Chapter 20 In the World of Stars
Textbook Questions and Answers
1. Write the proper words in the blanks:
(meridian, horizon, twelve, nine, apparent, celestial, ecliptic)
Question a.
When seen from a great distance, the sky seems to be touching the ground along a circle. This circle is called the …………… .
Answer:
horizon
Question b.
The ………….. is used while defining the zodiac sign.
Answer:
meridian
Question c.
Classified according to seasons, one season will have ………… nakshatras.
Answer:
nine
Question d.
The rising of the sun in the east and its setting in the west is the ………. motion of the sun.
Answer:
apparent
2. A star rises at 8 pm. tonight. At what time will it rise after a month? Why?
Question a.
A star rises at 8 pm. tonight. At what time will it rise after a month? Why?
Answer:
- Str s rise and set 4 minutes earlier every day. If star rises at 8 pm tonight, it will rise at 7:56 pm tomorrow.
- It will rise at 5:24 pm after a month.
- The sun and the moon are seen to move from the west to the east against the background of stars.
- The sun moves through one degree every day and the moon through 12 to 13 degrees.
- This happens due to the motion of the earth around the sun and the moon around the earth which affects the duration of the stars and shortens its time period.
3. What is meant by “The sun enters a nakshatra?” It is said that in the rainy season the sun enters the mrug nakshatra. What does it mean?
Question a.
What is meant by “The sun enters a nakshatra?” It is said that in the rainy season the sun enters the mrug nakshatra. What does it mean?
Answer:
- When we look at the sun we see not only the sun but also constellation behind the sun.
- The constellation cannot be seen in bright sunlight but it is indeed present behind the sun.
- As the earth changes its position, a different constellation or zodiac sign or raashi appears behind the sun.
- This is what we express when we say that the sun enters a particular zodiac sign or raashi.
- In rainy season due to the perceived motion of the sun, it enters mrug nakshatra and that is how it is expressed.
4. Answer the following questions.
Question a.
What is a constellation?
Answer:
A group of stars occupying a small portion of the celestial sphere is called a constellation.
Question b.
What points should be considered before a skywatch?
Answer:
- The place for sky watching should be away from the city and as far as possible it should be new moon night.
- Binoculars or telescopes should be used for skywatch.
- Identifying the pole star in the north makes the skywatch easier. Hence the pole star should be used as a reference point for skywatch.
- As the stars in the west set early, sky watching should begin with stars in the west.
- (a) On a sky map, the north and south are towards the bottom and top of the map respectively, (b) This is because the sky map is to be held overhead in such a way that the direction we face is at the bottom side.
Question c.
It is wrong to say that the planets, stars and nakshatras affect human life. Why?
Answer:
- Science has proved that the constituents of the solar system e.g. planets, satellites and comets as also distant stars and constellations do not have any influence on human life.
- Man has stepped on the moon and will conquer Mars in the 21st century.
- Hence, in this age of science, holding on to beliefs which have been proved wrong by numerous scientific tests, is an unnecessary waste of time and energy.
- It is important to consider all these issues with a scientific frame of mind.
5. Write a paragraph on the birth and life cycle of stars using following figure.
Question a.
Write a paragraph on the birth and life cycle of stars using following figure.
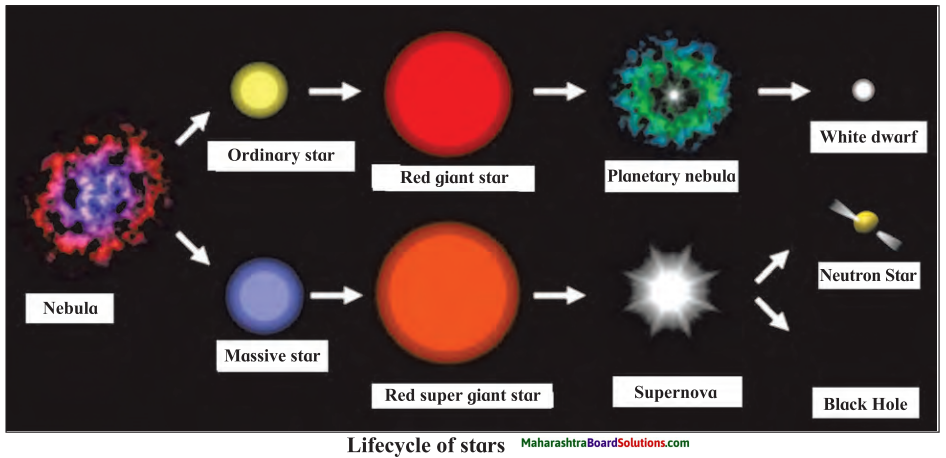
Stars are born out of nebulae. Nebulae are clouds made up mainly of hydrogen gas and dust particles which are attracted towards one another by the force of gravity, (i) As a result of pressure, the internal temperature increases and the cloud becomes dense and spherical in shape, (ii) From the diagram, life cycle of two stars can be explained.
(a) Ordinary star: (i) The ordinary star forms a Red giant star at the later stage of its evolution when it runs out of hydrogen gas at its core. (ii) At the end stage of its life it forms a white dwarf. Stars like the sun become white dwarf when its nuclear fuel is totally exhausted. (iii) It is 1% in diameter of its original size.
(b) Massive Star: (i) Massive star forms Red super giant star at the end of its life cycle, (ii) They are also called super red giants with a relatively cool outer surface, (iii) Supernova is the explosive death of the star of the end of its life with the brightness of 100 million stars in a short amount of time, (iv) A neutron star is the dense core of the supernova. (v) It is the smallest and the densest star known to exist with a 10 km radius, (vi) Neutron stars sometimes end as a black hole, (vii) Black holes are not seen from telescopes and are identified by their intense gravitational pull where even light cannot escape.
Project:
Question a.
Visit a planetarium, collect information and present it in your school on Science day.
Important Questions and Answers
Fill in the blanks:
Question 1.
The different group of stars is known as ………….. .
Answer:
constellation
Question 2.
The pole star is ………….. .
Answer:
North star
Question 3.
The moon moves around the earth in about ………….. days.
Answer:
27 days
Question 4.
The celestial objects are ………….. .
Answer:
The stars
Question 5.
The star that lies close to the aris of rotation of the earth ………….. .
Answer:
Pole star
Question 6.
The definite elliptical path in which a planet revolves around the sun is called ………….. .
Answer:
Orbit
Question 7.
Our earth as well as the sun belongs to the galaxy which has a spiral shape called ………….. .
Answer:
milky way
Question 8.
………….. is made up of five bright stars which are distributed along the figure of the letter M.
Answer:
Sharmishtha
Question 9.
The pole star has ……………. on one-side and ……………… on the other.
Answer:
Saptarashi, Sharmishtha
Question 10.
The continuous empty space between the planets and stars in the sky is called ………….. .
Answer:
space
Name the following:
Question 1.
The brightest star in the nakshatra.
Answer:
Yogatara
Question 2.
The stars forming a group that has a recognizable shape.
Answer:
Constellation
Question 3.
Millions of stars and planets present in the sky forming a group.
Answer:
Milky way
Question 4.
The clouds from which stars are bom.
Answer:
Nebulae
Question 5.
Saptarshi constellation in English.
Answer:
Great Bear
Question 6.
The festival celebrated when sun enters Makar raashi.
Answer:
Makara Sankranti
Question 7.
The brightest star in the Orion constellation.
Answer:
Sirius
State whether the following statements are True or False. Correct the false statements:
Question 1.
The hydrogen gas and dust particles in a nebulae are attracted towards each other by gravity.
Answer:
True
Question 2.
While standing on the ground, the celestial sphere exactly below our feet is called the Zenith.
Answer:
False. The point on the celestial sphere exactly above our head is called the Zenith
Question 3.
The circle describing the apparent motion of the earth around the sun is called the ecliptic.
Answer:
False. Ecliptic is the apparent motion of sun around the earth
Question 4.
Vrushchik or Scorpio is a constellation with 10 to 12 stars.
Answer:
True
Question 5.
Makar raashi is also known as Capricorn zodiac sign.
Answer:
True
Match the following:
Question a.
Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
1. Saptarshi | a. Divided into 88 constellations |
2. Mmg nakshatra. | b. In the north direction. |
3. Orion | c. Group of 7 bright stars (kite) |
4. Vrushchik | d. Made up of 5 bright stars (M) |
5. Pole star | e. 7 – 8 stars. |
6. Celestial sphere | f. Group of 10 -12 stars |
Answer:
Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
1. Saptarshi | c. Group of 7 bright stars (kite) |
2. Mmg nakshatra. | d. Made up of 5 bright stars (M) |
3. Orion | e. 7 – 8 stars. |
4. Vrushchik | a. Divided into 88 constellations |
5. Pole star | b. In the north direction. |
6. Celestial sphere | f. Group of 10 -12 stars |
Answer in one line:
Question 1.
In which direction stars move in the sky except polar star?
Answer:
When seen from earth, stars appear to move from east to west.
Question 2.
What activity does IUCAA carry out?
Answer:
IUCAA which is present in PUNE carries out fundamental research in astronomy.
Question 3.
Define constellation.
Answer: A group of stars occupying a small portion of the celestial sphere is called constellation.
Question 4.
What is Nakshatra?
Answer:
The moon completes one revolution around the earth in approximately 27 days. The portion celestial sphere traversed by the moon in one day is called a nakshatra.
Question 5.
What is yogatara?
Answer:
A nakshatra is known from the brightest star that it contains. The brightest star is called the yogatara.
Define the following:
Question 1.
Horizon
Answer:
Far away the sky seems to be touching the ground. The line at which they meet is caled horizon.
Question 2.
Zenith
Answer:
While standing on the ground the point on the celestial sphere exactly above our head is called the Zenith.
Question 3.
Nadir
Answer:
While standing on the ground the point on the celestial sphere exactly below our feet is called the nadir.
Question 4.
Meridian
Answer:
The great circle which passes through both the celestial poles and the observer’s zenith and nadir is called a meridian.
Question 5.
Celestial equator
Answer:
If we uniformly expand earth’s equator in all directions indefinitely, it will penetrate the celestial sphere along a circle. This circle is known as the celestial equator.
Question 6.
Ecliptic
Answer:
The earth moves around the sun, but seen from the earth, the sun appears to move along a circle on the celestial sphere. This circle describing the apparent motion of the sun around the ‘ earth is called the ecliptic.
Question 7.
Zodiac sign
Answer:
The ecliptic has been imagined to divided into 12 equal parts. Each part subtends 30 degrees at the centre of the celestial sphere. Each of these part is called a raashi or zodiac sign.
Question 8.
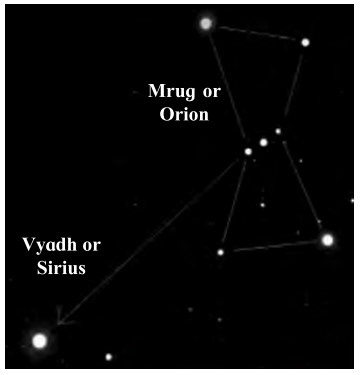
Mrug Nakshatra or Orion
Answer:
It has 7 – 8 starts of which four are at the comers of quadrangle. The line passing through the three middle stars of the constellation when extended meets a very bright star. This is Vyadh or Sirius.
Find out.
Answer the following questions
Question 1.
Using a Marathi calendar collect information about 27 nakshatras, and divide them into the following 3 categories.
(i) Monsoon Nakshatra (ii) Winter Nakshatra (iii) Summer Nakshatra
Answer:
27 nakshtras: Ashwini, Bharani, Krittika, Rohini, Mrigashirasha, Ardra, Punarvasu, Pushya, Ashlesha, Magha, PurvaPhalguni, Uttara Phalguni, Hasta, Chitra, Swati, Vishakha, Anuradha, Jyeshtha, Mula, Purva Ashadha, Uttara Ashadha, Abhijit, Shravana, Dhanishtha, Shatabhishta, Purva Bhadrapada, Uttara Bhadrapada, Revati
Monsoon Season | Winter Season | Summer Season |
Ashwini Karthe | Krittika | Visakha |
Bharani Karthe | Rohini | Anuradha |
Arudra Karthe | Mrigashirsha | Jyeshtha |
Pushyani | Ardra | Mula |
Aslesha | Punarvasu | Purva Ashadha |
Magha | Uttara Ashadha | |
Purva Phalguni | Shravana | |
Uttara Phalguni | ||
Chitra | ||
Hasta |
Question 2.
Write the difference between constellations Saptarshi and Mrug nakshatra
Answer:
Saptarshi | Mrug nakshatra |
1. It is made up of five bright stars which are distributed along the figure of the letter M. | 1. It is made up of seven-eight stars of which four are at the corners of a quadrangle. |
2. Pole star is the brightest star in the constellation. | 2. Sirius is the brigh jveutr0n Starie constellation. |
3. It is on the meridian in the month of April and in the month of October. | 3. It is on the meridian in the month of February and in June. |
4. In English, it is called the Great Bear. | 4. In English, it is called Orion. |
Question 3.
Draw sketches to show the relative position of prominent stars in Ursa major and Orion.
Answer:
a. Ursa major (Saptarshi) appears like a big dipper, (or kite shape). There are 3 bright stars in the handle and 4 stars in the bowl of the dipper. (It can be seen during April in summer in northern skies).
(b) Orion appears like a hunter. Three bright stars appear in the belt, 5 bright stars are arranged in the form of a quadrilateral. (It is visible during winter in the northern skies)
Question 4.
Why is the pole star important for sky watch?
Answer:
- Identifying the Pole Star in the north makes the sky watch easier. Hence the pole star should be used as a reference point for skywatch.
-
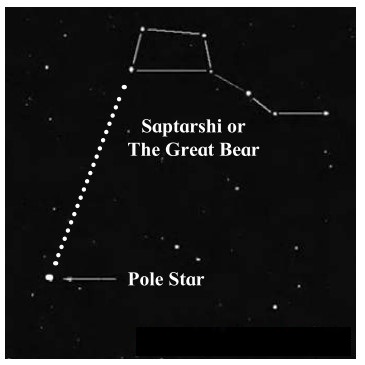
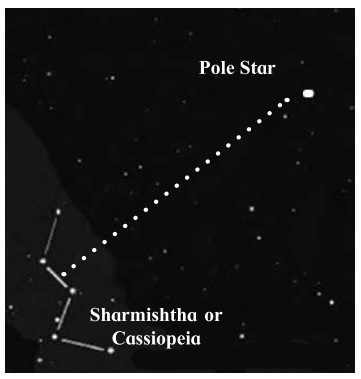
If we extend one side of the quadrangle of Saptarshi, it reaches the Pole Star.
The pole star has Saptarshi on one side and Sharmishtha on the other.
Question 5.
What is the relation between the pole star and the constellations Saptarshi and Sharmishtha?
Answer:
- Saptarshi is in the shape of a quandrangle with a tail made up 3 stars resembling a kite. If we extend one side of the quadrangle it reaches the Pole Star.
- The constellations of Saptarshi and Sharmishtha are useful in locating the Pole Star.
- The perpendicular bisector of the line joining the third and fourth stars in Sharmishtha goes towards the Pole star.
- The Pole Star has Saptarshi on one side and Sharmishtha on the other.
Use your brain power!
Answer the following questions.
Question 1.
One Zodiac Sign = ………….. nakshatras
Answer:
27 nakshatras. Each nakshatra is divided in padas or charan. Every nakshatra has 4 padas. These 27 nakshatra complete the entire circle of 360° of zodiac.
The zodiac comprises of 360°.
Question 2.
Is sun the only star present in our Milky Way galaxy?
Answer:
No. Sun is not the only star present in the Milky Way. There are lakhs of stars in the Milky Way, some of them being many times bigger than our sun. Some of them have their own planetary systems with a great diversity in colour, brightness, as well as size.