
- You reach home and find the table laid with your favourite dish cooked by your mother.
- You receive a phone call telling you that your best friend is undergoing an operation and needs blood.
- Recall an incident in your childhood when you were insulted by an adult.
Answer:
- I will feel angry but also afraid. I will jump out of the way
- I will feel happy and surprised.
- I will fear but feel concerned and be motivated to arrange for the blood.
- Students are expected to answer this question by themselves.
Activity 5 (Textbook Page. No. 49)
THINK, ANALYSE AND ACT
You see a snake ….. with reference to the above given components fill the process with your interpretations, feelings and actions.
Answer:
