Chapter 3 Human Settlements and Land Use
1. Identify the correct correlation.
A : Assertion R : Reasoning
Question 1.
A – Settlements can be of various types.
R – Various physical factors affect the growth of settlements.
(a) Only A is correct.
(b) Only R is correct.
(c) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
(d) Both A and R are correct but R is not the correct explanation of A.
Answer:
(d) Both A and R are correct but R is not the correct explanation of A.
Question 2.
A – When cities grow, their functions also grow.
R – Cities can have only one function.
(a) Only A is correct.
(b) Only R is correct.
(c) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
(d) Both A and R are correct but R is not the correct explanation of A.
Answer:
(a) Only A is correct.
2. Give geographical reasons.
Question 1.
Not all rural settlements change into urban settlements.
Answer:
- The area between rural and urban is called rural-urban fringe.
- Villages are beyond the rural-urban fringe and cities have different land use pattern.
- In villages, land is mainly used for agriculture and related activities such as permanent pasture, grazing land, miscellaneous tree crops and groves, fallow land etc.
- In city areas land is mainly used for industries, residential purpose, recreation, transportation etc.
- Since the villages are far away from the city, they maintain their distinct identity and do not change into urban settlement.
Question 2.
In rural settlements, land use is related to agriculture.
Answer:
- Generally, the land in rural areas is used for agriculture and related activities.
- The classification of the land use in rural areas is done according to the Land Records Department.
- As per Land Records Department, the land in rural areas is mainly used for activities related to agriculture, such as some land is under permanent pastures and grazing lands or some under tree crops or culturable waste-land or fallow land etc.
- Thus, all the above types of land use around the rural settlements are related to mainly agriculture.
Question 3.
Rural-urban fringe have the characteristics of both urban and rural settlements.
Answer:
- The area between urban and rural areas is called rural-urban fringe.
- It has the characteristics of both urban as well as rural areas, since it is a transition zone between the two.
- Thus, in rural-urban fringe there is a mixture of urban-rural land use.
- In some rural areas apart from the land use for agriculture, some agricultural land has been converted into residential and industrial uses.
- The villages in rural fringe are partly affected by urbanization.
- Thus, rural-urban fringe has the characteristics of both urban and rural settlements.
Question 4.
Growth of urban areas is linked to land use.
Answer:
- Land use in urban areas is different from land use in rural areas.
- In rural areas the land use is closely related to agricultural activities like cultivation of different crops, plantation of trees, permanent pastures, grazing land, cultivation of tree crops, fallow land etc.
- On the other hand, land use in urban areas is varied and closely related to housing and economic activities.
- As the population of the urban area increases, more and more non-agricultural activities develop in urban areas.
- Growth of urban areas depends upon area under construction, industries, different types of institutions such as school, college, insurance companies, bank etc.
- Recreational activities, transportation are the other urban land uses.
- Thus, growth of urban areas is linked with land use.
3. Write short notes on.
Question 1.
Interrelationship between urban and rural settlement.
Answer:
- Settlements can be divided into urban and rural on the basis of their functions.
- Rural settlements are smaller than urban settlements.
- In rural areas agriculture and allied agricultural activities like livestock rearing, fishing, lumbering etc., are developed.
- In urban areas, industries, construction and economic activities like trade, transport and communication, banking and insurance are the important activities.
- The development industries need various raw material and services which are supplied by rural areas.
- For example, cotton grown in rural areas is supplied to cotton textile industries in urban areas. Everyday many rural people commute to urban areas to work in different activities.
- Thus, there is good interrelationship between urban and rural areas since they depend on each other.
Question 2.
Problems of urban settlements.
Answer:
- Most of the urban areas have very large size of population and density of population is also very high.
- When cities increase in size, many changes occur. These changes are related to land use and structure of the city.
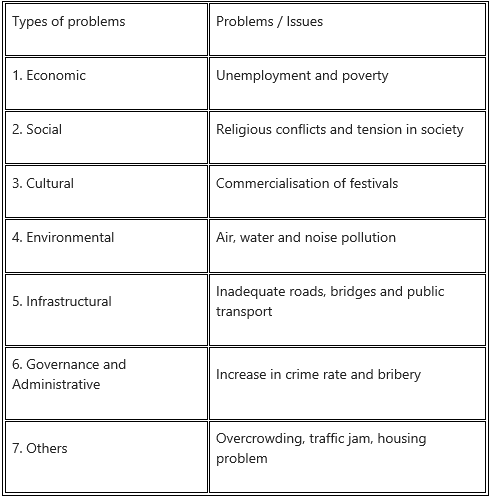
- The large size of population and high density create number of socio-economic, cultural, infrastructural, administrative and environmental problems.
- The air, water and noise pollution, development of slums, traffic jam, overcrowding in trains and buses, waste disposal etc., are some of the serious problems in most of the urban settlements.
Question 3.
Suburbs
Answer:
- In the outer part of the urban areas there are small towns or small cities, they are known as suburbs.
- When big cities become overcrowded and overpopulated, the further development starts outside city area and thus suburbs develop.
- For example, Dombivali, Kalyan, Ambarnath etc., are the suburbs of Mumbai.
- Suburbs generally consists of residential housing and shops of low order, which act as central place for the local community.
- Often, suburbs are the most recent growth of an urban area and their end marks the urban fringe.
- With increase in population there is growth of suburb, the growth of suburbs may result in urban sprawl.
Question 4.
Mixed land use.
Answer:
- Mixed land use is observed in some of the urban areas.
- It is an area where different types of land use exist together.
- In some cities residential, industrial, commercial, administrative functions are found in an integrated manner.
- In many cities in developing countries one can find schools, clinics, houses, business shops at one place itself.
- Generally mixed land use is found in cities which are growing very fast, because land in the city is not sufficient to reserve certain areas for certain land use, therefore there is mixed land use.
4. Answer the following questions in detail.
Question 1.
Explain the characteristics of rural settlement.
Answer:
- On the basis of functions, settlements can be divided into two types – rural and urban.
- Agriculture and allied agricultural activities like fishing, livestock rearing, lumbering etc., are most economic activities in rural areas.
- The classification of land use in rural areas is done according to Land Records Department.
- As per Land Records Department the land in rural areas is mainly used for activities related to agriculture, such as some land is under agriculture, some under permanent pastures and grazing lands or some under tree crops or culturable waste-land or fallow land etc.
- Most of rural settlements are semi-clustered or fragmented and small in size.
- Primary activities like agriculture, lumbering, fishing, livestock rearing is more developed in rural settlements.
- In rural areas, sometimes agricultural areas are converted into residential or industrial areas.
- Many people in rural areas daily commute to city areas for work, thus rural and urban areas are connected with each other.
- There is an area between rural and urban area which is called rural-urban fringe, rural settlements are beyond the rural-urban fringe.
Question 2.
What factors are responsible for development of various patterns in settlement? Give examples.
Answer:
1. Patterns of settlements are affected by various physical factors like relief, soils, climate, availability of water supply etc.
2. Physical factors influence the type and spacing of settlements, which results into various patterns of settlements.
3. Type of soil and quality of soil are two important factors which affect rural settlements.
4. Fertile plains and valleys have thick, rich and fertile alluvial soil, which supports agriculture, so nucleated settlements develop in these areas. For example, most of the villages in Ganga plains have nucleated settlements.
5. Settlements develop as per the relief of that area. For example, Foothill settlements develop at the foot of mountain, hilltop settlements develop at the top of the hill. For example, hilltop settlement at Shimla or Manali.
6. In the areas of mountainous or hilly relief, due to inaccessibility, there are dispersed or isolated settlements. For example, dispersed or isolated settlements in Himalaya mountains.
7. Sometimes settlements develop along the coastline, canal, river, road, or railway line. They are in straight line; they are called linear settlements. For example, settlements along Konkan coastline and settlements along Mumbai-Pune road.
8. Climate also affects development of settlements. Areas of extreme climate are avoided by people. Therefore, such areas have dispersed settlements.
9. For example, due to extreme hot climate there are dispersed settlements in Rajasthan and due to extreme cold climate, there are isolated settlements in the polar regions.
10. Water is essential for human development. Therefore, many settlements develop around lakes or natural tanks, they are circular settlements.
11. Sometimes settlements develop at the confluence of two rivers, the settlements grow in all three sides, they are triangular settlements. For example, Karad town is on the confluence of Krishna and Koyna river.
12. Sometimes settlements grow around the mines, or any central object. This centre point provides source of livelihood to the people. Thus, radial pattern of settlement develops. For example, radial settlements around coal mines in the State of Bihar.
5. Differentiate between.
Question 1.
Land Use and Land Cover
Answer:
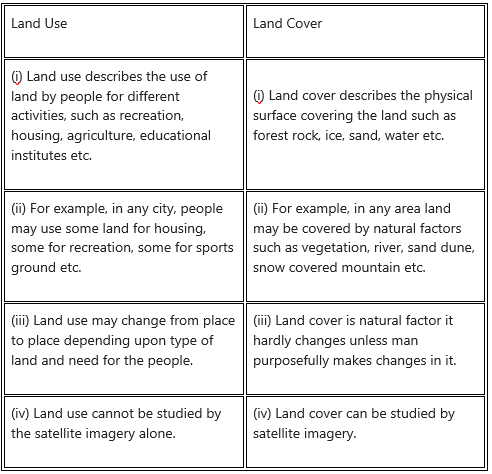
Question 2.
Barren and Non-agricultural Land
Answer:
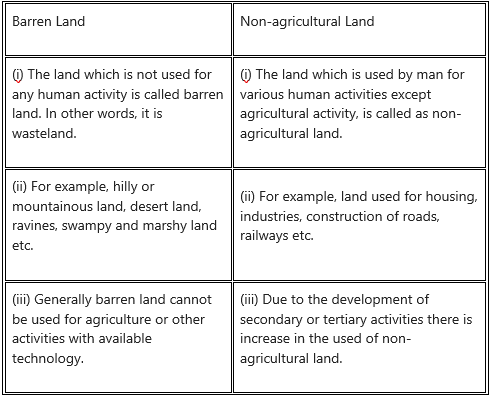
Question 3.
Radial pattern and Circular Pattern
Answer:
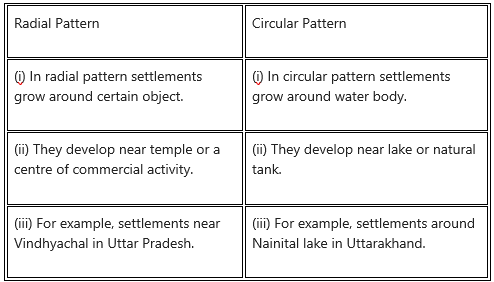
Question 4.
Nucleated and Dispersed Settlement
Answer:

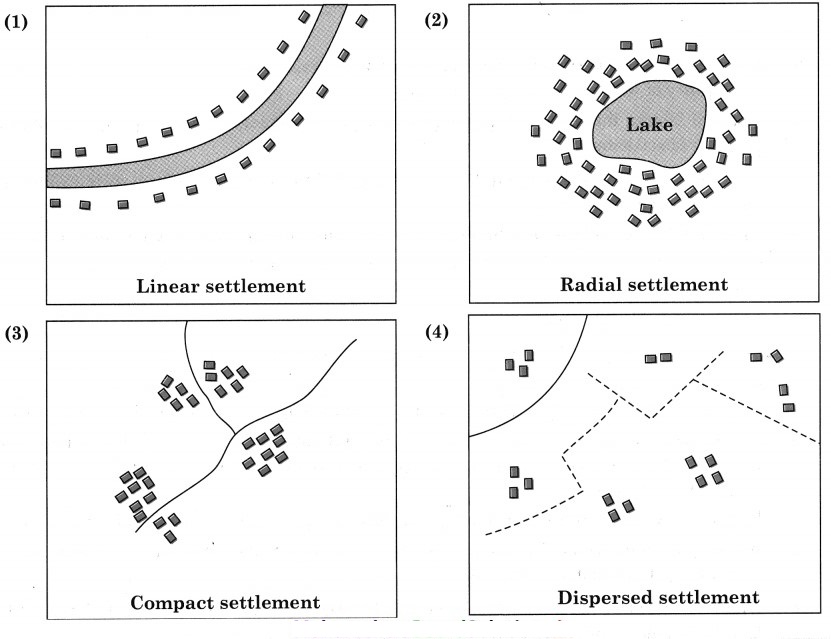
6. Draw a neat and labelled diagram
(1) Linear settlement
(2) Radial settlement
(3) Compact settlement
(4) Dispersed settlement
Answer:
7. Write a note in your own words about how land used in Lonar city has evolved. Refer the map on textbook page no. 30.
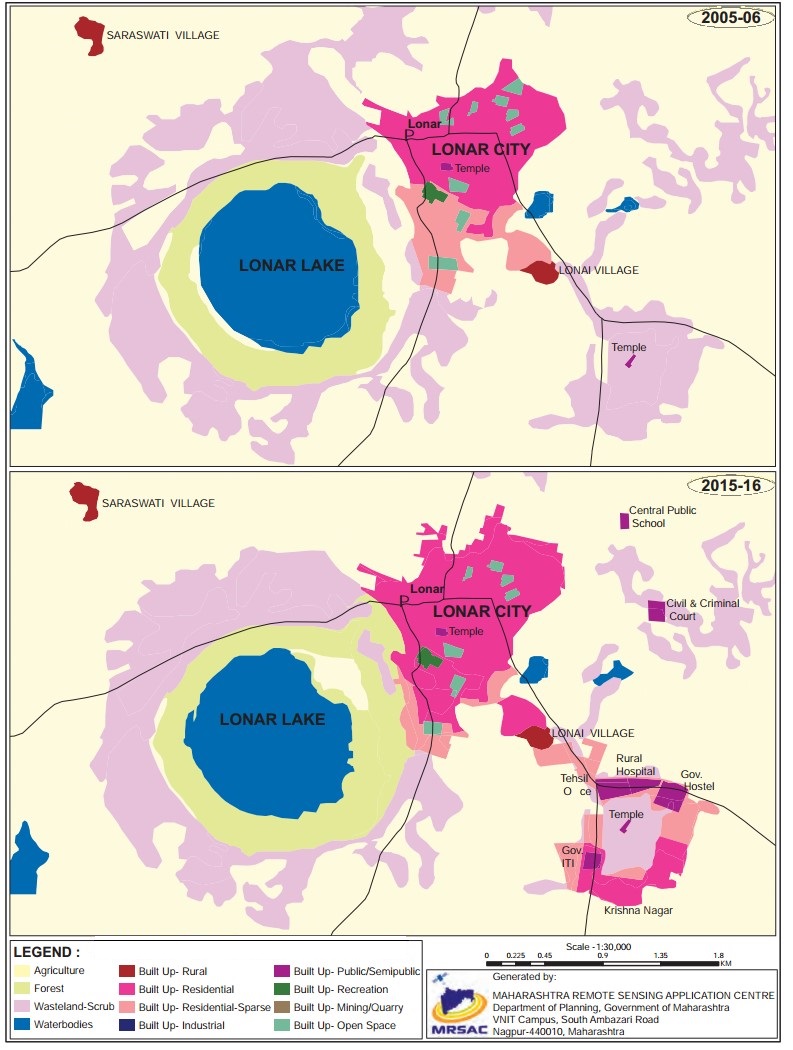
Answer:
- Two maps of Lonar city are given. One map is of the year 2005-06 and another is of 2015-16.
- These two maps show the changes in land use that have taken place in the span of 10 years.
- The following changes have been registered.
- There is no change in the size of Lonar lake.
- The area occupied by Lonar city has increased substantially.
- Forest area around the lake has increased.
- An area under waste land/ scrubs have increased.
- Around the temple in the southeast, on the waste scrub land a new rural hospital, government hostel, government ITI, Tahsil office etc., has been developed. This newly developed area has been named as Krishna Nagar, which is not in 2005-06 map.
- To the north-east of the Lonar city two more building have been constructed. One is central public school and another is civil and criminal court.
- To the south of the temple in the heart of Lonar city built up residential area is spreading over built up residential sparse.
- Overall built up residential sparse is increasing in all directions around Lonar lake and south-eat of the Lonar city and thus there is encroachment over agricultural land.
8. Read the given passage and answer the following questions.
Different types of human settlements include hamlets, villages, small towns, large towns, isolated places, cities and conurbations. In some systems, types of human settlements are broken up into urban, suburban and rural; for example, the U.S. Census Bureau divides settlements into urban or rural categories based on precise definitions. Small settlements, such as hamlets and villages, have low populations and restricted access to services, larger types of settlements, such as cities, have higher populations, higher densities and greater access to services.
For example, a village may have only one or two general stores, while a large metropolis may have many specialized stores and chain stores. These differences are known as low-order service settlements and high-order service settlements. Larger settlements also have a sphere of influence affecting surrounding settlements. Settlements may also be divided by the site chosen, such as sites selected based on resources, trading points, defensive sites, shelter and relationship to water resources. The functions of human settlements also differ, as settlements may be established as ports, market towns and resorts. Types of rural settlements may also be classified by function, such as proximity to farming, fishing and mining. Settlements that focus on one economic activity are called single functional settlements. Human settlements may be permanent or temporary. For example, a refugee camp is a temporary settlement, while a city is a permanent settlement.
Question 1.
Which human settlements are mentioned in the passage above?
Answer:
Hamlets, villages, small towns, large towns, isolated places, cities and conurbations are the types of settlements mentioned in the passage.
Question 2.
On what basis are urban and rural areas classified?
Answer:
Settlement are classified on the basis of the size of population, density, access to higher order and lower order services, site chosen, functions, permanent or temporary etc.
Question 3.
What are the functions carried out in rural settlement?
Answer:
Functions carried out in rural settlements are farming, fishing, mining, one or two general stores, etc.
Question 4.
Explain the difference between low-order services and higher order service settlements.
Answer:
-
The hamlets and villages have low population and restricted access to lower order services.
For example, a village may have only one or two general stores. They are called low order settlements. - Large metropolitan cities have higher population, higher density and greater services of higher order.
- For example, large metropolitans may have chain stores, malls, departmental stores, super markets etc. They are called higher order settlements.
Questions and Answers
Try These
Question 1.
Observe Fig 3.2 A to F (Textbook Page No. 22-23). They show various patterns of settlements. Try to understand the difference between them. Carefully read their characteristics in the second column. According to the applicable characteristics, write alphabet of the image settlement in the place provided below characteristics.
Answer:

Question 2.
Can you identify problems faced by your city/town/village in terms of any of the following? (Textbook Page No. 27)
Answer:
Make friends with maps!
Question 1.
See map of Ichalkaranji city (Textbook Page No. 28) and observe how changes have occurred in the city over the years. Answer the questions that follow.
(i) Enlist the colours used for showing land uses in the index.
(ii) What do the blue and black lines show?
(iii) What is the name of the river in the map?
(iv) Name any two villages shown on the map.
(v) Which city is shown on the map?
(vi) Which periods do the map belongs to?
(vii) Which land covers have reduced? What are their colours?
(viii)Which landcovers seen to have increased? what are their colours?
(ix) Which land cover has been replaced by increased landcovers?
(x) Write a conclusive note comparing both the maps.
Answer:
(i)
- Yellow for agriculture
- Green for forest
- Pink for residential land use
- Dark blue for industrial land use
- Dark green for recreation
- Brown for mining/ quarry
- Violet for public/semi public
(ii) Blue lines show rivers and black lines show roads.
(iii) Panchaganaga river
(iv) Jambhali and Haroli villages
(v) Ichalkaranji
(vi) 2007 and 2017
(vii) Open space-dark green colour, forest – light green colour, wasteland – light violet colour residential sparse – light orange
(viii) Following landcovers have increased landcover for residential area – colour pink, Landcover for industrial area colour dark blue
(ix) Following land cover have been replaced by increased landcovers. Residential sparse areas are replaced by residential built up land use, open space is replaced by residential built up area and wastelands are replaced by industries.
(x) Map A shows land use and land cover map of Ichalkaranji city in the year 2007.
- Map B shows land use and land cover map of Ichalkaranji city in the year 2017.
- Both the maps show that there is land use for agriculture, industries, transportation, residential purpose, recreational purpose, mining around the city, village settlements etc.
- In both the maps there is land is covered by Forest, waterbodies, wasteland/ scrubs, Panchaganaga river etc.
- The landcover in 2017 as compared to landcover in 2007 have been reduced for forest, residential sparse, open space and wasteland.
- The landcover in 2017 as compared to landcover in 2007 have been increased for industries and built up residential areas.
- Residential sparse areas are replaced by residential built up land use, open space is replaced by residential built up area and wasteland are replaced by industries.
Can you tell? (Textbook Page No. 27)
You know what is urban and what is rural. What will you call the area that lies between them?
Answer:
- The area between urban and rural areas is called rural-urban fringe.
- It is characterised by the urban as well as rural characteristics, since it is transition zone between the two.
- Thus, in rural-urban fringe there is a mixture of urban-rural land use.
- In some rural areas apart from the land use for agriculture, some agricultural land has been converted into residential and industrial uses.
- Thus, villages in rural fringe are partly affected by urbanization.
- Thus rural-urban and fringe have the characteristics of both urban and rural settlements.
Find out (Textbook Page No. 27)
Compare the cover page of Std. XII text book with Std. XI geography text book. Discuss and write a short paragraph about changes in land use / land cover in your own words.
Answer:
Geography Cover Page (Textbook of standard XI)
- Depicts the natural landscape.
- There are two snow covered mountains peaks and rivers having their source in these mountains.
- At the foot of the mountain there is fan shape deposit of silt.
- The river has developed number of meanders and an ox-bow lake.
- The slope of the mountains is covered with coniferous forest and on the lower ground at the foot of the mountain there is mixed forest.
- There is a sandy beach. Along the beach there are coconut trees.
Geography Cover Page (Textbook of standard XII)
- Depicts cultural/man made development super imposed on natural landscape.
- A quarry is developed at the foot of mountain.
- There is deforestation and development of two villages and a town on the right bank of the river.
- On this bank of river there is development of industry as well.
- Number of multi-story building have come up on the left bank of the river including a mall and hospital.
- Power line, concrete road and railway have developed in the last 10 years.
- On the beach hotels, rest houses, sport activities have been developed for tourists and therefore number of tourists are seen on the beach.
- The natural landscape on cover of the textbook of Std. XI changes into cultural landscape on the cover page of geography textbook of Std. XII.
Let’s recall (Textbook Page No. 24)
Can you differentiate between urban and rural settlements?
Answer:
- On the basis of functions, settlements are divided into two types – rural settlement and urban settlement.
- There is difference in land use in rural and urban settlements.
- In rural areas the land use is closely related to agricultural activities like cultivation of different crops, plantation of trees, permanent pastures, grazing land, cultivation of tree crops, fallow land etc.
- Where as in urban areas land use is for industries, construction and economic activities like trade, transport and communication, banking and insurance etc.
- Urban settlements are large and compact, since population is more compared to available land.
- Rural settlements are small and dispersed, since population is less compared to available land.
Think about it (Textbook Page No. 24)
Can a town have only one function? Why do the cities become multi-functional?
Answer:
1. Towns do not have only one function.
2. Some towns have one important and major function. They are known by that function. But they have many other functions also. For example, Shirdi in Maharashtra is known for religious function but it has other functions like tourism, education, commercial etc.
3. Cities become multifunctional as they grow. With increase in population demand for various functions increases. As cities grow in size many changes occur and therefore land use also changes.
4. For example, when any city develops as industrial centre, its main function is industries. But as people start coming to that city for employment opportunities, the city grows. Then other functions like educational institutes, business centres, recreational centres, etc., functions develop to fulfil the needs of increasing population. Thus, cities become multi-functional.
Question 1.
Observe Fig. (Textbook Page No. 21) and answer the following questions.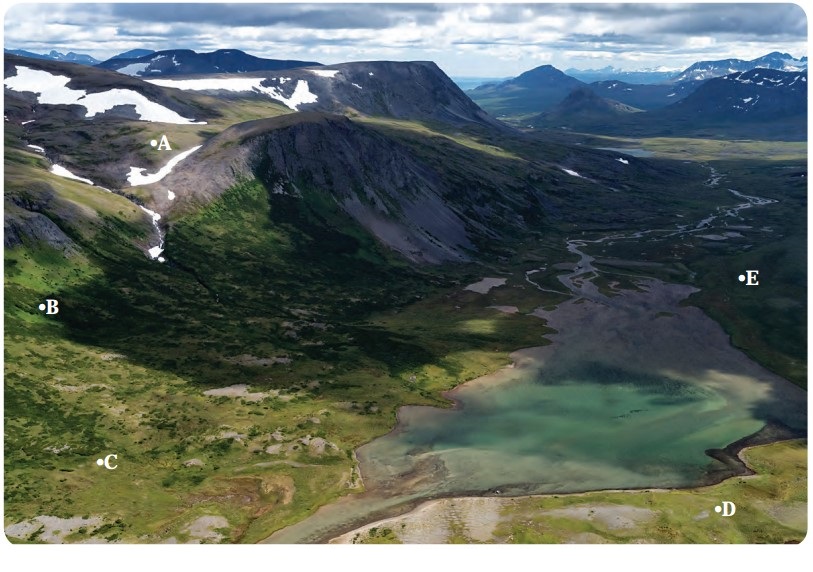
(i) Where are humans’ settlements likely to develop: A, B, C, D or E? Why?
(ii) In the above figure in which place human settlement is not likely to develop? Why?
(iii) Looking at the figure above, what factor do you think could contribute to the development of human settlements?
(iv) Can economic factors be important along with physical factors for the development of human settlements?
(v) Do physical factors affect the economic activity of human settlements?
(vi) Make a list of factors which affect development of settlements in an area.
Answer:
(i) Human settlement is likely to develop at C and D.
The most important factor responsible for the development of settlement is river. Hence, agriculture seems to be the most important activity and development of agriculture needs fertile soil and water supply which is readily available here.
(ii) Human settlement is not likely to develop at A and B. This is because of steep slope and rugged terrain.
(iii) The most important factors that could contribute to the development of human settlements are availability of water from the river and fertile soil on the bank of river.
(iv) Yes, economic factors are equally important along with physical factors for the development of human settlements. For example, industries need development of roads to carry raw material or agriculture also needs development of roads. Many settlements are developed along roads or railway lines.
(v) Yes, physical factors affect the economic activity in the development of human settlement. For example, agriculture is’ an important activity which is affected by relief and water supply. It can be developed where fertile soil and sufficient water supply is available.
(vi) The factors which affect development of settlements are relief, terrain, climate, soil, water supply, altitude, drainage, minerals etc.
Question 2.
Visit http://censusindia.gov.in/2011-prov-results/paper2/data_files/India2/1.%20Data%20 Highlight.pdf to know how cities are divided into various types in India on the basis of their populations. Also look for examples from Maharashtra. Refer to the website and complete the table as given below : (Textbook Page No. 24)
Answer:


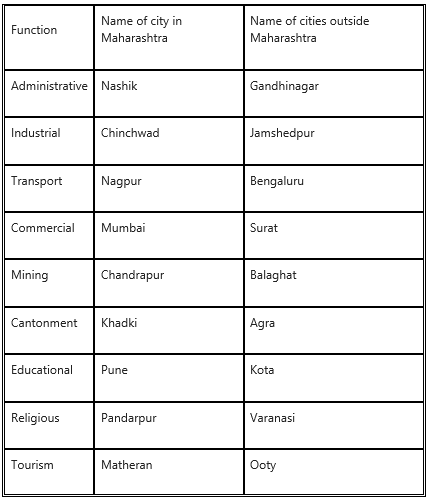
Question 3.
On the basis of dominant or specialised functions, Indian cities and towns can be broadly classified as follows. Complete the following table with examples from Maharashtra and India. (Textbook Page No. 24)
Answer: