MARCH 2019
GEOGRAPHY
Q. 1. Complete the following sentences, by choosing the appropriate alternatives from those given and rewrite the sentences in your answer-book:
(1) Brazil is covered mainly by …………………….. …
(i) Highlands
(ii) Plains
(iii) Mountainous regions
(iv) Dissected hills
(2) India’s climate is of …………………….. type.
(i) Humid
(ii) Monsoon
(iii) Equatorial
(iv) Cold
(3) Teak is mainly found in the …………………….. type of forest.
(i) Coastal
(ii) Thorny and bush
(iii) Deciduous
(iv) Coniferous
(4) Brazil is the largest exporter of ……………………… in the world.
(i) Mineral oil
(ii) Tea
(iii) Bajra
(iv) Coffee
Ans. 1. (1) (i) Brazil is covered mainly by Highlands.
(2) (ii) India’s climate is of Monsoon type.
(3) (iii) Teak is mainly found in the Decidous type of forest.
(4) (iv) Brazil is the largest exporter of Coffee in the world.
Q. 2. Find the odd one out:
(1) States in India :
(i) Madhya Pradesh
(ii) Maharashtra
(iii) Meghalaya
(iv) Maranhao
(2) With reference to flora of India :
(i) Deodar
(ii) Anjan
(iii) Orchid
(iv) Banyan
(3) Members of BRICS :
(i) Brazil
(ii) India
(iii) China
(iv) Saudi Arabia
(4) Favourable factors affecting population distribution :
(i) Nearness to sea
(iii) Cultivable land
(ii) Lack of roads
(iv) New cities and towns
Ans. 2. (1) (iv) Maranhao
(3) (iv) Saudi Arabia
(2) (iii) Orchid
(4) (ii) Lack of roads
Q. 3. State whether the sentences are right or wrong and correct the wrong ones and rewrite the sentence (any four) :
(1) During field visit, vegetation is not the indicator of difference in precipitation.”
(2) The river Ganga originates from the Yamunotri glacier.
(3) Brazil is mainly located in the Southern hemisphere.
(4) The western part of Brazil is densely populated.
(5) Like the Indian economy, the Brazilian economy is also of mixed type.
Ans. 3. (1) Answer is not given due to the reduced syllabus.
(2) Wrong – The river Ganga originates from the Gangotri glacier.
(3) Right
(4) Wrong – The western part of Brazil is sparsely populated.
(5) Right
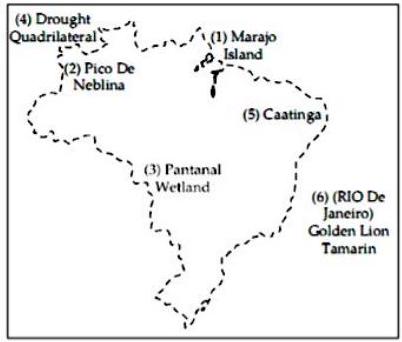
Q. 4. (a) Mark the following in the outline map of Brazil supplied to you, write the names and give index (any four) :
(1) Marajo Island
(2) Pico-De-Neblina
(3) Pantanal Wetland
(4) Drought Quadrilateral(5) Caatinga
(6) Golden Lion-Tamarin.
(b) Observe the given map and answer the questions given below it (any four) :

Questions :
(1) What does the map show?
(2) Name any two airports in the eastern coast.
(3) In which states, railway routes do not exist?
(4) Name the Southernmost railway station of India.
(5) Which is the important railway station on the route of Mumbai-Mangalore ?
(6) Name the Northernmost airport of India.
Ans. (a)
(b) 1. The map shows important railway routes and airports in India.
- Visakhapatnam and Chennai are the two ports in the eastern coast of India.
- There are no railway routes in the state of Meghalaya.
- Kanyakumari is the southernmost railway station of India.
- Vasco da Gama is the important railway station on the route of MumbaiBangalore.
- Delhi is the Northernmost airport of India.
Q. 5. Give geographical reasons for the following (any two) :
(1) There are fewer natural ports on the eastern coast of India.
(2) The evergreen rain forests in Brazil are rightly called the ‘Lungs of the world’.
(3) Settlements are sparse in north-eastern Brazil.
(4) A dense network of railways has developed in the North Indian plains.
Ans. 5. (1) The eastern coasts are emergent or shallow, so the bigger ships cannot enter close to the land, which causes inconvenience to load and unload materials. The eastern rivers form deltas. As a result, the ships can enter and leave only during tides. So, there are fewer natural ports on the eastern coast of India.
(2) Evergreen forest are found in the regions where there is heavy rainfall throughout the year. Due to the evergreen rainforests in Brazil, large amount of oxygen is released in the environment. This reduces the carbon dioxide levels in the environment. Therefore, evergreen rain forests in Brazil are called the ‘Lungs of the world’.
(3) The thick equatorial rainforest zones are in the nort-east. There are limitations on use and exploitation of natural resources. Transport facilities are very poor in the region due to poor infrastructural facilities. The climate here is unhealthy and unfit for settlement. So, settlements are sparse in North-eastern Brazil.
(4) Railway network is relatively less dense in the hilly states in the north and northeast, in the central parts of India and the desert area of Rajasthan, while it is dense in the North Indian plains due to its vast levelled land, industrialisation, high population density and urbanisation, rich agricultural resources due to fertile soil and plenty of water resources.
Q. 6. (a) With the help of given statistical data prepare a simple bar graph and answer the following questions :
(1961-2011)
Year |
| ||
1961 | 18.0 | ||
1971 | 18.2 | ||
1981 | 23.3 | ||
1991 | 25.7 | ||
2001 | 27.8 | ||
2011 | 31.2 |
Questions :
(1) What is the interval of the data?
(2) Which decade shows slow rate of urbanisation?
(3) Which decade shows high rate of urbanisation?
OR
(b) Observe the following graphs and answer the questions given below them :
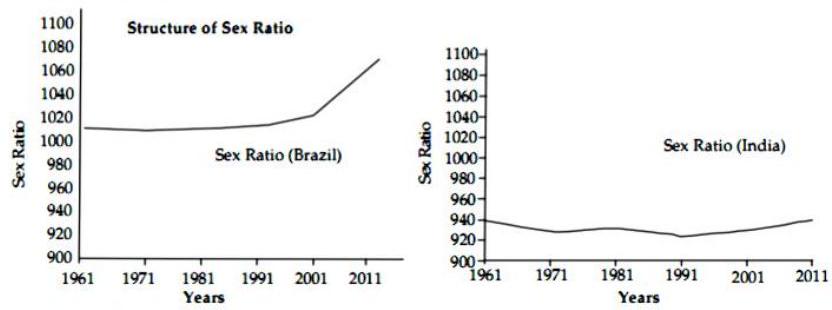
Questions :
(1) What do the above graphs show ?
(2) Which country has highest male population?
(3) Which country has highest female population?
(4) Which country has rapid increase in female population after 2001 ?
(5) What was the female population in India in 1961 ?
(6) Which country has more than 1000 female population?

Ans. 6. (a) (1) The interval of the data is ten years.
(2) The decade 1961 to 1971 shows slow rate of urbanisation.
(3) The decade 2001 and 2011 shows high rate of urbanisation.

OR
(b) (1) The above graphs show the sex ratio of Brazil and India.
(2) India has highest male population.
(3) Brazil has highest female population.
(4) Brazil has rapid increase in female population after 2001.
(5) The female population was 940 in India in 1961.
(6) Brazil has more than 1000 female population.
Q. 7. Answer the following questions in detail (any two) :
(1) How will you manage the litter during the field visit ?*
(2) How are the Brazil and India different from each other in terms of location ?
(3) Write the factors affecting climate of Brazil.
(4) What are the similarities and differences in the fishing activities in Brazil and India?
Ans. 7. (1) Answer is not given due to the reduced syllabus.
(2) India is located in the northern and the eastern hemisphere whereas Brazil is located in the western and the southern hemisphere. India is located in the Asian continent whereas Brazil is located in the South American continent. India has the Arabian Sea to its west, Indian Ocean to its south and Bay of Bengal to its east whereas Brazil has the Atlantic Ocean to its northern and eastern coasts.
(3) As Brazil has vast latitudinal extent, it experiences wide range of climatic variations. Brazil gets rainfall from the South-East trade winds and the NorthEast trade winds. Parts of the Brazilian highlands extend up to the northern
coast. The escarpments act as obstruction to the winds coming from the sea and cause orographic type of rainfall in the coastal region.
Beyond the highlands, the effect of these winds gets reduced. As a result, the rainfall is minimal considering the temperatures in Brazil, the northern part of Brazil is hot, while the temperatures in the southern part are comparatively lower. Near the equator at Brazilian coasts, temperature does not vary much. In the coastal regions, near the equator differences in temperatures are negligible. The winds move in the vertical direction in this region. Similarly, the convergence zone of the trade winds is weak here. That is why tropical cyclones rarely visit coasts of Brazil.
(4) Similarities in the fishing activities in Brazil and India:
Both the countries have a long coastline and marine fishing is well-developed. Fishing is important in both the counties as it helps in augmenting food supply, generating employment and earning foreign exchange.
Differences in fishing activities in Brazil and India :
Marine fishing and island fishing are the two types of fishing. In Brazil, marine though there are a large number of rivers in Brazil.
In India, inland fishing is undertaken on a large scale and marine fishing is undertaken on a small scale.