Chapter 6 Social Responsibilities of Business
Chapter 6 Social Responsibilities of Business
1. (A) Select the correct options and rewrite the sentence
Question 1.
Business is a ………………. activity.
(a) socio-economic
(b) service
(c) charitable
Answer:
socio-economic
Question 2.
Business organisation should try to make ……………… utilisation of natural resources.
(a) minimum
(b) maximum
(c) optimum
Answer:
optimum
Question 3.
For economic growth and national security ………………. stability is required.
(a) political
(b) social
(c) economic
Answer:
political
Question 4.
Making timely payment of proper taxes is the responsibility of organisation towards ………………
(a) Shareholders
(b) Customers
(c) Government
Answer:
Government
Question 5.
Businessmen are ………………… of the society.
(a) Representatives
(b) Leaders
(c) Trustees
Answer:
Trustees
Question 6.
Business should provide periodic information to ………………
(a) customers
b) owners
(c) employees
Answer:
owners
Question 7.
Business should offer adequate opportunities of promotion to their ………………
(a) employees
(b) customers
(c) investors
Answer:
employees
Question 8.
The term ‘Ethics’ is derived from the ………………. word ‘Ethos’ which means character.
(a) Latin
(b) French
(c) Greek
Answer:
Greek
Question 9.
Business ethics refers to the ……………… system of principles.
(a) economic
(b) social
(c) moral
Answer:
moral
Question 10.
Business organisation should protect health and provide safety measures to ………………
(a) employees
(b) owners
(c) investors
Answer:
employees
Question 11.
At least ………………….. of the average net profit should be spent on C.S.R.
(a) 5%
(b) 2%
(c) 3%.
Answer:
2%.
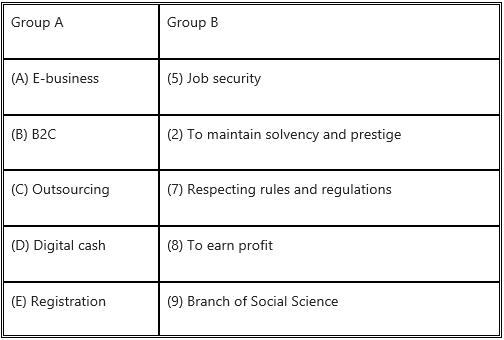
1. (B) Match the pairs
Question 1.
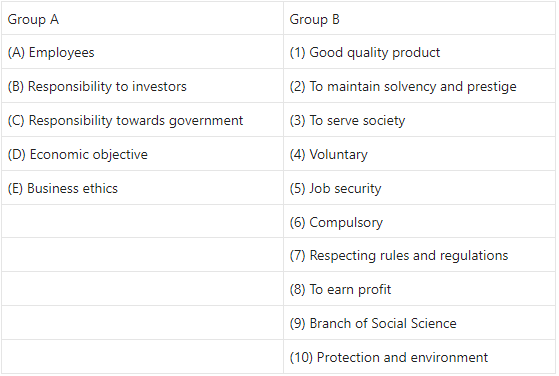
Answer:
1. (C) Give one word/phrase/term for the following statement
Question 1.
Name the philosophy related to social responsibility propounded by Mahatma Gandhi.
Answer:
Trusteeship
Question 2.
Duties, obligations of business directed towards welfare of society.
Answer:
Social Responsibility
Question 3.
Getting good quality products is the basic right of this group of society.
Answer:
Consumers
Question 4.
Providing fair returns on investment is the responsibility of organisation towards this group.
Answer:
Investors
Question 5.
Rules of standard dealing with morality in business environment.
Answer:
Business Ethics
Question 6.
An activity motivated by profit.
Answer:
Business
Question 7.
Earning foreign exchange is the responsibility of the organisation towards this group.
Answer:
Government
Question 8.
Employment generation is the responsibility of the organisation towards this group.
Answer:
Society
1. (D) State whether following statement are true or false
Question 1.
Businessmen are trustees of the society.
Answer:
True
Question 2.
Business ethics is a code of conduct.
Answer:
True
Question 3.
The commercial organisation are expected to uplift the weaker section of the society.
Answer:
True
Question 4.
It is the responsibility of commercial organisation to maintain industrial peace.
Answer:
True
Question 5.
Owners should not get complete and accurate information about the financial position.
Answer:
False
Question 6.
Media does not play important role in public life.
Answer:
False
Question 7.
Social responsibility is broader than legal responsibility of business.
Answer:
True
1. (E) Find the odd one
Question 1.
Job security, health and safety measures, good working condition, reasonable profit.
Answer:
reasonable profit
Question 2.
Good quality products, fair prices, honest advertising, prevent congestion in cities.
Answer:
prevent congestion in cities
Question 3.
Timely payment of taxes, earning foreign exchange, creating goodwill, political stability.
Answer:
creating goodwill
Question 4.
Protection of environment, maintain transparency, employment generation, development of backward region.
Answer:
maintain transparency
Question 5.
Proper conduct of meeting, careful use of capital, fair prices of products, maintain solvency and prestige.
Answer:
fair prices of products.
1. (F) Complete the sentences
Question 1.
Business organisation can maximise profitability by …………….. wastage.
Answer:
minimising
Question 2.
Social responsibility is broader than …………….. responsibility.
Answer:
legal
Question 3.
The concept of trusteeship was propounded by ……………….
Answer:
Mahatma Gandhi
Question 4.
Business should earn ………………. profit.
Answer:
reasonable
Question 5.
……………….. should be fixed according to the nature and importance of work.
Answer:
Remuneration
Question 6.
The word ‘Ethics’ is derived from the Greek word ………………..
Answer:
Ethos
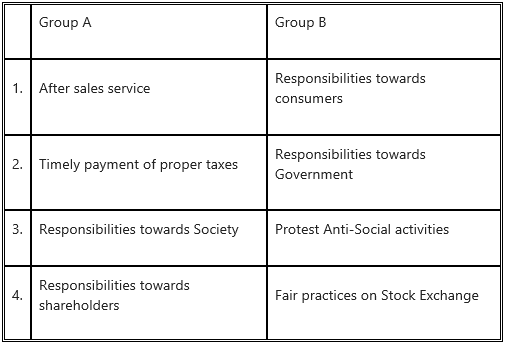
1. (g) Select the correct option
(Responsibilities towards shareholders, Responsibilities towards consumers, Responsibilities towards government. Responsibilities towards society)
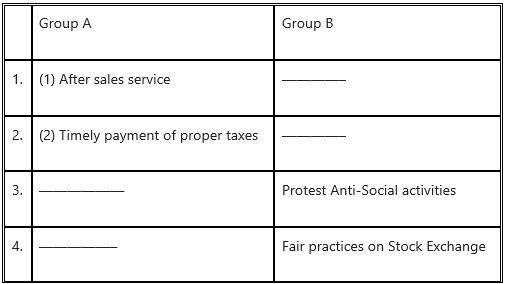
Answer:
1. (H) Answer in one sentence
Question 1.
Who can raise voice against business malpractices?
Answer:
Media can raise voice against business malpractices.
Question 2.
What should be done by management to keep workers updated?
Answer:
Guidance methods like ‘Introduction Training’, Refresher Training should be conducted to keep employees updated on the latest development to increase their efficiency and confidence.
Question 3.
What type of advertising should be avoided?
Answer:
False, misleading and vulgar advertisement should be avoided by the organisations.
Question 4.
What organisation should do to improve quality of goods and to reduce cost of production?
Answer:
Organisation should conduct research and development to improve the quality of goods and to reduce the cost of production which in turn will minimise the final prices charged to consumers.
1. (I) Correct the underlined word and rewrite the sentence
Question 1.
Social responsibility is narrower term than legal responsibility of business.
Answer:
Social responsibility is broader term than legal responsibility of business.
Question 2.
All sorts of fair practices related to stock exchange should be avoided.
Answer:
All sorts of unfair practices related to stock exchange should be avoided.
Question 3.
Management and union should agree strikes and lockouts to protect the interest of both the parties.
Answer:
Management and union should ban strikes and lockouts to protect the interest of both the parties.
Question 4.
MRP (Maximum Retail Price) should not be printed on every packet.
Answer:
MRP (Maximum Retail Price) should be printed on every packet.
Question 5.
Dishonest advertising can be appreciated by customers in the long run.
Answer:
Honest advertising can be appreciated by customers in the long run.
Question 6.
Financial help should be provided by business organisation for anti-social activities.
Answer:
Financial help should not be provided by business organisation for anti-social activities.
Question 7.
Business ethics is a compulsory term.
Answer:
Business ethics is a voluntary term.
Question 8.
Business ethics is not a relative term.
Answer:
Business ethics is a relative term.
Question 9.
Social values are based on perceptions of right or wrong.
Answer:
Moral values are based on perceptions of right or wrong.
Question 10.
Moral values provide general guidelines for social conduct.
Answer:
Social values provide general guidelines for social conduct.
2. Explain the following term/concept
Question 1.
Social Responsibility.
Answer:
(1) Good Quality Products : It is the responsibility of a commercial organisation to produce and supply good quality products and services. To improve the quality, every business unit must have quality control department to reject inferior and substandard products. In this respect, International Standards Organisation (ISO) is the latest trend towards quality control. This ensures customers’ loyalty to products.
(2) Fair Prices : The commercial organisation must charge fair and reasonable prices for its goods. Maximum Retail Price (M.R.E) inclusive of all taxes must be printed on all packed products. The customers should not be cheated by being charged higher prices. It is not fair and practicable to fool the customers every time. Such practices bring disrepute to the organisation and spoil its image in the long run.
(3) Customer’s Safety : The organisation must ensure that the product supplied has no adverse effect on the life and health of the consumers. Unsafe products must not be marketed by the organisation. The manufacturers of the genuine products must warn the consumers about the imitation and unsafe products well in time.
Question 2.
Concept of Trusteeship.
Answer:
(1) Trusteeship is a socio-economic philosophy that was propounded by Mahatma Gandhi. According to the principle of trusteeship, “A business must be carried out in trust, legally and morally for the benefit and welfare of the people.” Businessmen are treated to be trustees of society.
(2) Trusteeship provides a means through which rich or wealthy people become trustees of different trusts that take care or look after the welfare (well-being) of the people in the society. Business organisations function and operate within society. They are the part and parcel of the society to which they belong. Therefore, it is now realised that the activity which is harmful to the society is not good (suitable) for the business organisations.
Question 3.
Business Ethics.
Answer:
Meaning : The word ‘ethics’ is derived from Greek word ‘Ethos’ which refers to human character and conduct. The dictionary meaning of ‘ethics’ is moral principles that control or influence a person’s behaviour. The term ‘business ethics’ refers to a system of moral principles or rules of conduct applied to business operations or activities. It is a code of conduct for regulating the activities of business towards society and others. Ethics is a branch of social science.
According to Wheeler, “Business ethics is an art or science of maintaining harmonious relationship with society, its various groups and institutions as well as reorganising the moral responsibility for the right or wrong conduct of business
Question 4.
Moral Values.
Answer:
(1) Moral values are the standards of right and wrong which govern an individual’s behaviour and choices. Moral values may be derived from society, government, religion or self. Moral values are based on the understanding of right and wrong. Business ethics deals with morality in the business environment.
(2) Business may be guided by some moral principles such as not to get involved in unfair trade practices, to be honest and truthful about quality, not to sell adulterated products as pure product, not to give false and misleading advertisements, charging fair prices, paying taxes, duties and fees to the government honestly, and in schedule time, etc.
Question 5.
Social Values.
Answer:
(1) Social values are set of moral principles that provide the general guidelines for our social conduct. Social values constitute an important aspect of the culture of the society. They are based on tradition, ego, honesty, integrity, fairness, hard work, co-operation, forgiveness, etc.
(2) Social values are the values (standards) concerned with the social aspects of human life, e.g. truth, justice, kindness, generosity, tolerance, patriotism, respect for seniors, excellence, etc. The business organisations should develop social, values through educative advertising, cultural programmes, national integration programmes, assistance to the educational institutes, etc.
3. Study the following case/situation and express your opinion
Question 1.
Yashwant Co. Ltd. is providing facilities for their female staff like day care centre for kids and work from home facility. Even management takes their suggestions while taking the decisions though they are members of trade union.
(i) By doing this they are following social responsibilities towards which interest groups?
(ii) What values are they presenting?
(iii) What kind of responsibilities employer follows in above case?
Answer:
(i) By treating the staff with dignity and respect the company follows the social responsibilities towards the employees.
(ii) Yashwant Co. Ltd. are presenting social values by showing co-operation to their female staff.
(iii) Management takes the employees’ suggestions while taking the decisions even though they are members of trade union. By doing this, management recognizes the right of employees to join, Trade Unions. The company also does not restrict employees from forming Trade Union. Thus they follow social responsibility towards employees.
Question 2.
An organisation manufacturing paints has been enjoying a prominent market position since many years. It has been dumping its untreated poisonous waste on the river bank: which has created many health problems for the nearby villages.
(i) Which responsibility is neglected by manufacturing organisation?
(ii) What kind of pollution are they doing?
(iii) What precautionary measures they need to take?
Answer:
(i) Responsibility towards protection of environment is regulated by manufacturing industries.
(ii) They are creating water pollution by dumping its untreated poisonous waste on the river bank.
(iii) Proper waste management techniques should be adopted by the organisation under which waste should be reduced, effort should be made to reuse the waste. Waste that cannot be reduced or reused should be recycled.
Question 3.
A vehicle manufacturing company has adopted the following practices:
(A) Only those components will be used by the company which are environment-friendly.
(B) There will be discharge of harmful wastes only after their proper treatment.
(C) Pollution level of every vehicle will be maintained as per international standards.
(i) By doing this, business organisation follows social responsibility towards which interest group?
(ii) What kind of pollution do they want to avoid ?
(iii) What kind of message do they want to convey ?
Answer:
(i) Business organisation follows social responsibility towards society for protection of environment.
(ii) They want to avoid air pollution.
(iii) They want to convey the message that business should be committed to protect the environment and should not create imbalance in nature.
4. Answer in brief
Question 1.
Give any four types of social responsibilities towards consumers.
Answer:
The social responsibilities of commercial organisation towards consumers are explained as follows:
(1) Good Quality Products : It is the responsibility of a commercial organisation to produce and supply good quality products and services. To improve the quality, every business unit must have quality control department to reject inferior and substandard products. In this respect, International Standards Organisation (ISO) is the latest trend towards quality control. This ensures customers’ loyalty to products.
(2) Fair Prices : The commercial organisation must charge fair and reasonable prices for its goods. Maximum Retail Price (M.R.E) inclusive of all taxes must be printed on all packed products. The customers should not be cheated by being charged higher prices. It is not fair and practicable to fool the customers every time. Such practices bring disrepute to the organisation and spoil its image in the long run.
(3) Customer’s Safety : The organisation must ensure that the product supplied has no adverse effect on the life and health of the consumers. Unsafe products must not be marketed by the organisation. The manufacturers of the genuine products must warn the consumers about the imitation and unsafe products well in time.
(4) Honest Advertising : The advertisement conveys varied information of the products like the facts, features, side effects, advantages, uses, etc. to the customers. The commercial organisations must see to it that their advertisement should not mislead the consumers by exaggerating the actual facts. The commercial organisations must not indulge in vulgar, false and misleading advertisement. Honest advertisements are always appreciated by the consumers and become beneficial in the long run.
(5) After Sales Service: The commercial organisation should offer quick, satisfactory and efficient after sales service specially in the case of consumer durable products for their maintenance during the period of warranty. Effective and efficient after sales services enable them to establish and maintain good relation with the consumers.
Question 2.
What is Business Ethics ? What are elements of business ethics ?
Answer:
[A] Meaning : The word ‘ethics’ is derived from Greek word ‘Ethos’ which refers to human character and conduct. The dictionary meaning of ‘ethics’ is moral principles that control or influence a person’s behaviour. The term ‘business ethics’ refers to a system of moral principles or rules of conduct applied to business operations or activities. It is a code of conduct for regulating the activities of business towards society and others. Ethics is a branch of social science.
According to Wheeler, “Business ethics is an art or science of maintaining harmonious relationship with society, its various groups and institutions as well as reorganising the moral responsibility for the right or wrong conduct of business.
[B] Elements of business ethics : The elements of business ethics are explained as follows:
(1) Trustworthiness : Every business unit or organisation must work in all areas to maintain trustworthiness. This increases the confidence of clients or customers in the organisation. The clients usually believe in organisations for reliability and quality performance. Company or organisation functions and prospers on character, i fairness, truth, honour and ability.
(2) Honest service delivery : It is much better to be honest about what one can do rather than making empty promises. Empty or false promises ruin the reputation of the business organisation. Business organisation should fulfil or complete all its commitments and obligations and leave every customer feeling well served and satisfied.
(3) Confidentiality : The company or business organisation should strictly obey and follow its i internal confidential policy. It is utmost important for every business organisation to keep in secret the confidential details of its own clients. For private gain it should not disclose such information to any one. Similarly, it should not use any means to get information from competitors about certain formulae or methods of production.
(4) Openness : Good business ethics and continuous improvement also come from keeping an open mind. Business unit should follow the principle of openness. It should regularly demand opinions and feedback from both clients and team members. Even in times of business disagreement, business unit should welcome other’s opinions and ideas with respect and courtesy.
(5) Other common business ethics : (1) A large portion of our society is composed of common people with low purchasing power. Business enterprises should consider likes, dislikes and financial position of these people and accordingly manufacture and provide goods and services. (2) The guaranties and warranties given by the manufacturer should be proper and acceptable by the customers. (3) Advertisements given by the businessmen should not cross limit of decency.
Question 3.
State responsibilities of business towards government.
Answer:
Responsibilities of business towards government:
(1) Timely payment of taxes : Business organisations are expected to pay various taxes such as sales tax, income tax, corporate tax, excise duty, wealth tax, etc. levied by the government from time to time. These funds enable the government to undertake various development projects.
(2) Observing rules and regulations : The business organisations are expected to comply with the various laws, rules and regulations enacted by the government. The company should follow the laws regarding obtaining license of business operation, price determination and production, etc. They should conduct business in lawful manner.
(3) Earning foreign exchange : The business organisations Eire expected to export their products to foreign countries to earn foreign exchange. Foreign exchange is required by the government to import various goods, valuable and important products.
(4) Economic development : The government sets the targets for balanced growth and rapid economic development of the country. The business organisation is expected to provide necessary support to the government.
(5) Implementing socio-economic policies : The business organisations are expected to provide co-operation and required funds to the government in implementing various socio-economic programmes and policies.
Question 4.
State any four CSR activities.
Answer:
CSR, supports the following activities:
- Eradicating hunger, poverty & malnutrition, promoting preventive health care & sanitation & making available safe drinking water.
- Promoting education, including special education & employment enhancing vocation skills especially among children, women, elderly & the differently abled & livelihood enhancement projects.
- Reducing child mortality and improving maternal health by providing good hospital facilities and low cost medicines.
- Ensuring environmental sustainability, ecological balance, protection of flora & fauna, animal welfare, agro forestry, conservation of natural resources & maintaining quality of soil, air & water.
- Employment enhancing vocational skills, etc.
5. Justify the following statements.
Question 1.
Role of media has major influence on business organisation.
Answer:
(1) Media refers to the various means used by advertisers to inform the public about the products or services. The mass media include the press, social media, radio and television. Active media plays crucial role in the life of the people. Through internet, reach of social media to common people has become very easy.
(2) Media has efficiency to disburse any information, wrong policy, unfair trade practice adopted by any business organisation at a very fast pace to public at large that too at every corner of the world. Media is very vibrant and active.
(3) Media connects the people and creates influence on masses. It can make propaganda (or raise voice) against business malpractices and exploitation of consumers. It can do publicity through repetition of messages by different means.
(4) Newspapers, radio, television, internet, social media, etc. can easily give publicity to unfair practices of business organisations. So, media makes business organisations understand social values and exerts major influence.
Question 2.
Business should allow workers participation in management.
Answer:
(1) Workers are the real architects of success in any business unit. Investments in human resources (capital) gives rich rewards in the long run.
(2) The success and failure of the business organisations to greater extent depend on the support and participation of employees. Therefore, business organisations should encourage workers to participate in management through various schemes like giving suggestions, saving costs, quality circles, profit sharing co-ownership, etc.
(3) When workers are given opportunity to participate in the management, it will raise their morale. This in turn will give the workers a sense of belongingness. They will take an active part in completion of the work assigned to them.
(4) Workers’ participation in the management r enables the organisation to win the confidence of employees. It creates and maintains good, healthy and improved relationship between labour and management which is necessary for the success of any organisation.
Question 3.
Expectations of society towards business are changing.
Answer:
(1) Today the world is changing and expanding very fast. Social demands have changed gradually over the years. The business has to respond them positively.
(2) Now the people all over the globe are well aware of their rights. Overall knowledge level has also increased. In order to fulfil the growing needs of the people, the business firms must operate as per the expectations of society. Business units must give society what it actually wants.
(3) Consumer satisfaction is the ultimate purpose of business activities. A business organisation must give priority to consumer satisfaction over profit motive. Its survival, progress and reputation depend upon the consumer satisfaction. It must win the confidence of its customers by giving them useful services.
(4) Business organisations are expected to act in broad public interest and serve the objectives of mankind and society at large along with the objectives of earning profit. It must provide quality products to society at reasonable prices and above all contribute to the social welfare.
Question 4.
Business organisations should avoid environmental pollution and ecological imbalance.
Answer:
(1) Functioning of business units and industrialisation create air, water and sound pollution. The carbon particles, dust, harmful gases, chemicals, etc. create air pollution.
(2) Harmful chemicals, untreated sewage, industrial waste, fertilizers, pesticides, refuse, e-waste, etc. when get mixed with water, creates water pollution. Aeroplanes, motor vehicles, construction machines and industrial equipment create sound pollution.
(3) The business organisations are expected to take all possible measures to prevent air, water and sound pollution and to maintain the ecological balance. For the well-being of society every organisation should assist the concerned organisations engaged in pollution control programmes such as plantation of trees, preservation of wildlife and natural resources.
(4) Protecting the environment and maintaining ecological balance in the following manner:
- Business organisations save cost and money through minimising waste
- Business organi¬sations which follow green practices (plantation of more and more trees) get support from customers
- Business organisations which take precautions to protect environment create awareness among employees
- Protection of environment process cut carbon emission and create conditions for green growth which is beneficial to society
-
Business organisations showing awareness towards environment protection get support and encouragement from the government.
Thus, business organisation should avoid environmental pollution and ecological imbalance.
Question 5.
All sorts of unfair practices related to stock exchange should be avoided.
Answer:
(1) The persons who provide finance for short term as well as for long term to the company are called owners or investors. They invest their money and accept risk factor. Management is expected to provide full and factual information about the financial performance of the company to the owners and investors.
(2) Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) plays a pivotal role in regulating and maintaining the interests of investors in the securities market. Law prohibits any sort of activity that are manipulative or unfair in the securities market. Thus, business organisations must avoid unfair practices related to stock exchange like insider trading, providing wrong and secret information about buying/selling or dealing with securities, etc. Any breach in the above mentioned practices may be considered unlawful and be made accountable by SEBI.
(3) Therefore, business organisation should consider responsibilities toward the owners and should avoid all sorts of unfair practices related to stock exchange.
Question 6.
Business ethics contains moral and social values for doing business.
Answer:
(1) Business Ethics refer to code of conduct that a business organisation are expected to follow while doing a business. According to ‘Wheeler’, “Business ethics is an art or science of maintaining harmonious relationship with society, its various groups and institutions as well as recognizing the moral responsibility for right or wrong conduct of business. ”
(2) Moral values are based on perceptions of right and wrong. They provide the general guidelines for distinguishing between wrong and right path of business, between good and bad, fair and unfair, just and unjust, legal and illegal, proper and improper in respect to human actions. Ethics contain moral values for doing business, Honesty, transparency, fairness, integrity, etc. are moral values that create goodwill and gives economic gain in the long run.
(3) Social values form an important part of the culture of the society. They provide general guidelines for social conduct. Values such as fundamental rights, patriotism, respect for human dignity, rationality, sacrifice, equality, democracy, etc. influence our behaviour in many ways. These social values made the business socially acceptable. As business is a part of society, it can be successful in the long run by adopting social values.
Question 7.
Business ethics can be considered as a tool for social development.
Answer:
(1) Business ethics is a code of conduct evolved for regulating the activities of business towards the society and others.
(2) It calls for the importance of fair treatment to be given to the consumers, workers, suppliers, shareholders, competitors, government and the community at large. Business ethics promote the principles of honesty, sincerity, fairness, justice in business dealings.
(3) It protects the interests of all the constituents of the society. It creates healthy and competitive business atmosphere. It induces businessmen to introduce social security and welfare measures.
(4) The businessmen promote activities enhancing the cultural values of the society. Thus, business ethics, if practised by businessmen in the right spirit, can be considered as a tool for social development.
6. Attempt the following
Question 1.
What is social responsibility of commercial organisation towards consumers ?
Answer:
The social responsibilities of commercial organisation towards consumers are explained as follows:
(1) Good Quality Products : It is the responsibility of a commercial organisation to produce and supply good quality products and services. To improve the quality, every business unit must have quality control department to reject inferior and substandard products. In this respect, International Standards Organisation (ISO) is the latest trend towards quality control. This ensures customers’ loyalty to products.
(2) Fair Prices : The commercial organisation must charge fair and reasonable prices for its goods. Maximum Retail Price (M.R.E) inclusive of all taxes must be printed on all packed products. The customers should not be cheated by being charged higher prices. It is not fair and practicable to fool the customers every time. Such practices bring disrepute to the organisation and spoil its image in the long run.
(3) Customer’s Safety : The organisation must ensure that the product supplied has no adverse effect on the life and health of the consumers. Unsafe products must not be marketed by the organisation. The manufacturers of the genuine products must warn the consumers about the imitation and unsafe products well in time.
(4) Honest Advertising : The advertisement conveys varied information of the products like the facts, features, side effects, advantages, uses, etc. to the customers. The commercial organisations must see to it that their advertisement should not mislead the consumers by exaggerating the actual facts. The commercial organisations must not indulge in vulgar, false and misleading advertisement. Honest advertisements are always appreciated by the consumers and become beneficial in the long run.
(5) After Sales Service: The commercial organisation should offer quick, satisfactory and efficient after sales service specially in the case of consumer durable products for their maintenance during the period of warranty. Effective and efficient after sales services enable them to establish and maintain good relation with the consumers.
(6) Research and Development: The commercial organisation is expected to conduct research and development for the purpose of improving the quality of the product and reducing the cost of production. The commercial organisations must provide quality and branded products such as BIS – Bureau of Indian Standards, AGMARK – Agricultural Marketing, ISI – Indian Standards Institute, etc.
(7) Regular Supply: The commercial organisations are expected to provide goods and services to the consumers regularly as and when needed by them. The commercial organisations are not supposed to create artificial scarcity of goods by hoarding. They should not indulge in black marketing.
(8) Attend Complaints : The commercial organisations must attend to the complaints of consumers without any delay. For this, every organisation should implement quick, effective and suitable grievances redressal system. Suggestions of the customers for the improvement of products should be welcomed and gratefully acknowledged. Required modification in the products should be carried out.
(9) Training: The commercial organisation should organise training to their regular and potential consumers, from time to time, either free of cost or by charging nominal fees.
(10) Avoid Customer Exploitation : In order to avoid exploitation of consumers, the commercial organisations should not indulge in unfair trade practices. To protect the interest of consumers, organisations should avoid monopolistic competition in the market.
Question 2.
State different types of responsibilities towards society.
Answer:
The following are the social responsibilities of a business unit towards society community/ public in general:
(1) Protection of environment : In recent years, pollution becomes one of the major problems. Industries, chemical plants, cement plants, etc. create air pollution and water pollution. The business organisations must take all possible measures to prevent or minimise air and water pollution and maintain ecological balance.
(2) Better and maximum use of resources : The business firms must make proper and optimum use of available resources in the larger interest of the society. The resources such as water, land, fuel, raw materials, etc. should be used fairly and efficiently. However, care should be taken not to misuse or waste such resources.
(3) Reservation for weaker section : For upliftment of economically weaker section of society, the business organisations are expected to reserve certain positions in their organisations. They should also provide financial and other necessary help to them wherever expected.
(4) Development of backward regions : The society expects that the business firms should start their industries in less developed (backward) areas to create employment opportunities. It will increase purchasing power among these people. In this manner, business organisations should make development in backward regions.
(5) Protect against anti-social activities : The business organisations should neither undertake nor participate in anti-social activities. They should not provide any financial assistance to anti-social elements. The business firms should avoid anti-social activities such as smuggling, association with underworld (criminal) people, bribing government officials, etc.
Question 3.
Describe the responsibilities of commercial organisation towards investors.
Answer:
Responsibilities of business towards investors:
(1) Proper conduct of meetings : Whenever need arises, a company should call and organise meetings of investors to provide information about the business. Prior to meeting, proper notice and agenda should be sent well in advance. During the period of financial crisis, investors should be convinced and taken into confidence. Reasons for failure should be explained to the investors to gain their confidence.
(2) Return on Investment : Investors invest their money in the company by accepting risk. They are entitled by get fair returns on their investment at regular interval in the form of interest. Investors expect the following from the business organisations : (a) fair returns on their investment, (b) safety of their investment and (c) steady and gradual appreciation of the business.
(3) Handling grievances : A company is required to pay attention and handle the grievances and complaints of the investors amicably. There should be orderly procedure to solve and deal with grievances without any delay. The business management should answer all the queries of investors regarding any issue in satisfactory manner.
(4) Maintain transparency : Investors supply funds for long term and for working capital to carry on business more efficiently. Investors expect that business firms should maintain high degree of transparency in their operations.
(5) Proper disclosure of information : A company is expected to disclose full and factual information through regular reports, circulars and statement of profit. The company must provide its financial performance more correctly so that prospective investors are able to take right decisions to invest their money in future.
(6) Maintain solvency and prestige : Business organisation or a company is expected to maintain sound financial position, prestige, solvency and goodwill to gain confidence of investors. For this, company should undertake innovation, research and expansion programme on the continuous basis.
Question 4.
Describe the features of Business Ethics.
Answer:
The features of Business Ethics are explained as below:
(1) Code of conduct : Business ethics is a code of conduct developed and evolved for regulating business activities toward welfare of society. It explains what activities one is suppose to do and not do for the welfare of the society. All business units must follows this code of conduct.
(2) Based on moral and social values : Business ethics comprises social and moral principles i.e. rules for carrying out business activities smoothly. This contains self control, consumer protection and welfare, fair treatment to social group, service to society, not to harm (exploit) others, etc.
(3) Gives protection to social groups : Business ethics protects the interests of all the constituents (groups) of the society which include consumers, creditors, employees, small businessmen, shareholders, government, etc.
(4) Provides basic framework : Business ethics specifies the social, cultural, legal, economic and other limits of business within which business units are expected to plan, work out and conduct their functions and activities.
(5) Voluntary : The businessmen must follow (accept) business ethics voluntarily, i.e. on their own. Business ethics must be similar to self¬discipline. It should not be made compulsory by law.
(6) Requires education and guidance : Prior to introduction of business ethics in the organisation, businessmen must be properly educated, trained and given guidance. The businessmen must be convinced and motivated to implement business ethics.
(7) Relative term : Business ethics is a relative term. It differs or changes from one business to another business and from one country to another.
In one country whatever is considered good may be banned or bad for other country.
(8) New concept : Business ethics is considered as newer concept. It is strictly followed and applied in developed, i.e. advanced countries. It is not accepted and followed in developing and poor (backward) countries.
Question 5.
What is Corporate Social Responsibility?
Answer:
(1) Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) is the recent and newest management strategy which creates positive impact on society while doing business. It is a global concept. It is self regulating business model which aims at contributing towards social welfare and support ethically oriented practices. CSR makes a company socially accountable and responsible. CSR makes a company accountable towards itself, its stakeholders, public in general, etc. By undertaking and practising social responsibility company can be alert and awake about social, economic and environmental aspects of the society.
(2) According to UNIDO (United Nations Industrial Development Organization), “Corporate Social Responsibility is a management concept whereby companies integrate social and environmental concerns in their business operations and interactions with their stakeholders”.
According to Section 135 of the Companies Act, 2013 and Companies (CSR Policy) Rules 2014, the companies having net worth of 1500 Cr. or more or turnover of 1000 Cr. or more; or net profit of 15 Cr. or more during any financial year have to form a Corporate Social Responsibility Committee of the Board. The Board’s report will give information about the compositions of CSR committee with effect from 1st April, 2014.
(3) In every financial year, all companies should spend at least 2% of average net profits of last 3 years on their CSR policy. The CSR committee consists of 4 directors who meet at least 2 times in a year to discuss and review the CSR policy and CSR activities, prepare budget, explain the way to implement projects and to establish a transparent means to check progress.
(4) CSR, supports the following activities:
- Eradicating hunger, poverty & malnutrition, promoting preventive health care & sanitation & making available safe drinking water.
- Promoting education, including special education & employment enhancing vocation skills especially among children, women, elderly & the differently abled & livelihood enhancement projects.
- Reducing child mortality and improving maternal health by providing good hospital facilities and low cost medicines.
- Ensuring environmental sustainability, ecological balance, protection of flora & fauna, animal welfare, agro forestry, conservation of natural resources & maintaining quality of soil, air & water.
- Employment enhancing vocational skills, etc.
(5) Penalties for non-compliance of CSR activities (duties) would attract a fine of not less than Rs 50,000 which may increase to Rs 25,00,000 and every officer of the company in default is given punishment of imprisonment for 3 years or with fine of Rs 50,000 which may increase to Rs 5,00,000 or with both.
7. Answer the following
Question 1.
Explain the responsibilities of business towards employees.
Answer:
The responsibilities of business towards employees are explained as follows:
(1) Job security: Job security (guarantee) gives mental peace to the employees. In order to encourage employees to work with full concentration, dedication and commitment, the business organisation must give job security and frame rules for confirmation of their service and strictly adhere to them. This will in turn raise their morale, interest and loyalty towards the organisation.
(2) Fair remuneration : The business organisation should pay adequate and attractive salaries along with incentives like overtime allowance, bonus, etc. to all employees. Wages or salaries payable to employees should be fixed by considering nature of work. The business organisations should frame suitable wage plans for increments and timely revision of wages.
(3) Health and safety measures : The business organisations is expected to take necessary steps for protecting the health and hygiene of the employees. Proper sanitation, canteen, medical facilities, hygienic conditions, etc. must be provided to them. Proper maintenance of machines and premises must be done to prevent accidents and control pollution. Business organisation should provide safety equipment such as helmets, safety goggles, gloves, shoes, masks, etc. to the employees.
(4) Good working condition : The business organisations must provide good working conditions to their employees such as adequate lighting, ventilation, safe drinking water, etc. The business organisations are expected to take necessary steps to avoid and minimise air, sound and water pollution. The business organisation must fix proper working hours and norms (shiftwise, if any) with due provisions for lunch break, tea intervals, restrooms, etc.
(5) Recognition of Trade Unions : The business organisation must recognise the right of a worker to join a recognised trade union. The management or employer should not prevent workers from forming a trade union. The management should not follow the policy of “Divide and Rule”. Further, the management should solve the problems of the workers amicably by holding face to face interactions, talks, meetings and negotiations with unions. The management and union should agree to ban lockouts and strikes to protect the interest of both the parties. A business organisation is expected to maintain industrial harmony and peace.
(6) Education and training : The business organisations are expected to take efforts to educate and train the employees. Depending on the nature of job, the business organisation should offer education, training and guidance to their employees free of cost. To update their knowledge, on the latest development and to increase the S efficiency of the employees, the organisation should arrange ‘Refresher in service training’ and ‘Introduction Training’ at regular intervals.
(7) Workers participation in management : The business organisations are expected to encourage workers to participant in the management by forming workers’ committee. The management should encourage the workers ; through different schemes like suggestion schemes, profit sharing, etc. These schemes enable the management to raise employees’ morale and help the management to give them a sense of belonging.
(8) Promotion and career opportunities : Business organisations should offer enough opportunities of promotion to their qualified and talented employees. They should give detailed information about qualification, skills and I experience required to get promotions. This will increase awareness and motivate the workers to work hard.
(9) Proper grievance procedure : The organi-sation must introduce a suitable grievance (redressal) procedure to deal with the employees’ complaints. All their queries or problems should be sorted out and solved quickly and amicably.
The employees must feel satisfied that their complaints are attended properly. Management or employer must investigate and take necessary actions to settle the grievances and complaints.
(10) Miscellaneous : Management or employer should-
- give fair treatment to all employees.
- recognise, appreciate and encourage special skills and talents of the employees.
- introduce code of conduct for the employees.
- protect religious, social, political rights of the employees.
- allow employees to form informal groups.
Question 2.
Define the concept of Social Responsibility and what is the need for social responsibility.
Answer:
[A] Meaning and Definition : Social responsibility is an obligation of the business organisation to take those decisions and perform those actions which are desirable to fulfil the objectives and add values to our society. The business organisations are expected to perform all the activities of their business in such a manner that such activities will not cause any harm to any part of the society.
In other words, the business enterprises should undertake such activities which will protect and contribute to the interest of society and fulfil their expectations. According to Howard D. Bowen “Social Responsibility is to pursue those policies to make those decisions, or to follow those lines of action which are desirable in terms of the objectives and values of our society.” In brief, social responsibility comprises of an element of voluntary action taken by the business people for the benefit of the society.
[B] Need for social responsibility:
(1) Concept of Trusteeship : Trusteeship is a socio-economic philosophy that was advocated by Mahatma Gandhi. According to it, rich (wealthy) people would be trustees of the trusts that take care of the welfare of the people in general. Businessmen are treated as trustees of society.
(2) Changing expectations of society : Over the years, society’s expectations from the business organisation have undergone severe change. In earlier days, business firms were recognised as the providers of goods and services. However in recent years society expects that every business organisation as a responsible citizen should contribute towards social welfare of the people in the society.
(3) Reputation : Business organisations spend large amount of money in brand building and in creating and strengthening their favourable image. The business organisations which care for every organ of the society and contribute to social well¬being enjoy a good reputation in the society. Such organisations always get good support from the public which in turn increases sales, profitability, attraction of talent and sustained growth.
(4) Protection of environment : It is the social responsibility of the business organisations to make proper and careful use of country’s natural resources. They should not cause environmental pollution (degradation) like contamination pollution of water resources, depletion of ozone layer, etc. Such type of pollutions result in poor health of the community and put a question mark on the survival of human species/race.
(5) Optimum utilisation of resources : Usually, large business organisations have huge amount of resources such as manpower, talent, finance and expert at their disposal to use. It is the social responsibility of business organisations to make optimum use of available resources to protect society’s interests. The organisation should always avoid wastage of resources.
(6) Pressure of trade union : The workers have now become more conscious of their rights and privileges. In recent years, trade unions play significant role in business environment. The workers have realised that their efforts contribute to the profits of the business organisation and expect management to pay them fair wages, bonus, etc. to minimise or avoid conflicts between trade unions and management. The business organisations should understand the responsibility towards employees to avoid conflicts and act accordingly.
(7) Growth of consumer movement : Advancement and growth in education, development of mass media and growing competition in the market create awareness among the consumers about their rights and powers. Hence, business organisation are required to follow consumer-oriented policies.
(8) Government control : From the side of business organisation, government rules and regulations are not desirable. This is because government put certain restrictions and limit the freedom of business organisations. In order to put moral and legal pressure on business, the government has enacted several laws such as Consumer Protection Act, 1986, Air Pollution Act, Food Adulteration Act, etc.
(9) Long term self interest : A business organisation and its image stand to earn handsome profit in the long run if its motive is providing services to the society. When the workers, consumers, shareholders, government officials and members of the public feel that a business organisation is indifferent to the social interests, they may withdraw their support to end co¬operation. Therefore, it is in the long-term interest of the business organisation to be socially useful and fulfil its social responsibility.
(10) Complexities of social problems : Many a time some business organisations themselves create social problems such as discrimination in treatment, unsafe workplaces, different types of pollutions, etc. It is the moral and social obligation of the business organisation to solve these social problems.
(11) Globalisation : In globalisation, business activities are conducted throughout the world. In recent years, the entire globe (world) has becomes the market place for buying and selling goods and services produced in any part of the world. Globalisation creates and provides more opportunities, threats and challenges to the business organisations. Those countries in the world which have followed good and fair trade practices capture and influence the entire world trade.
(12) Role of media : By using internet, it is easier to approach the common people. Media is dynamic and active which can influence large number of people in the society. Media is useful to raise voice against malpractice and exploitation of the consumers. Media plays important and active role in public life. Thus, Business organisation should not neglect the social values.
Question 3.
Explain the responsibilities of a business unit towards society at a large.
Answer:
The following are the social responsibilities of a business unit towards society community/ public in general:
(1) Protection of environment : In recent years, pollution becomes one of the major problems. Industries, chemical plants, cement plants, etc. create air pollution and water pollution. The business organisations must take all possible measures to prevent or minimise air and water pollution and maintain ecological balance.
(2) Better and maximum use of resources : The business firms must make proper and optimum use of available resources in the larger interest of the society. The resources such as water, land, fuel, raw materials, etc. should be used fairly and efficiently. However, care should be taken not to misuse or waste such resources.
(3) Reservation for weaker section : For upliftment of economically weaker section of society, the business organisations are expected to reserve certain positions in their organisations. They should also provide financial and other necessary help to them wherever expected.
(4) Development of backward regions : The society expects that the business firms should start their industries in less developed (backward) areas to create employment opportunities. It will increase purchasing power among these people. In this manner, business organisations should make development in backward regions.
(5) Protect against anti-social activities : The business organisations should neither undertake nor participate in anti-social activities. They should not provide any financial assistance to anti-social elements. The business firms should avoid anti-social activities such as smuggling, association with underworld (criminal) people, bribing government officials, etc.
(6) Financial assistance : The society expects financial helps and donations from the business organisations for various social welfare activities such as eradication of poverty, illiteracy, etc. The society also expects financial assistance from them to organise various awareness programmes like anti-drug campaigns, antinoise pollution campaigns, etc.
(7) Prevent congestions : The society expects that the business firms start industries in industrial zones and at different locations. It will minimise the adverse effects like pollution and overcrowded cities in residential areas. This facilitates business firms to provide jobs to local people. This in turn avoids congestion in big cities.
(8) Employment generation : The business units should generate and provide better job opportunities to young and well qualified people in all sections of the society. It should make maximum efforts to generate employment through expansion and diversification of its business. This will avoid unemployment and poverty in the society.
Question 4.
What are the responsibilities of business towards investors and government?
Answer:
[A] Responsibilities of business towards investors:
(1) Proper conduct of meetings : Whenever need arises, a company should call and organise meetings of investors to provide information about the business. Prior to meeting, proper notice and agenda should be sent well in advance. During the period of financial crisis, investors should be convinced and taken into confidence. Reasons for failure should be explained to the investors to gain their confidence.
(2) Return on Investment : Investors invest their money in the company by accepting risk. They are entitled by get fair returns on their investment at regular interval in the form of interest. Investors expect the following from the business organisations : (a) fair returns on their investment, (b) safety of their investment and (c) steady and gradual appreciation of the business.
(3) Handling grievances : A company is required to pay attention and handle the grievances and complaints of the investors amicably. There should be orderly procedure to solve and deal with grievances without any delay. The business management should answer all the queries of investors regarding any issue in satisfactory manner.
(4) Maintain transparency : Investors supply funds for long term and for working capital to carry on business more efficiently. Investors expect that business firms should maintain high degree of transparency in their operations.
(5) Proper disclosure of information : A company is expected to disclose full and factual information through regular reports, circulars and statement of profit. The company must provide its financial performance more correctly so that prospective investors are able to take right decisions to invest their money in future.
(6) Maintain solvency and prestige : Business organisation or a company is expected to maintain sound financial position, prestige, solvency and goodwill to gain confidence of investors. For this, company should undertake innovation, research and expansion programme on the continuous basis.
[B] Responsibilities of business towards government:
(1) Timely payment of taxes : Business organisations are expected to pay various taxes such as sales tax, income tax, corporate tax, excise duty, wealth tax, etc. levied by the government from time to time. These funds enable the government to undertake various development projects.
(2) Observing rules and regulations : The business organisations are expected to comply with the various laws, rules and regulations enacted by the government. The company should follow the laws regarding obtaining license of business operation, price determination and production, etc. They should conduct business in lawful manner.
(3) Earning foreign exchange : The business organisations Eire expected to export their products to foreign countries to earn foreign exchange. Foreign exchange is required by the government to import various goods, valuable and important products.
(4) Economic development : The government sets the targets for balanced growth and rapid economic development of the country. The business organisation is expected to provide necessary support to the government.
(5) Implementing socio-economic policies : The business organisations are expected to provide co-operation and required funds to the government in implementing various socio-economic programmes and policies.
(6) Suggestions to the Government: The business organisations are expected to give suggestions to the government in framing important policies such as Industrial Policy, Import-Export Policy, Licensing Policy, etc. They are helpful to government in framing organisation friendly policies.
(7) No favours : The business organisation should not take any favour from the government officials by giving bribes or influencing them in any matter.
(8) Contributing to government treasury: The business organisation must contribute by extending financial aid to the government during emergencies and natural calamities like floods.