04 Thermodynamics
Multiple Choice Questions
1. The first law of thermodynamics is concerned with the conservation of
(A) momentum
(C) temperature
(B) energy
(D) mass
Ans. (B) energy
2. A graph of pressure versus volume for an ideal gas for different processes is as shown. In the graph curve represents

(A) isochoric process
(B) isothermal process
(C) isobaric process
(D) adiabatic process
Ans. (C) isobaric process
3. The first law of thermodynamics is consistent with the law of conservation of
(A) momentum
(B) energy
(C) mass
(D) velocity
Ans. (B) energy
Theory Questions
- Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics
1. State zeroth law of thermodynamics. What are the limitations of first law of thermodynamics? [July 22]
Ans: Statement of zeroth law of thermodynamics: If two systems are each in thermal equilibrium with a third system, they are also in thermal equilibrium with each other.
The limitations of first law of thermodynamics:
i. First law of thermodynamics does not tell us whether any particular process can actually occur.
ii. According to the first law of thermodynamics, heat may, on its own, flow from an object at higher temperature to one at lower temperature as well as it can flow from an object at lower temperature to one at higher temperature. Practically, heat cannot flow from an object at lower temperature to another at higher temperature. The First law of thermodynamics does not predict this practical observation. iii. According to the first law, all of the heat available could be converted into work. Similarly, all the work could be converted into heat. This is practically impossible.
4.5 First Law of Thermodynamics
1. State first law of thermodynamics.
Ans: The change in the internal energy of a system is the difference between the heat supplied to the system and the work done by the system on its surroundings

When the amount of heat is added to a system, its internal energy is increased by an amount
and the remaining is lost in the form of work done
on the surrounding.
- Thermodynamic State Variables
1. What are mechanical equilibrium and thermal equilibrium?
Ans:
i. Mechanical equilibrium:
a. For a system to be in mechanical equilibrium, there should not be any unbalanced forces acting within the system and between the system and its surrounding.
b. Also, the pressure in the system should be same throughout the system and should not change. with time.
ii. Thermal equilibrium:
For a system to be in thermal equilibrium, the temperature of the system should be uniform throughout and it should not change with time. A system when in thermal equilibrium is described in terms of state variables.
- Thermodynamic Process
1. What is isothermal process?
Ans: A process in which change in pressure and volume takes place at a constant temperature is called an isothermal process or isothermal change.
2. What is a thermodynamic process? Give any two types of it.
Ans:
Thermodynamic process: A process by which two or more of state variables of a system can be changed is called a thermodynamic process or a thermodynamic change.
Types of thermodynamic processes:
i. Quasi-static process
ii. isothermal process
iii. adiabatic process
iv. isochoric process
v. isobaric process
vi. reversible process
vii. irreversible process
viii. cyclic process
(Any two types)
3. In which thermodynamic process the total internal energy of system remains constant?
Ans: The total internal energy of system remains constant in isothermal process.
4. Derive an expression for the work done during an isothermal process.
Ans:
i. Consider the isothermal expansion of an ideal gas.
ii. Let its initial volume be and the final volume be
.
iii. The work done in an infinitesimally small isothermal expansion is given by,

iv. The total work done in bringing out the expansion from the initial volume to the final volume
is given by,

v. But, for an ideal gas, . Using this in the equation (1) we get,


Numericals
4.5 First Law of Thermodynamics
1. The initial pressure and volume of a gas enclosed in a cylinder are and
respectively. If the work done in compressing the gas at constant pressure is
, find the final volume of the gas.
Solution:
Given: ,
To find: Final volume
Formula:
Calculation: The gas is compressed,
From formula,



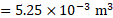
Ans: The final volume of the gas will be .
2. of work is done on certain volume of a gas. If the gas releases
of heat, calculate the change in internal energy of the gas. [Mar 23] OR
A system releases of heat while
of work is done on the system. Calculate the change in internal energy of the gas. [July 22]
Solution:
Given:
To find: Change in internal energy
Formula:
Calculation: From formula,

Ans: Change in internal energy is .
4.7 Thermodynamic Process
1. An ideal mono-atomic gas is adiabatically compressed so that its final temperature is twice its initial temperature. Calculate the ratio of final pressure to its initial pressure.
Solution:
Given: As the gas is monatomic,

To find: Ratio of final pressure to its initial pressure
Formula:
Calculation: From formula,

On taking cube of both sides, we get

Taking square root of both sides, we get

Ans: The ratio of final pressure to its initial pressure is