Chapter 8 Biomes
1. (A) Complete the chain.
Question 1.
A | B | C |
(1) Boreal forest | (1) Hardwood species of tree | (1) Siberia |
(2) Deserts | (2) Tropical deciduous forest | (2) Myanmar |
(3) Teak | (3) Wide spectrum of bio-diversity | (3) Sahara Desert |
(4) Tropical rainforest | (4) Tundra region | (4) Brazil |
(5) Taiga forest | (5) Greenland | |
(6) Narrow spectrum of bio-diversity |
Answer:
A | B | C |
(1) Boreal forest | (1) Taiga forest | (1) Siberia |
(2) Deserts | (2) Narrow spectrum of bio-diversity | (2) Sahara Desert |
(3) Teak | (3) Tropical deciduous forest | (3) Myanmar |
(4) Tropical rainforest | (4) Hardwood species of tree | (4) Brazil |
(B) Choose the correct option by identifying the correct correlation in the sentences.
Question 1.
Ecosystem consists of interaction between ………………….. and abiotic factors.
(a) biotic
(b) animals
(c) human beings
(d) plants
Answer:
(a) biotic
Question 2.
The original meaning of savannah is ………………….
(a) land with many trees
(b) extensive perennial grassland
(c) land which is full of trees with much grass
(d) land which is without trees but with much grass
Answer:
(b) extensive perennial grassland
Question 3.
In Africa, tropical evergreen forest is predominantly found in ………………….
(a) Amazon basin
(b) Sahara Desert
(c) Congo basin
(d) Savannah
Answer:
(c) Congo basin
Question 4.
Mediterranean forest is also known as ………………… forests.
(a) hardwood
(b) chaparral
(c) manmade
(d) softwood
Answer:
(b) chaparral
2. (A) Arrange the given statements as per given instructions.
Question 1.
Arrange the following biomes in proper order from Equator to Pole.
(a) Tundra
(b) Tropical Rainforest
(c) Boreal forest
(d) Sahara Desert
Answer:
(b), (d), (c), (a)
2. (B) Identify the incorrect factor.
Question 1.
Trees in the tropical rainforest
(a) Mahogany
(b) Ebony
(c) Pine
(d) Rosewood
Answer:
(c) Pine
Question 2.
Temperate grassland in the world
(a) Prairies – North America
(b) Steppes – Eurasia
(c) Downs – Africa
(d) Pampas – South America
Answer:
(c) Downs – Africa
Question 3.
Major hot deserts in the world are
(a) Gobi – Asia
(b) Kalahari – Africa
(c) Atacama – South America
(d) Arabian – Asia.
Answer:
(a) Gobi – Asia
3. Give geographical reasons.
Question 1.
The trees in the tropical rainforests are broad-leaved while those in the taiga are coniferous.
Answer:
- Tropical rainforest biome has high temperature and heavy rainfall almost throughout the year.
- The trees grow very densely and very little sunlight falls on the ground of the forest.
- So, plants near the ground have broad leaves to capture as much sunlight as possible.
- Such leaves can cope in hot, wet tropical climates because they counteract the day-time heat-trapping effect using transpiration.
- The taiga biome has cold winter with severe snowfall. Therefore, to adapt to this condition:
- Coniferous trees that grow here have thick bark to protect against the cold.
- They are tall, cone-shaped, with flexible branches that taper to the ground and due to their waxy leaves the snow does not stay on the trees.
- The pine cones protect the seeds in winter
Question 2.
Desert biomes have thorny vegetation.
Answer:
- There is scarcity of rainfall in the desert biomes.
- Normally plants lose their moisture through their pores which are present on their leaves and stems.
- Desert plants need to avoid the loss of water through these pores to lock in the minimum levels of moisture that they have.
- Hence desert plants have leaves which are modified into thorns to control loss of water through transpiration.
Therefore, desert biomes have thorny vegetation.
Question 3.
Lumbering activity has developed in Taiga forests.
Answer:
- Lumbering is an economic activity involving felling, hauling and logging of timber.
- It is well developed in the Taiga coniferous forests because the coniferous forests have soft-wooded trees which are easy to fell with modern machines.
- Softwood has great demand in the international market.
- The lack of dense undergrowth and creepers help in easy cutting of these trees.
- The presence of one type of tree over a large extent, makes commercial lumbering activity more economical.
Hence, lumbering activity has developed in Taiga forests.
Question 4.
Mediterranean biome has proved to be a catalyst to the development of cinema industry.
Answer:
- The Mediterranean biome has hot or warm and dry summers and mild or cool and wet winters.
- Clear skies, bright sunshine, natural beauty, pleasant climate and flowers have contributed to the development of cinema industry.
- Due to clear sky and fine weather outdoor shooting is possible throughout the year.
4. Write short notes on.
Question 1.
Agriculture in temperate grassland biome.
Answer:
- The climate of the Temperate Grassland biome is favourable for agriculture and animal rearing.
- In grassland regions such as the Prairies, Steppes, Downs, Pampas, Velds, etc., extensive type of agriculture has developed.
- Crops like maize, wheat are produced on a large scale.
- The fields extend to hundreds of hectares and therefore, advanced machines are used for agriculture.
- As these areas have abundant yields, the countries lying in this biome are famous as exporters.
- The extent of commercial agriculture is increasing in this area.
Question 2.
Human Life in Tundra biome.
Answer:
- Human settlements are very sparse because of very cold climate.
- Lapps, Samoyeds and Eskimos live in adverse climate.
- Life of Eskimos has changed after they come into contact with westernisers.
- As they have started getting advanced instruments, their life and fishing methods have changed. Thus, they have started exploitation of fish at a higher speed in this biome.
- Due to increased transportation and means of communication there is lot of development in this region. There is improvement in the standard of living of people.
- Due to development there is adverse effect on protected factors of this biome.
Question 3.
Animal adaptation in grasslands.
Answer:
- The Tropical Grasslands (Savannah) extend between 10° to 20° N and S.
- The abundance of grass cover and its perennial nature have made savannah biomes rich in herbivore animals.
- Seasonal change in colour of grass has provided natural shelter for animals.
- These grassland supports large number of hoofed animals.
- A variety of herbivore animals of different sizes from rabbits to elephants are found here.
- With rich herbivore density, these grasslands also support a number of carnivorous animals.
- In temperate grassland region soft and juicy grass grows, therefore animal life is rich and varied.
- Herbivore animals like zebras, wolves, deer, gazelles and wild horses are found. Coyote is a carnivore.
Question 4.
Marine Biomes.
Answer:
The biomes we find in ocean/sea water are called marine biome. Approximately 70% of the earth’s surface is covered by oceans. There are three layers in Marine biomes:
(i) Euphotic Layer:
- It is the top layer of the Marine biome.
- The sunlight reaches there.
- It is around 200 m deep.
- It is home to many fishes, sea turtles jellyfish, seals, coral, zooplankton and mangroves.
(ii) Disphotic Layer:
- It is the middle layer.
- Some light penetrates to the bottom part.
- It is about 1000 m deep from mean sea level.
- Except few phytoplankton sunk from upper layer, plants are not found here
- In this layer animals are adapted to darkness, cold water and high pressure.
- Swordfish, eels, sea dragon, cattle fish, squid and wolfish are found.
(iii) Aphotic layer:
- It is the deepest layer.
- It ranges from 1000 m to 4000 m depth.
- No light penetrates here, therefore there is no living plant life in this layer.
- Bioluminescent jellyfish, angler fish, hatchet fish, elusive giant squid, etc., are found in this layer.
- Beyond this layer lies the darkest and the deepest zone extending up to the sea floor. Here animals are adapted to survive on detritus under even greatest pressure.
5. Differentiate between
Question 1.
Biome and Ecosystem.
Answer:
Biome | Ecosystem |
(i) An area where different types of flora and fauna live together in the same region in the same type of climatic conditions is called a biome. | (i) In a given region, the interaction between biotic and abiotic factors is known as ecosystem. |
(ii) The boundaries of different biomes on land are determined mainly by climatic conditions like rainfall, temperature, humidity, amount of insolation received and soil conditions. | (ii) The biotic factors are plants, animals and bacteria. The abiotic factors consist of soil, water, sunlight and nutrients. |
(iii) There can be many ecosystems in a biome. | (iii) There are different trophic levels in an ecosystem. |
Question 2.
Tropical and Temperate Grassland Biome.
Answer:
Tropical Grassland Biome | Temperate Grassland Biome |
(i) It is located between 10° to 20° N and S. | (i) It is located between 40° to 55° N and S. |
(ii) It is characterised by a continuous cover of perennial grass that grows about 3 m to 6 m height, known as elephant grass and there are a few shrubs and trees. | (ii) Grass is a dominant vegetation. It is soft. Not many types of trees are found. The various species of grass include purple needle grass, blue grama, buffalo grass and galleta. |
(iii) It is rich in herbivorous animals like rabbits, antelopes, buffaloes, zebras, rhinos, giraffes, elephants, warthogs, etc. It also supports a number of carnivores like lions, leopards, cheetah, wild dogs, jackals, hyenas, and birds like vultures, great Indian bustards, twitter and ostriches. | (iii) It is rich and varied in animal life. Herbivore animals include gazelles, zebras, wild horses, wolves, deer, rabbits, etc. In the veld grasslands, ostriches are found. In the Downs of Australia, kangaroos and dingoes are found. |
Question 3.
Human activities in Tropical Evergreen and Monsoon Regions.
Answer:
Human activities in Tropical Evergreen | Human activities in Monsoon Regions |
(i) Human life is not very easy in this climate. | (i) Human life is easier than that in the rainforest. |
(ii) Indigenous humans in these parts are still in their primitive stage. | (ii) Primary and secondary occupations based on forests are found here. |
(iii) Indigenous tribes are Pygmies in Congo, Boro Indians in Amazon, Sentinels, Onges, Jarawahs, etc., in Andaman and Nicobar Islands in India. | (iii) Various tribal communities inhabit the regions under this biome. |
(iv) They are engaged in primary activities like gathering of forest products, hunting, fishing, etc. Secondary activities are not developed. | (iv) Animal rearing for milk and meat production is carried out. Primary and secondary activities based on forest products are also developed. |
6. Answer in detail.
Question 1.
Give an account of the Desert Biome with the help of the following points
(i) Location
(ii) Plant life
(iii) Animal life
(iv) Human life
Answer:
(i) Location: The Tropical Desert biome has the latitudinal extent of 20° to 30° N and S.
(ii) Plant Life : The vegetal life is dispersed. It includes date palms, and thorny trees such as khejari, acacia, and bushes like century plant, cactus, etc. There is hardly any vegetal cover due to the dry climatic conditions.
Characteristics of forests:
- Thick leaves with capacity to store water.
- Thorny nature reduces speed of evaporation, safety from animals.
- Trunk like leaves carry out photosynthesis.
(iii) Animal life:
- As the vegetation is sparse, bio-diversity is also limited.
- There are relatively few large animals in the desert.
- The animals are small and tend to burrow, or stay in hideaways till dusk to avoid the heat. They are adapted to survive in hot climate with very little water.
- They are mainly small carnivores, camels, many species of snakes, types of lizards, desert turtles, rats, mongoose along with goats, sheep, donkeys, etc.
Birds : Ostriches, various raptors; guinea fowl and bustards; desert eagle owls and barn owls; sand larks and pale crag martins; and brown-necked and fan-tailed ravens.
Insects : House flies, beetles, moths, types of termites, etc.
(iv) Human life:
- The extreme temperatures make human life very difficult here.
- Depending on the availability of water, animal husbandry or agriculture might be followed.
- Human settlements are found only near oases, in a dispersed pattern. Nomadic life is found in some areas. In the earlier times, Bedouin tribes used to trade by traveling on camels.
Question 2.
Explain the reasons behind deforestation in your area. What measures will you suggest to minimize deforestation?
Answer:
I am a resident of Goregaon, very close to the Aarey Colony which was formerly called the Aarey Milk Colony due to the presence of the Aarey Dairy that provided milk to the City of Mumbai. It was once known as the Lungs of Mumbai. It also housed a variety of flora and fauna. But soon deforestation began in phases. First came residential areas, followed by the Film City and now it is the metro car shed. In spite of protests from several citizen’s groups, NGOs and celebrities, more than 2000 trees were felled overnight, forcing the Supreme Court to intervene.
I would suggest the government to shift the metro car shed to some other location and immediately start planting saplings to replace the destroyed trees.
Intext Questions and Answers
Let us recall.
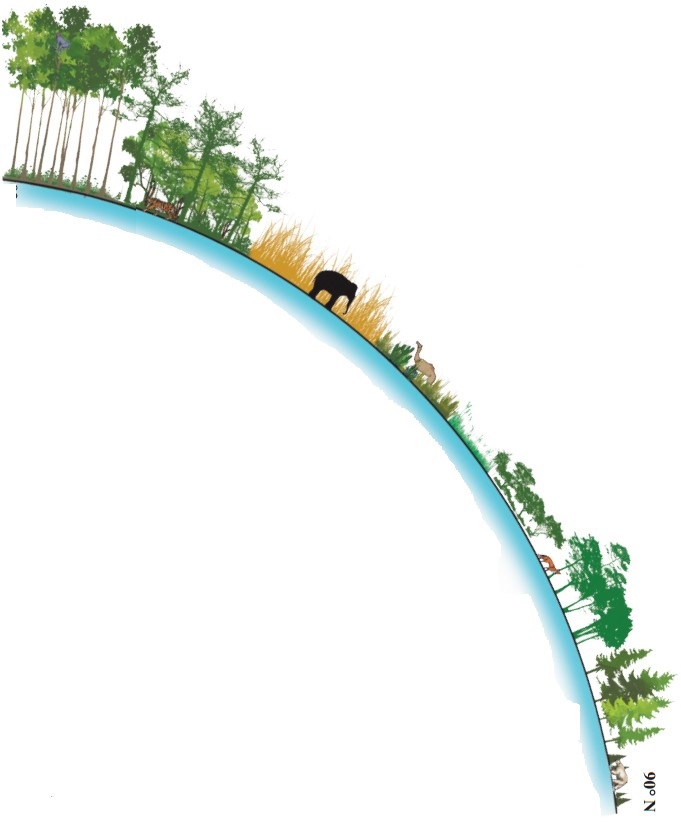
Look at the fig. 8.1. Answer the following questions (Textbook Page No. 84)

Question 1.
What does the figure show?
Answer:
The figure shows the vegetation and animal life from equator to polar areas.
Question 2.
What do the numbers on the figure represent?
Answer:
The numbers in the figure represent latitudes.
Question 3.
How does the latitude influence vegetation?
Answer:
Vegetation in any area depend upon the elements of climate such as temperature, rainfall, humidity, soil condition and amount of insolation received. These conditions vary with latitude. For example, in the lower latitudes that is near the equator there is hot and wet climate, so dense evergreen forests grow. But in higher latitudes due to extreme cold climate and heavy snowfall, there are hardly trees but mosses and lichen grow.
Following vegetation grows in different latitudes:
0° to 10° N and S – Dense, evergreen, hardwood forest
5° to 30° N and S – Tropical deciduous forest
10° to 20° N and S – Tropical grasslands
20° to 30° N and S – Tropical Desert.
30° to 40° N and S – Mediterranean (Evergreen and Deciduous Forest)
40° to 50° N and S – Temperate Deciduous Forest.
40° to 55° N and S – Temperate Grasslands.
50° to 55° N – Taiga (Coniferous Forests)
65° to 90° N – Tundra
Question 4.
How does Latitude influence the fauna of a place?
Answer:
As the vegetation changes with latitude, depending upon vegetation and climate, fauna also changes as per following.
- 0° to 10° N and S – Monkeys, birds from the vulture family, hornbills, parrots, various species of insects, butterflies and reptiles.
- 5° to 30° N and S – Microscopic organisms to large elephants, hippopotamus, rhinos, tiger, lion, gaur, monkeys, etc.
Birds : Coucal, hornbills, Asian koel, peacock, vultures, falcon, pigeons, sparrows, etc.
Insects : Ants, butterflies, insects and worms are in plenty.
10° to 20° N and S – Rich in herbivore animals, ranging from rabbits to elephants. Main species – antelopes, buffalo, zebra, rhinos, wild beasts, giraffes, warthogs, etc. The carnivore like cats, lions, leopards, cheetah, wild dogs, jackals, hyenas, etc.
Birds : Vulture, great Indian bustards, twitter and ostriches.
20° to 30° N and S – Mainly carnivores, camels, rats, mongoose, desert turtles, many species of snakes, types of lizards, goats, sheep, donkeys, etc.
Insects : Houseflies, beetles, moths, types of termites, etc.
30° to 40° N and S – Rabbits, deer, goats, pigs, horses, brown bears, fox, berry deer, wild cats, goats and sheep.
Birds : Vultures, eagles.
Alligators, reptiles.
Insects : Various types of insects and honeybees.
40° to 50° N and S – Animals having thick and soft fur like brown bears, red fox, sable, mink, etc. are found.
Birds : Peregrine, falcon, woodpecker, cardinals.
Insects : Many types of insects.
40° to 55° N and S – Rich and varied animal life. Herbivores include gazelles, zebras, wild horses wolves, deer, rabbits, coyote is a carnivore. Ostriches are found in veld grasslands. Kangaroos and dingoes are found in the Downs of Australia.
50° to 55° N – The animals have thick hides and a thick layer of fats and are hairy.
E.g., reindeer, grizzly bears, elk, caribou, etc., are herbivores. Fox mountain lions, puma and panthers are the carnivores.
65° N to 90° N – Very scarce animal life. Thick fur and layer of fats in their body helps them to face very cold climate. Herbivores such as musk ox, bears, reindeer, caribou, lemming, rabbits along with carnivores like Arctic fox, dogs, jackals are found.
Birds : Ptarmigan, ravens, snowy owls and redpolls are found. Majority are migrants. Seals, walruses are found in coastal areas.
Question 5.
Which latitude will have more biodiversity?
Answer:
Biodiversity is very high in 0° to 10° N and S and 5° to 30° N and S.
Question 2.
Make a list of products found in your home which have come from this biome. (Textbook Page No. 88)
Answer:
This biome is Tropical Deciduous biome. The wood obtained from the teak tree is used for making furniture. Bamboo is used during painting of buildings. Bamboo products like mats, basket is used in our daily life. We use sandalwood soap, agarbatti as well as paste during pujas and rosewood paste for healing of wounds. We also find in our homes many ayurvedic medicines made from plants of these forests.
Think about it.
Question 1.
Besides latitudes, what other conditions influence the biome? (Textbook Page No. 84)
Answer:
Besides latitudes climate, trophic level, human activities development of agriculture, industries, transportation, tourism etc., also influence the biome.
Question 2.
In which region in India, is desertification occurring? (Textbook Page No. 89)
Answer:
Desertification is occurring in Rajasthan, Delhi, Goa, Maharashtra, Jharkhand, Nagaland, Tripura and Himachal Pradesh.
Question 3.
Why is this type of biome not found in Southern Hemisphere? (Textbook Page No. 93)
Answer:
Taiga biome is from 50° to 55° latitude. There is no landmass from 50° to 55° in southern hemisphere, therefore this type of biome is not found in southern hemisphere.
Question 4.
Which activities of human life are affected most by the cold climate? (Textbook Page No. 94)
Answer:
The very cold climate results in sparse human settlements.
It affects human health, the soil and agriculture.
Very cold climate causes thick fog that affects aviation, road, railway and water transport.
Try this.
Question 1.
Find out more differences between an ecosystem and a biome. You can use the following points: scale of area occupied, types, flow of nutrients and energy, examples, etc. (Textbook Page No. 86)
Answer:
Biome | Ecosystem |
(i) An area where different types of flora and fauna live together in the same region in the same type of climatic conditions is called a biome. | (i) In a given region, the interaction between biotic and abiotic factors is known as ecosystem. |
(ii) The boundaries of different biomes on land are determined mainly by climatic conditions like rainfall, temperature, humidity, amount of insolation received and soil conditions. | (ii) The biotic factors are plants, animals and bacteria. The abiotic factors consist of soil, water, sunlight and nutrients. |
(iii) There can be many ecosystems in a biome. | (iii) There are different trophic levels in an ecosystem. |
Question 2.
Write the names of major countries that lie in this biome. (Textbook Page No. 86)
Answer:
This is Tropical Rainforest biome. The countries in this biome are Brazil, Congo, Ecuador; Indonesia, Peru, Columbia, Bolivia, Gabon, Guyana, India, Laos, Malaysia, Cameroon, Central African Republic, Mexico, Myanmar, Papua New Guinea, Suriname and Venezuela.
Question 3.
Write the names of major countries that lie in this biome. (Textbook Page No. 87)
Answer:
Central India, Bangladesh, Burma, Thailand, Vietnam, Laos, Cambodia, southern part of China and northern part of Australia.
Question 4.
Write the names of the major countries that lie in this biome. (Textbook Page No. 88)
Answer:
This is Savannah Grassland biome
Africa : Kenya, Zimbabwe, Botswana, South Africa and Namibia.
Australia, Central America : Belize and Honduras.
South America : Venezuela and Columbia, Southern Asia.
Question 5.
Write the names of the major countries that lie in this biome. (Textbook Page No. 89)
Answer:
This is tropical desert biome. Sahara Desert in North Africa, the Australian Desert of Australia, the Arabian Desert and Syrian Desert in Western Asia, the Kalahari Desert in Southern Africa, Sonoran Desert in the U.S. and Mexico, Mojave Desert in the U.S., Thar Desert in India and Pakistan, Dasht-e-Margo and Registan Desert in Afghanistan and Dasht-e-Kavir and Dasht-e Lut in Iran.
Question 6.
Write the names of major countries that lie in this biome. (Textbook Page No. 90)
Answer:
This is Mediterranean biome. The major countries are Portugal, Spain, southern France, Italy, Yugoslavia, Turkey, Syria, Israel, Lebanon. Northern Africa, central Chile, California in USA, south west Africa and south west Australia.
Question 7.
Write the names of the major countries that lie in this biome. (Textbook Page No. 91)
Answer:
This biome is Temperate Deciduous biome. The major countries are the eastern parts of the United States and Canada, most of Europe and parts of China and Japan.
Read the following news item. (Textbook Page No. 91)
A grizzly bear that killed a mother and her baby in Yukon last fall was emaciated and desperately pursuing unusual food sources at the time of the attack, according to an investigation by the territory’s government. Valerie Theoret, 37, and her 10-month-old daughter, Adele Roesholt, died on Nov. 26, 2018, when a grizzly bear attacked them near their trapping cabin in the remote Einarson Lake area northeast of the village of Mayo. Gordon Hitchcock, chief conservation officer for the Government of Yukon, said the 18-year-old male grizzly bear was emaciated to the point that it was incapable of hibernation.
Additionally, it was in significant and chronic pain from having eaten a porcupine which bears do not typically eat – and had quills penetrating its digestive system from mouth to stomach, “This bear had started turning to uncommon food sources,” said Mr. Hitchcock, who presented findings of a necropsy in Whitehorse on Wednesday. -CNN News
Question 1.
Why do such things occur?
Answer:
Such things occur because man has done encroachment in the habitats of animals. Animals are not getting sufficient food, so they are attacking on human beings.
Question 2.
Give examples of such similar incidents in Maharashtra wherein some animal has attacked people in particular region.
Answer:
In Junnar taluka in Pune district, leopard attacked and killed one small girl and goat.
Question 1.
Write the names of the major countries that lie in this biome. (Textbook Page No. 92)
Answer:
The biome is temperate grassland region. The major countries are Prairies in USA and Canada, Steppes in Russia, Downs in Australia, Pampas in Argentina, Veld in south Africa.
Question 2.
Write the names of the major countries that lie in this biome. (Textbook Page No. 92)
Answer:
This is the Taiga biome. The major countries are parts North America, Eurasia, especially Canada and Russia respectively. In Northern Europe, the countries are Finland, Norway and Sweden and spans across Alaska and Scandinavia.
Question 3.
Write the names of the major countries that lie in this biome. (Textbook Page No. 93)
Answer:
This is Tundra biome. The major countries in this Biome are parts of the U.S., State of Alaska and the countries of Canada, Greenland, Iceland, Norway and Russia.
Question 4.
Write the names of the major regions in this biome. (Textbook Page No. 94)
Answer:
This biome is mountain or highland region. The Himalayas in Asia, the Scottish Highlands, the Scandinavian Mountains, American Cordillera in North and South Americas, the Rift mountains of Africa, Carpathian and Pyrenees Mountains in Europe and the Caucasus Mountains.
Can you tell? (Textbook Page No. 86)
Question 1.
A person staying in Sahara Desert and a person staying in Arabian Desert belong to the same biome or ecosystem?
Answer:
Yes, the person staying in Sahara Desert and a person staying in Arabian desert belong to the same biome or ecosystem, since climatic conditions are same. But there may be slight variation depending upon the impact of human activities.
Question 2.
(i) The tropical deserts are mainly found in which direction of the continents? What could be the reason behind their formation there?
(ii) In which continent is desert not found? (Textbook Page No. 90)
Answer:
(i) Most of the world’s tropical deserts are located in the western margins of continents in the subtropics because the prevailing winds in the tropics are Tropical Easterly Winds. The Tropical Easterly Winds become dry by the time they reach the western margins of the continents and so they bring no rainfall.
(ii) There is no continent without a desert region. Despite its thick ice, Antarctica is classified as a desert because very little moisture falls from the sky.
Question 3.
In India, where do you find such fruits? What are the reasons for them being found here? (Textbook Page No. 93)
Answer:
The fruits like raspberry, strawberry, blueberry, gooseberry, salmonberry are found in the twin hill towns of Panchgani and Mahabaleshwar because of the cool climate in the summers.
Find out! (Textbook Page No. 86)
Question 1.
Find out the regions in this biome where plantation agriculture has developed.
Answer:
The regions where plantation agriculture is developed are tea plantations in NE India and Indonesia, coffee, cocoa and rubber plantations in Brazil, sugarcane plantations in Java island, rubber plantations in Malaysia and Indonesia, cocoa and coffee plantations in Africa.
Question 2.
Look for the names of the tribes dependent on this biome in India including Maharashtra along with their habitats and show them on a map of India. (Textbook Page No. 87)
Answer:
Major Tribes in India
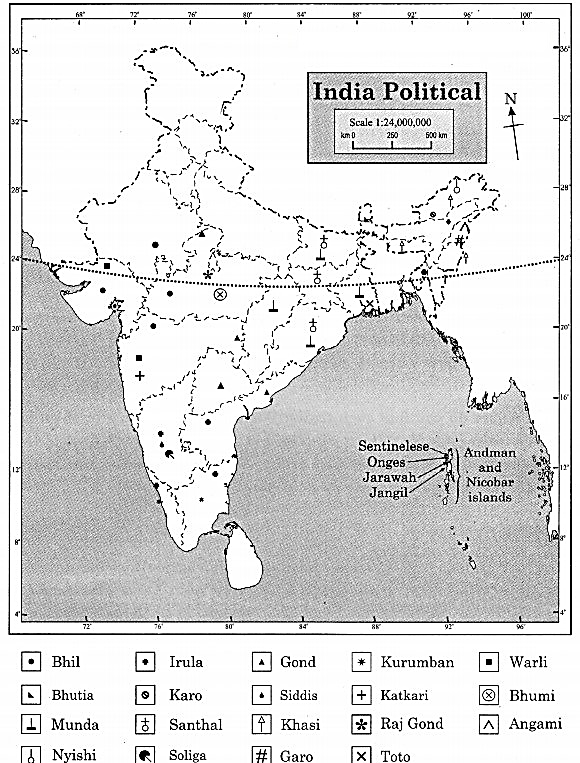
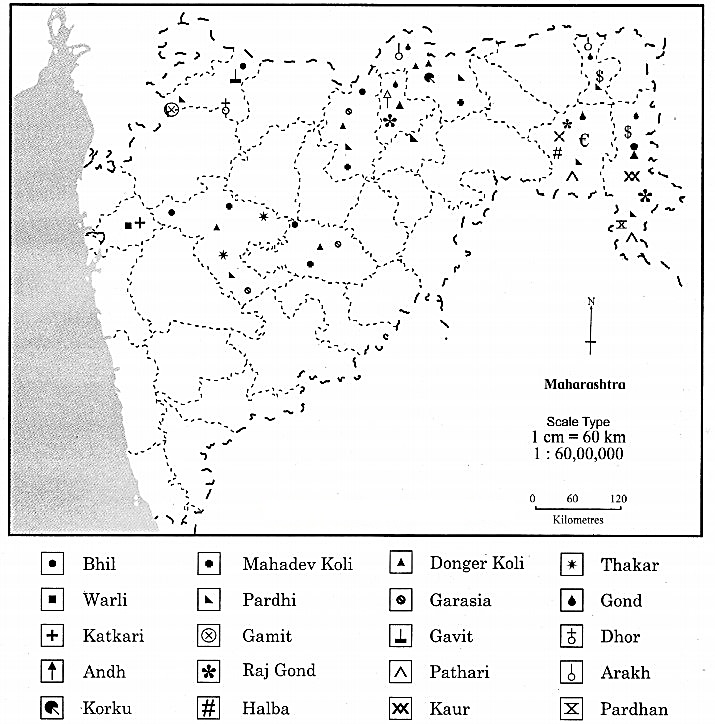
Question 3.
Obtain information regarding the tribes inhabiting this biome. Find out about their habitat, lifestyle, conventional ways of living with nature, cultural heritage, etc. (Textbook Page No. 89)
Answer:
This Biome is the Savannah Grassland biome. The Masai is a Nilotic ethnic group.
- Habitat : Northern, Central and Southern Kenya and Northern Tanzania, near the game parks of the African Great Lakes.
- Lifestyle : Traditionally semi-nomadic lifestyle. They speak ‘Maa’ language. The religions followed are Maasai, Christianity, Islam. They are famous for their fearsome reputation as warriors and cattle-rustlers.
- Conventional ways of living with nature : They are basically cattle-rearers, depending on the Savannah grassland for grazing of cattle.
- Cultural Heritage : It is strongly patriarchal in nature. Masai worship a single deity called ‘Enkai’ or ‘Engai’. They are known for their intricate jewellery for decades.
Question 4.
Find out the names of countries who produce and export wheat and maize. (Textbook Page No. 92)
Answer:
The countries which produce and export wheat are Canada, USA, European union, Russian federation. The countries which produce and export maize are USA, Argentina, Brazil, Russian federation, and Ukraine.