Chapter 9 Depository System
1A. Select the correct answer from the options given below and rewrite the statements.
Question 1.
In physical mode, securities are held in ____________ form.
(a) Paper
(b) Dematerialization
(c) Electronic
Answer:
(a) Paper
Question 2.
Risk of losing certificates exist in ____________ mode.
(a) Physical
(b) Dematerialization
(c) Digital
Answer:
(a) Physical
Question 3.
In Depository system, securities are held in ____________ form.
(a) Scrip based
(b) Electronic
(c) Physical
Answer:
(b) Electronic
Question 4.
____________ is the institute which facilitates electronic holding of securities.
(a) Depository Participant
(b) Issuer
(c) Depository
Answer:
(c) Depository
Question 5.
There is no payment of ____________ when securities are demated.
(a) Octroi
(b) Wealth Tax
(c) Stamp Duty
Answer:
(c) Stamp Duty
Question 6.
Depository Act was passed in ____________
(a) 1919
(b) 1996
(c) 1999
Answer:
(b) 1996
Question 7.
India has a ____________ depository system.
(a) Sole
(b) Multi
(c) Single
Answer:
(b) Multi
Question 8.
____________ is a constituent of depository system.
(a) Government
(b) Issuer
(c) Trust
Answer:
(b) Issuer
Question 9.
____________ is the oldest depository in India.
(a) Dow Jones
(b) NSDL
(c) CDSL
Answer:
(b) NSDL
Question 10.
Demat account is opened by ____________
(a) Beneficial owner
(b) CDSL
(c) SEBI
Answer:
(a) Beneficial owner
Question 11.
Demated shares are ____________
(a) Non-transferable
(b) Fungible
(c) Bearer
Answer:
(b) Fungible
Question 12.
____________ is a unique code given to a security.
(a) IBM
(b) BBM
(c) ISIN
Answer:
(c) ISIN
Question 13.
In India ISIN for corporate securities is allotted by ____________
(a) NSDL
(b) Central Government
(c) State Government
Answer:
(a) NSDL
Question 14.
____________ has to apply for ISIN.
(a) Company
(b) Depository Participant
(c) Depositors
Answer:
(a) Company
Question 15.
____________ has to pay charges to maintain Demat Account.
(a) Investor
(b) Issuer
(c) Depositor
Answer:
(a) Investor
Question 16.
NSDL is promoted by ____________
(a) NSE
(b) BSE
(c) FTSE
Answer:
(a) NSE
Question 17.
CDSL is promoted by ____________
(a) NSE
(b) BSE
(c) FTSE
Answer:
(b) BSE
1B. Match the pairs.
Question 1.
Group ‘A’ | Group ‘B’ |
(a) Bad delivery | (1) 1956 |
(b) Depository Act | (2) A 12 digits number code |
(c) ISIN | (3) Connects Government and Bank |
(d) Depository Participant | (4) Second Depository in India |
(e) CDSL | (5) The issuer company |
(f) Depository | (6) Problem faced in physical mode |
(g) Beneficial owner | (7) A 10 digits number/code |
(8) Connect depository and investor | |
(9) First depository in the world | |
(10) Custodian of securities in electronic form | |
(11) Problem faced in electronic mode | |
(12) 1996 | |
(13) Government organization | |
(14) The investor |
Answer:
Group ‘A’ | Group ‘B’ |
(a) Bad delivery | (6) Problem faced in physical mode |
(b) Depository Act | (12) 1996 |
(c) ISIN | (2) A 12 digits number code |
(d) Depository Participant | (8) Connect depository and investor |
(e) CDSL | (4) Second Depository in India |
(f) Depository | (10) Custodian of securities in electronic form |
(g) Beneficial owner | (14) The investor |
1C. Write a word or a term or a phrase that can substitute each of the following statements.
Question 1.
This mode of holding securities may result in loss and theft of certificates.
Answer:
Physical mode of securities
Question 2.
The organization holds the securities in electronic mode.
Answer:
Depository
Question 3.
This system eliminates storing of certificates.
Answer:
Depository system
Question 4.
This system allows faster and easier transfer of securities.
Answer:
Depository system
Question 5.
The oldest Depository of India.
Answer:
NSDL (National Security Depository limited)
Question 6.
The country where the Depository system started for the first time.
Answer:
Germany
Question 7.
The registered owner of securities.
Answer:
Beneficial Owner
Question 8.
The agent of the Depository.
Answer:
Depository Participant
Question 9.
This process converts securities into an electronic form from a physical form.
Answer:
Dematerialization
Question 10.
This process converts securities into physical form from electronic form.
Answer:
Rematerialization
Question 11.
This means securities are without distinctive identity numbers.
Answer:
Fungibility
Question 12.
This is the unique code for security given in the Depository system.
Answer:
International Securities Identification Number
1D. State whether the following statements are true or false.
Question 1.
The physical mode of holding Securities is risky.
Answer:
True
Question 2.
Allotment of Securities takes a longer time when in physical mode.
Answer:
True
Question 3.
Transfer of Securities is easier in electronic mode.
Answer:
True
Question 4.
Bad delivery is likely in the Depository system.
Answer:
False
Question 5.
The depository system began in the USA for the first time in the world.
Answer:
False
Question 6.
India has a multi-depository system.
Answer:
True
Question 7.
The depository system is very similar to the banking system.
Answer:
True
Question 8.
DP is a constituent of the Depository system.
Answer:
True
Question 9.
DP is an Agent of the Depository.
Answer:
True
Question 10.
A bank can work as a DP.
Answer:
True
Question 11.
DRF is required for conversion from physical to electronic.
Answer:
True
Question 12.
ISIN is a unique code given to the specific Securities.
Answer:
True
1E. Find the odd one.
Question 1.
Elimination of storage of certificates, theft of certificates, torn certificates
Answer:
Elimination of storage of certificates
Question 2.
NSDL, CDSL, NBFC
Answer:
NBFC
Question 3.
Depository, DP, RBI
Answer:
RBI
Question 4.
DP, BO, State Government
Answer:
State government
Question 5.
Issuer, BO, Central Government
Answer:
Central government
Question 6.
DRF, RRF, PPF
Answer:
PPF
1F. Complete the sentences.
Question 1.
Central location for keeping Securities in demated form is ____________
Answer:
Depository
Question 2.
Freezing of debit/credit of Securities is possible in ____________
Answer:
Dematerialized Securities
Question 3.
First Depository of the world started in the year ____________
Answer:
1947
Question 4.
The Indian Depository Act was passed in the year ____________
Answer:
1996
Question 5.
Link between Depository and investor is ____________
Answer:
Depository participant
Question 6.
Account of Securities of the investor is maintained by ____________
Answer:
Depository Participant
Question 7.
The process which converts physical Securities in electronic form is ____________
Answer:
Dematerialization
Question 8.
The process which converts digital Securities in physical form is ____________
Answer:
Rematerialization
Question 9.
The issuer company must register with ____________
Answer:
Depository
Question 10.
The unique code identifying a security is ____________
Answer:
(ISIN) International Securities Identification Number
Question 11.
The first Depository of India is ____________
Answer:
NSDL (National Security Depository Limited)
1G. Select the correct option from the bracket.
Question (I).
Group ‘A’ | Group ‘B’ |
(a) Dematerialization | (1) ……………….. |
(b) …………………….. | (2) DP |
(c) First Depository of world | (3) ………………… |
(d) CDSL | (4) ……………….. |
(1999, Agent of Depository, Germany, Physical to electronic)
Answer:
Group ‘A’ | Group ‘B’ |
(a) Dematerialization | (1) Physical to Electronic |
(b) Agent of Depository | (2) DP |
(c) First Depository of world | (3) Germany |
(d) CDSL | (4) 1999 |
Question (II).
Group ‘A’ | Group ‘B’ |
(a) First Depository in India | (1) ………………………… |
(b) …………………….. | (2) Rematerialisation |
(c) Fungibility | (3) ………………………… |
(d) …………………… | (4) ISIN |
(12 digital code, NSDL, Electronic to physical, No distinctive number)
Answer:
Group ‘A’ | Group ‘B’ |
(a) First Depository in India | (1) NSDL |
(b) Electronic to Physical | (2) Rematerialisation |
(c) Fungibility | (3) No distinctive number |
(d) 12 digital code | (4) ISIN |
1H. Answer in one sentence.
Question 1.
What is the Depository system?
Answer:
A depository system is a system where Securities are held in electronic form.
Question 2.
Give examples of actions termed as corporate action.
Answer:
Payment of dividend, issue of Bonus Shares, offering of right Shares, Early Redemption of Debentures, Mergers and Acquisitions, etc.
Question 3.
When was Depository Act passed in India?
Answer:
Depository Act was passed in India in the year 1996.
Question 4.
What is a DP?
Answer:
DP means Depository participant, who is an agent of Depository.
Question 5.
What is Dematerialisation?
Answer:
Dematerialization is the process of converting physical Securities into electronic.
Question 6.
What is Rematerialization?
Answer:
Rematerialization is the process of converting electronic Securities into physical.
Question 7.
What is ISIN?
Answer:
ISIN is the unique code given to the specific Securities of the company. ISIN refers to ‘International Securities Identification Number’.
Question 8.
Name the Depositories in India?
Answer:
- National Security Depository Limited (NSDL)
- Central Depository Services Limited (CDSL)
1I. Correct the underlined words and rewrite the following sentences.
Question 1.
The electronic mode of holding Securities is risky.
Answer:
The physical mode of holding Securities is risky.
Question 2.
Allotment and Transfer of Securities are time-consuming in electronic mode.
Answer:
Allotment and Transfer of Securities are time-consuming in physical mode.
Question 3.
Banking system leads to a script less capital market.
Answer:
Depository system leads to a scriptless capital market.
Question 4.
Storage of certificates is not required in the physical mode of holding.
Answer:
Storage of certificates is not required in the electronic mode of holding.
Question 5.
India has a single Depository system.
Answer:
India has a multi Depository system.
Question 6.
Depository participant in India has to register under the Partnership Act.
Answer:
Depository participant in India has to register under the Depository Act.
Question 7.
Demat accounts are opened and maintained by the Depository.
Answer:
Demat accounts are opened and maintained by the Depository Participant.
Question 8.
Securities are fungible in physical mode.
Answer:
Securities are fungible in electronic mode.
Question 9.
ISIN is a code given to a company.
Answer:
ISIN is a code given to the security of a company.
Question 10.
ISIN of Indian government Securities is issued by NSDL.
Answer:
ISIN of Indian government Securities is issued by RBI.
1J. Arrange in proper order.
Question 1.
(a) Gets statement of Account
(b) Open Demat Account
(c) Submit DRF
Answer:
(a) Submit DRF
(b) Open Demat Account
(c) Gets statement of Account
Question 2.
(a) Investor (BO) submits an application for Securities to the issuer company
(b) Depository intimates the DP about crediting Bo’s Account
(c) Issuer company gives details of allotment to Depository.
Answer:
(a) Investor (BO) submits an application for Securities to the issuer company
(b) Issuer company gives details of allotment to Depository
(c) Issuer company gives details of allotment to Depository
2. Explain the following terms/concepts.
Question 1.
Depository System
Answer:
- In the Depository system, securities are held in electronic form.
- The transfer and settlement of securities are done electronically.
- The Depository System maintains accounts of the shareholder, enables transfer, collects dividends, bonus shares, etc. on behalf of the shareholder.
- This system is also called a scriptless trading system.
- It keeps the securities safe. It offers scope for paperless trading by using state-of-art technology.
Question 2.
Dematerialization
Answer:
- Dematerialization is a process whereby a client can get physical certificates converted into electronic mode.
- For this client has to surrender the certificates along with the Demat Request Form (DRF) to the DP.
Question 3.
Rematerialization
- Rematerialization is the process whereby a client can get his electronic holdings of securities converted into physical certificates.
- For this client has to give a written request in the form of Remat Request Form (RRF) to the DP.
Question 4.
Fungibility
Answer:
- Fungibility means the state of being interchangeable. Securities issued by the same company of the same class have the same value no matter who owns them.
- The securities held in electronic form are fungible which means they don’t have distinctive numbers.
Question 5.
ISIN
Answer:
- ISIN is a standard numbering system that is accepted globally.
- ISIN consists of a 12 (twelve) digit alpha-numeric code which is divided into 3 (Three) parts.
- The company has to apply for ISIN for its securities with documents like a prospectus.
3. Study the following case/situation and express your opinion.
1. Mr. Z holds 100 shares of peculiar Co. Ltd. In physical mode and wishes to convert the same in electronic mode:
Question (a).
Mr. Z holds a savings bank account with CFDH Bank Ltd. Can he deposit his shares in this account for Demat?
Answer:
No. He can’t, as it is a savings bank account.
Question (b).
What type of account is needed for the same?
Answer:
For holding electronic securities, he needs to open a Demat A/c with the Depository Participant (DP).
Question (c).
Is it the RBI that will be the custodian of shares of Mr. Z after demating?
Answer:
No. RBI won’t be the custodian. After demating concerned ‘Depository’ (NSDL/CDSL) will be the custodian of the shares of Mr. Z.
2. Mr. R holds 100 shares of Peculiar Co. Ltd. In Demat mode.
Question (a).
He wants to transfer one share each to his wife, daughter, and son. Can he do so?
Answer:
Yes, Mr. R can do so, as under dematerialized securities market lot is of one share.
Question (b).
Does he need to submit DRF or DIS if he wants to transfer his shares?
Answer:
He needs to submit DIS (Delivery Instruction Slip) if he wants to transfer his shares.
Question (c).
Can he nominate his wife in his Demat account?
Answer:
Yes. Mr. R can nominate his wife for the Demat account.
3. Mrs. Z wishes to open a Demat account in her name.
Question (a).
Can she open the account going to the Mumbai office of NSDL?
Answer:
No, Mrs. 2 cannot go directly to the Mumbai office of NSDL.
Question (b).
Is she required to pay for the opening of the account and its maintenance?
Answer:
Yes, she is required to pay for the opening of the account and its maintenance.
Question (c).
Does she have to send the shares to the respective company for demating?
Answer:
Yes, she has to send her original share certificate through Depository Participant to the company.
4. Mr. L wants to demat his 25 shares of Peculiar Co. Ltd bearing certificate no 100 and distinctive no 76-100.
Question (a).
Which form is he required to fill as a written request to the DP?
Answer:
Mr. L is required to fill Demat Request Form (DRF) as a written request to DP.
Question (b).
Does he have to fill instrument of transfer if he wishes to transfer the same after demat?
Answer:
No, he needs to fill instrument of transfer after opening Demat A/c.
Question (c).
Does he have to quote certificate no. and distinctive no. if he wishes to transfer his shares after it is in Demat form?
Answer:
No, Mr. L need not quote certificate no. and distinctive no. if he wishes to transfer his shares after it is in Demat form.
5. Mr. S. holds 50 shares of Peculiar Co. Ltd in Demat form. The company has declared a dividend of Rs 5. Per-share and Bonus of 1 : 1 to its shareholders.
Question (a).
How will Mr. S get his dividend?
Answer:
Mr. S will get his dividend credited directly to his Demat A/c.
Question (b).
Will he get a Bonus share in Physical or Demat?
Answer:
He will get Bonus Share in his Demat A/c.
Question (c).
Who is entitled to dividend and Bonus: Mr. S or the depository? (NSDL in this case).
Answer:
Mr. S is entitled to dividends and Bonuses through the depository services.
4. Distinguish between the following.
Question 1.
Dematerialization and Rematerialization.
Answer:
Points | Dematerialization | Rematerialization |
1. Meaning | Conversion of physical securities into electronic form is known as ‘Dematerialization’ | Conversion of electronic securities into physical form is known as ‘Rematerialization’ |
2. Conversion | Securities in physical/paper form are converted into electronic form | The electronic form of securities are converted into physical form |
3. Form Used | ‘Demat Request Form (DRF) is submitted by the investor to the DP | ‘Remat Request Form’ (RRF) is submitted by the investor to the DP |
4. Process | It is an initial process | It is a reverse process |
5. Function/Sequence | It is a primary and principal function of the depository | It is a secondary and supporting function of the depository |
6. Distinctive numbers | Demat securities have no distinctive numbers | Remat securities will have certificates and distinctive numbers issued by the company |
7. Securities Maintenance Authority | The depository is the custodian of securities and records | The issuing company keeps the record. The investor also maintains the record |
8. Time Consumed | It is an easy and time-saving process | It is a complex and time-consuming process |
5. Answer in brief.
Question 1.
Explain the disadvantages of the physical mode of holding securities.
Answer:
Securities mean shares, debentures, bonds, units of mutual funds, securities are held in physical form or paper form. Following are the problems/disadvantages of holding the securities in electronic form:
(i) Risk factor:
Paper certificates can be lost, damaged, torn, stolen, or misplaced during transit, etc.
(ii) Efforts in Duplicating:
If the original certificate is lost it becomes difficult to obtain duplicate certificates. It consumes time, effort, and money.
(iii) Delay in the allotment:
Allotment of new securities in physical form requires a longer time.
(iv) Delay in Transfer and Transmission:
Handling and recording physical certificates take a lot of time in the transfer and transmission of securities.
(v) Risk of Bad Delivery:
Buying and selling securities can create problems if the certificates are torn, forged, etc.
Question 2.
Explain any four advantages of the Depository system to investors.
Answer:
Investor refers to the Beneficial Owner, the one who invests in the company’s securities.
Advantages of Depository System to the Investor are as follows:
(i) No Risk:
Risks related to physical certificates like delays, loss of certificates, theft, mutilation, bad deliveries, etc. are totally eliminated.
(ii) Safety of Investment:
The safest and secure way of holding securities is in the form of DEMAT. It is controlled under Depositories Act and monitored by SEBI. For e.g. If we don’t want to deal in securities, for the time being, we can freeze the account instructing DP to avoid unexpected debit or credit.
(iii) Easy Transfer of Shares:
- There is no need of filling transfer form and submitting documents.
- Stamp duty is not applicable in this process.
- Cash realization and security transfer take place very fast.
(iv) Updated information:
The investor receives updated information about his transactions and holdings from DP and also sometimes from Depository.
(v) Loan against securities:
An investor can raise a loan from the banks against the security of Dematerialized securities.
(vi) No ‘Lots’:
The lot system has been abolished. The market lot is one share for dematerialized securities.
(vii) Nomination Facility:
Nomination Facility is allowed under the Depository system. In the event of the death of the investor, the process becomes simple.
(viii) Automatic Credit:
The investor’s account is automatically credited or debited by the company. This is called ‘Corporate Action.’
For e.g. Payment of dividend, Bonus Issue, Right Issue, Redemption, etc.
Question 3.
Explain any four advantages of the Depository system to the company.
Answer:
Benefits/Advantages of Depository System:
(A) Investors:
(i) Safety:
A safe and secure way of holding securities is in electronic form/mode. The depository system is monitored by SEBI. The Investor can keep his account in a ‘Freeze/Lock’ mode to avoid/prevent unexpected debit or credit or both by giving instructions to the DP.
(ii) Easy Transfer of Shares:
These securities can be easily transferred in electronic mode. Filling out the transfer form and uploading the documents can be easily done online. It is a time and efforts saving process. No stamp duty is levied on the depository system.
(iii) Update and Intimation:
The investor can check his status of holding securities at any time. Depository Participant provides investors with his statement of accounts periodically.
(iv) Automatic Credit:
Under, the depository system the investor’s account is automatically credited/debited. This credit or debit of accounts is usually in case of Payment of Dividend, Issue of Bonus Shares, Offering of Rights Shares, Early Redemption of Debentures, Mergers, and Acquisitions, etc.
(B) Companies:
(i) Up-to-date Information:
The depository system enables the company to maintain the information of the investors holding. It also helps the company to keep updated information about its shareholding pattern. The company is able to know the particulars of beneficial owners and their holdings periodically.
(ii) Reduction in costs and efforts:
Due to the depository system, maintaining the documents physically, the printing of certificates has saved a lot of time and cost.
(iii) Better Relationships:
The transfer process under the depository system is prompt and free from defects. So, complaints against the company by an investor are avoided in this regard. This helps the company build a good corporate image.
(iv) International Investment:
Paperless trading is a boon for the company management as it provides better and quicker services to the investors staying within the country and abroad. This attracts investment from abroad.
Question 4.
Explain Depository as a constituent of Depository System.
Answer:
- The depository is a company registered under the Companies Act, to deal in securities.
- It holds the securities in electronic form.
- It is responsible for safeguarding the investor’s securities and preventing any manipulation of records and transactions.
- There is no direct access of investors with the Depository.
- It works as a link between the company and investors.
- Statement of accounts is provided to the investor periodically.
Question 5.
Explain DP as the constituent of the Depository System.
Answer:
- Depository Participant acts as a link between the Depository and the Investor. In other words, it is an agent of the depository.
- DP is registered under the SEBI Act. It enjoys rights and obligations as specified under SEBI Regulations of 1996.
- It is an intermediary appointed by Depository.
- DP directly deals with customers and sends a statement of accounts periodically.
- The DP has a unique number for identification.
- Banks, Financial Institutions, Stock Brokers, etc. can function as Depository Participants.
- Thus, it is rightly justified that DP is an important constituent of the Depository system.
6. Justify the following statements.
Question 1.
Electronic holding of securities is safer than physical holding.
Answer:
- Electronic holding of securities means holding the securities in dematerialized form.
- Conversion of physical certificates into electronic form is known as ‘Dematerialization’.
- Holding securities in electronic form eliminates a huge volume of paperwork.
- The use of technology facilitates paperless trading which eliminates storage and handling of certificates. It also helps in reducing costs and efforts.
- There is no risk of getting lost, damaged, torn, stolen, misplaced during transit, etc.
- Delay in transfer and allotment of securities is also avoided.
- Thus, it is rightly justified that, electronic holding of securities is safer than physical holding.
Question 2.
Depository provides easy and quicker transfer of shares.
Answer:
- Under the Depository system, securities are held in electronic form.
- Not only the transfer and settlement of securities are done electronically but it also maintains the accounts of the shareholder, collects dividends, bonus shares, etc. on behalf of the shareholder.
- Depository Participant acts as a link between the Depository and the Investor.
- No stamp duty is levied on the depository system.
- Processing time in the transfer of securities is reduced and neither the securities nor the cash is held up for an unnecessarily long time.
- Hence it is also called a “Scripless trading system”. Thus, it is rightly justified that the Depository provides easy and quicker transfer of shares.
Question 3.
Depository System results in reduced time, cost and efforts.
Answer:
- The depository System has a very important role to play in the successful functioning of the Capital market.
- Under Depository System, securities are held in electronic form.
- The transfer and settlement of securities are done electronically.
- The Depository system maintains accounts of the shareholder, enables transfer, collects dividends, bonus shares, etc. on behalf of the shareholder.
- It eliminates a huge volume of paperwork, storage, and handling of physical certificates.
- Thus, it is rightly justified that, Depository system results in reduced time, cost and efforts.
Question 4.
The depository system is very similar to the Banking system.
Answer:
- The depository system is similar to the Banking system in many aspects.
- Depository keeps the securities safe, just like the bank keeps the money of the account holder safe.
- In banks, funds are held in accounts having unique numbers. Similarly, securities are held in accounts having unique IDs.
- There is no physical handling of money in the bank. Similarly, there is no physical handling of securities by the depository.
- Bank facilitates the transfer of funds between accounts. Depository facilitates the transfer of securities between accounts.
- Thus, it is rightly justified that the Depository system is very similar to the Banking system.
Question 5.
DP is an important constituent of the Depository system.
Answer:
- Depository Participant acts as a link between the Depository and the Investor. In other words, it is an agent of the depository.
- DP is registered under the SEBI Act. It enjoys rights and obligations as specified under SEBI Regulations of 1996.
- It is an intermediary appointed by Depository.
- DP directly deals with customers and sends a statement of accounts periodically.
- The DP has a unique number for identification.
- Banks, Financial Institutions, Stock Brokers, etc. can function as Depository Participants.
- Thus, it is rightly justified that DP is an important constituent of the Depository system.
Question 6.
Depository system allows both: Physical to electronic and electronic to physical conversion.
Answer:
- Under the Depository system, physical certificates can be converted into electronic ones known as ‘Dematerialization’.
- Similarly, the conversion of electronic securities into physical certificates is known as ‘Rematerialization’.
- Due to Dematerialization transfer of securities takes place fast and transactions are also settled immediately. Whereas in Rematerialization, settlement of transactions in the physical system takes more time.
- In Rematerialization, storing and handling physical certificates is more time-consuming. Whereas in dematerialization, there is no handling of certificates.
- There are chances of certificates getting lost, damaged, torn, stolen, misplaced during transit, etc.
- In this technological world, Demat securities are more preferred over Rematerialized securities.
- Thus, it is rightly justified that the Depository system allows both: Physical to electronic and electronic to physical conversion.
Question 7.
ISIN is a necessary component of Demat.
Answer:
- International Securities Identification Number (ISIN) is a code that uniquely identifies a specific securities issue.
- ISINs are allotted by that country’s NNA (National Numbering Agency).
- ISIN is a standard numbering system that is accepted globally.
- The ISIN’s structure is currently defined by the International Organization of Standardization (ISO).
- ISIN consists of a 12 (twelve) digit alpha-numeric code which is divided into 3 (three) parts.
- The company has to apply for ISIN for its securities with documents like a prospectus.
- In India, issuing ISIN to securities is assigned by SEBI to NSDL (for Demat shares). SEBI works as NNA in India.
- Thus, from the above points, it is rightly justified that ISIN is a necessary component of Demat.
7. Answer the following.
Question 1.
What is Depository System? Explain its advantages?
Answer:
The depository system came into existence in the year 1996. It is a system where securities are held in electronic form. It also maintains accounts of the shareholder, enables transfer, collects dividends, bonus shares, etc. on behalf of the shareholder. In other words, it is also called a scriptless trading system.
Benefits/Advantages of Depository System:
(A) Investors:
(i) Safety:
A safe and secure way of holding securities is in electronic form/mode. The depository system is monitored by SEBI. The Investor can keep his account in a ‘Freeze/Lock’ mode to avoid/ prevent unexpected debit or credit or both by giving instructions to the DP.
(ii) Easy Transfer of Shares:
These securities can be easily transferred in electronic mode. Filling out transfer forms and uploading the documents can be easily done online. It is a time and efforts saving process. No stamp duty is levied on the depository system.
(iii) Update and Intimation:
The investor can check his status of holding securities at any time. Depository Participant provides investors with his statement of accounts periodically.
(iv) Automatic Credit:
Under, the depository system the investor’s account is automatically credited/debited. This credit or debit of accounts is usually in case of Payment of Dividend, Issue of Bonus Shares, Offering of Rights Shares, Early Redemption of Debentures, Mergers, and Acquisitions, etc.
(B) Companies:
(i) Up-to-date Information:
The depository system enables the company to maintain the information of the investors holding. It also helps the company to keep updated information about its shareholding pattern. The company is able to know the particulars of beneficial owners and their holdings periodically.
(ii) Reduction in costs and efforts:
Due to the depository system, maintaining the documents physically, the printing of certificates has saved a lot of time and cost.
(iii) Better Relationships:
The transfer process under the depository system is prompt and free from defects. So, complaints against the company by an investor is avoided in this regard. This helps the company build a good corporate image.
(iv) International Investment:
Paperless trading is a boon for the company management as it provides better and quicker services to the investors staying within the country and abroad. This attracts investment from abroad.
Question 2.
Explain the constituents of the depository system.
Answer:
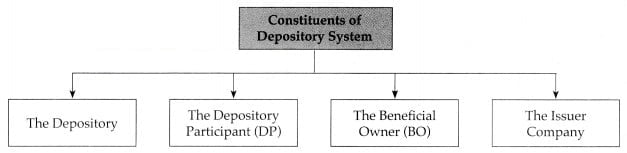
(i) Depository:
- Depository is an organization or a system where securities/shares are held in electric form.
- Depository transfers securities/shares between accounts on the instruction of the account holders.
- Depository contacts the customer through a depository participant.
- Transfer of shares is made through mere computerized book-entry in the depository.
- This becomes possible because shares are dematerialized.
- Only those securities which are held in the form of the share certificate are one’s names can be dematerialized.
-
At present, there are two depositories. They are:
- National Securities Depository Limited (NSDL)
- Central Depository Services Limited (CDSL).
(ii) Depository Participant:
- The depository participant is the representative of the depository.
- Depository participant acts as an intermediary between investors and depositories.
- The depository participants have an identity number for identification.
- It has to maintain accounts of securities of each investor.
- Depository participant gives intimation about holdings from time to time by sending a statement of holding.
- According to SEBI guidelines financial institutions, banks, stockbrokers can act as a depository participant.
(iii) Beneficial Owner:
- An investor is known as ‘Beneficial Owner’ on whose name Demat account is opened.
- He enjoys the rights and benefits of members such as getting dividends, getting bonus shares, to vote at meetings.
- He is allotted an account number where securities are held.
(iv) Issuer Company:
- It is a company that makes an issue of securities.
- It must get registered with the depository.