Chapter 6 Plant Water Relation
1. Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
In soil, water available for absorption by root is ……………..
(a) gravitational water
(b) capillary water
(c) hygroscopic water
(d) combined water
Answer:
(b) capillary water
Question 2.
The most widely accepted theory for ascent of sap is ……………..
(a) capillarity theory
(b) root pressure theory
(c) diffusion
(d) transpiration pull theory
Answer:
(d) transpiration pull theory
Question 3.
Water movement between the cells is due to ……………..
(a) T.E
(b) W.P
(c) D.P.D.
(d) incipient plasmolysis
Answer:
(c) D.P.D.
Question 4.
In guard cells, when sugar is converted into starch, the stomata pore ……………..
(a) closes almost completely
(b) opens partially
(c) opens fully
(d) remains unchanged
Answer:
(a) closes almost completely
Question 5.
Surface tension is due to ……………..
(a) diffusion
(b) osmosis
(c) gravitational force
(d) cohesion
Answer:
(d) cohesion
Question 6.
Which of the following type of solution has lower level of solutes than the solution?
(a) Isotonic
(b) Hypotonic
(c) Hypertonic
(d) Anisotonic
Answer:
(b) Hypotonie
Question 7.
During rainy season wooden doors warp and become difficult to open or to close because of ……………..
(a) plasmolysis
(b) imbibition
(c) osmosis
(d) diffusion
Answer:
(b) imbibition
Question 8.
Water absorption takes place through ……………..
(a) lateral root
(b) root cap
(c) root hair
(d) primary root
Answer:
(c) root hair
Question 9.
Due to low atmospheric pressure the rate of transpiration will ……………..
(a) increase
(b) decrease rapidly
(c) decrease slowly
(d) remain unaffected
Answer:
(a) increase
Question 10.
Osmosis is a property of ……………..
(a) solute
(b) solvent
(c) solution
(d) membrane
Answer:
(c) solution
2. Very short answer question
Question 1.
What is osmotic pressure?
Answer:
The pressure exerted due to osmosis is osmotic pressure.
Question 2.
Name the condition in which protoplasm of the plant cell shrinks.
Answer:
Plasmolysis
Question 3.
What happens when a pressure greater than the atmospheric pressure is applied to pure water or a solution?
Answer:
When a pressure greater than the atmospheric pressure is applied to pure water or a solution then water potential of pure water or solution increases.
Question 4.
Which type of solution will bring about deplasmolysis ?
Answer:
Placing a plasmolysed cell in hypotonic solution will bring about deplasmolysis.
Question 5.
Which type of plants have negative root pressure?
Answer:
Plants showing excessive transpiration have negative root pressure.
Question 6.
In which conditions transpiration pull will be affected?
Answer:
Due to temperature fluctuations during day and night gas bubbles may be formed which affects transpiration pull.
Question 7.
Mention the shape of guard cells in Cyperus.
Answer:
Kidney shaped and dumbbell shaped guard cells are seen.
Question 8.
Why do diurnal changes occur in osmotic potential of guard cells?
Answer:
Enzyme activity of phosphorylase converts starch into sugar during daytime and sugar is converted to starch during night. This causes changes in osmotic potential of guard cells.
Question 9.
What is symplast pathway?
Answer:
When water is absorbed by root hair it passes across from one living cell to other living cell through the plasmodesmatal connections between them, then it is called symplast pathway across the root.
3. Answer the Following Questions
Question 1.
Describe mechanism of absorption of water.
Answer:
- The absorption of water takes place by two modes, i.e. active absorption and passive absorption.
- Passive absorption is the chief method of absorption (98%).
- There is no expenditure of energy in passive absorption.
- Transpiration pull is a driving force and water moves depending upon concentration gradient. Water is pulled upwards.
- It occurs during daytime when there is active transpiration.
- Active absorption occurs usually during night time as due to closure of stomata transpiration stops.
- Water absorption is against D.ED. gradient, A.T.R energy is required which is available from respiration.
- Active absorption may be osmotic or non- osmotic type.
- For osmotic absorption root pressure has a role.
Question 2.
Discuss theories of water translocation.
Answer:
- Translocation of water is transport of water along with dissolved minerals from roots to aerial parts.
- The movement is against the gravity and described as ascent of sap.
- The translocation occurs through lumen of water conducting tissue xylem mainly vessels and tracheids.
- Different theories have been discussed for translocation mechanism like vital force theory (Root pressure), relay pump, physical force (capillary), etc.
- Cohesion tension theory or transpiration pull theory is most widely accepted theory.
Question 3.
What is transpiration? Describe mechanism of opening and closing of stomata.
Answer:
- The loss of water in the form of vapour is called transpiration.
- Stomatal transpiration is a main type of transpiration where minute pores are concerned with it.
- Stomata are bounded by two guard cells which in turn are surrounded by accessory cells.
- Opening and closing of stomata is controlled by turgidity of guard cells.
- When guard cells become turgid due to endosmosis their lateral thin and elastic wall bulges or stretch out.
- The inner thick and inelastic wall is pulled apart, thus the stoma opens during daytime.
- At night when guard cells become flaccid due to exosmosis the wall relaxes and stoma closes.
- Endosmosis and exosmosis takes place due to changes in osmotic potential of guard cells.
Question 4.
What is transpiration? Explain role of transpiration.
Answer:
Transpiration : The loss of water from plant body in the form of vapour is called transpiration.
Role of transpiration:
- Removal of excess of water
- Helps in passive absorption of water and minerals
- Helps in ascent of sap – transpiration pull
- Maintains turgor of cells
- Imparts cooling effect by reducing temperature 90% – 93% is stomatal transpiration and hence when stomata are open gaseous exchange takes place.
Question 5.
Explain root pressure theory and its limitations.
Answer:
- Root pressure theory is proposed by J. Pristley.
- For translocation of water, activity of living cells of root is responsible.
- Absorption of water by root hair is a constant and continuous process and due to this a hydrostatic pressure is developed in cortical cells.
- Owing to this hydrostatic pressure i.e. root pressure, water is forced into xylem and further conducted upwards.
- Root pressure is an osmotic phenomenon.
Limitation of this theory:
- Not applicable to tall plants above 20 metres.
- Even in absence of root pressure ascent of sap is noticed.
- In actively transpiring plants, root pressure is not developed.
- In taller gymnosperms, root pressure is zero.
- Xylem sap is under tension and shows negative hydrostatic pressure.
Question 6.
Explain capillarity theory of water translocation.
Answer:
- Capillarity theory of water translocation is proposed by Bohem.
- Capillarity is because of surface tension and cohesive forces and adhesive forces of water molecules.
- Xylem vessels and tracheids are tubular elements having their lumen.
- In these elements water column exists due to combined action of cohesive and adhesive forces of water and lignified wall.
- As a result of this capillarity water is raised upwards.
Question 7.
Why is transpiration called ‘a necessary evil’?
Answer:
- The loss of water in the form of water vapour is called transpiration.
- About 90 – 93% of transpiration occurs through stomata, small apertures located in the epidermis of leaves.
- For this process stomata must remain open and then only gaseous exchange by diffusion takes places.
- Gaseous exchange is necessary for respiration and photosynthesis. If stomata remain closed then it will affect productivity of plant.
- The process is necessary evil because water which is important for plant is lost in the process.
-
At the same time it helps in absorption of water and its translocation. Hence it cannot be avoided.
So Curtis has rightly called it as necessary evil.
Question 8.
Explain movement of water in the root.
Answer:
- Root hairs absorb water by imbibition then diffusion which is followed by osmosis.
- As water is taken inside the root hair cell it becomes turgid i.e. increase in turgor pressure (T.E)
- Root hair cell has less D.ED. but adjacent cortical cell has more D.PD.
- The inner cortical cell has more osmotic potential so it will suck water from root hair cell.
- Root hair cell becomes flaccid and ready to absorb soil water.
- Water is passed on similarly in inner cortical cells.
- Water moves rapidly through loose cortical cells up to endodermis and through passage cells in pericycle.
- From pericycle due to hydrostatic pressure developed it is forced into protoxylem.
Question 9.
(i) Osmosis
Answer:
It is a special type of diffusion of solvent through a semipermeable membrane.
(ii) Diffusion
Answer:
It is the movement of ions/ atoms/molecules of a substance from the region of higher concentration to the region of their lower concentration.
(iii) Plasmolysis
Answer:
Exo-osmosis in a living cell when placed in hypertonic solution is called plasmolysis.
(iv) Imbibition
Answer:
It is swelling up of hydrophilic colloids due to adsorption of water.
(v) Guttation
Answer:
The loss of water in the form of liquid is called guttation.
(vi) Transpiration
Answer:
The loss of water from plant body in the form of vapour is called transpiration.
(vii) Ascent of sap
Answer:
The transport of water with dissolved minerals in it from root to other aerial parts of plant against the gravity is called ascent of sap.
(viii) Active absorption
Answer:
Water absorption by activity of root which is against the D.PD. gradient along with expenditure of A.T.E energy generated by respiration is the process of active absorption.
(ix) Diffusion Pressure Deficit (D.P.D.)
Answer:
The difference in the diffusion pressures of pure solvent and the solvent in a solution is called diffusion pressure deficit.
(x) Turgor pressure
Answer:
It is the pressure exerted by turgid cell sap on to the cell membrane and cell wall.
(xi) Water potential
Answer:
Chemical potential of water is called water potential.
(xii) Wall pressure
Answer:
Thick and rigid cell wall exerts a counter pressure to turgor pressure developed on the cell sap is called wall pressure that operates in opposite direction.
(xiii) Root pressure
Answer:
As absorption of water by root hair being a continuous process, a sort of hydrostatic pressure is developed in living cells of root, this is called root pressure.
Question 10.
Osmotic Pressure (O.P) and Turgor Pressure (T.P)
Answer:

Question 11.
How are the minerals absorbed by the plants ?
Answer:
- Soil is the chief source of minerals for the plants.
- Minerals get dissolved in the soil water.
- Minerals are absorbed by the plants in the ionic form mainly through roots.
- Absorption of minerals is independent of water.
- Absorbed minerals are pulled upwards along with xylem sap.
- Mineral ions can be remobilized in the plant body form older parts to young plants E.g. Ions of S, P and N.
4. Long answer questions
Question 1.
Describe structure of root hair.
Answer: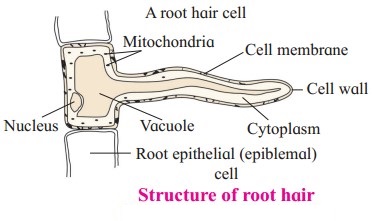
- Water from soil is absorbed by plants with the help of root hairs.
- Root hairs are present in zone of absorption.
- Epidermal cells form unicellular extensions which are short lived (ephemeral) structures i.e. root hairs.
- Root hairs are nothing but cytoplasmic extensions of epiblema cell.
- Root hairs are long tube like structures of about 1 to 10 mm.
- They are colourless, unbranched and very delicate structures.
- A large central vacuole is surrounded by thin layer of cytoplasm, plasma membrane and outer cell wall.
- The cell wall of root hair is thin and double layered with outer layer of pectin and inner layer of cellulose which is freely permeable.
Question 2.
Write on journey of water from soil to xylem in roots.
Answer:
- Unicellular root hairs which are tubular extensions of epiblema cells absorb readily available capillary water from soil.
- The three physical processes imbibition, diffusion and osmosis are concerned with absorption of water.
- Water molecules get adsorbed on cell wall of root hair (imbibition).
- They enter the root hair cell by diffusion through cell wall which is freely permeable.
- By process of osmosis they enter through plasma membrane which is semipermeable.
- The root hair cell becomes turgid and hence its turgor pressure increases and D.ED. value decreases.
- The adjacent cell of cortex has more D.ED. value as its osmotic potential is more.
- The cortical cell thus takes water from epidermal cell which is turgid. This process goes on due to gradient of suction pressure developed from cell to cell till thin walled passage cells of endodermis.
- From endodermis it will enter pericycle and then due to hydrostatic pressure it is forced in protoxylem cell.
- The pathway of water is by apoplast and symplast.
- When water passes through cell wall and intercellular spaces of cortex it is apoplast pathway.
- When water passes across living cells through their plasmodesmatal connections it is symplast pathway.
Question 3.
Explain cohesion theory of translocation of water.
Answer:
- This is very widely accepted theory of ascent of sap proposed by Dixon and Joly.
- It is based on principles of adhesion and cohesion of water molecules and transpiration by plants.
- A strong force of attraction existing between water molecules is cohesion and the force of attraction between water molecules and lignified walls of xylem elements is adhesion.
- Ascent of sap occurs through lumen of xylem elements.
- Owing to cohesive and adhesive forces a continuous water column is maintained in xylem from root to aerial parts i.e. leaves.
- Transpiration occurs through stomata and transpiration pull is developed in leaf vessels.
- This tension or pull is transmitted downwards through vein to roots which triggers ascent of sap.
- In transpiration, water is lost in vapour form and this increases D.PD. of mesophyll cells that are near guard cells.
- Mesophyll cells absorb water from xylem in leaf and a gradient of D.PD. or suction pressure (S. E) is set.
- Owing to this gradient from guard cell to xylem in leaf, a transpiration pull or tension is created in xylem.
- Hence water column is pulled upward passively against gravity.
Question 4.
Write on mechanism of opening and closing of stomata.
Answer:
- Transpiration takes place through stomata. Turgidity of guard cells controls opening and closing of stomata
- Turgor pressure exerted on unevenly thickened wall of guard cell is responsible for the movement.
- The outer thin wall which is elastic is stretched out which pulls inner thick inelastic wall and thus stomata open.
- When guard cells are flaccid that results in closure of stomata.
- According to starch-sugar in ter conversion theory enzyme phosphorylase converts starch to sugar during daytime.
- Sugar being osmotically active, the O.E of guard cells is increased. The water is absorbed from subsidiary cells. Due to turgidity walls are stretched and stoma opens.
- During night-time sugar is converted to starch and hence guard cells loose water and become flaccid. Hence there is closure of stomata.
- According to proton transport theory, the movement is due to transport of H+ and K+ ions.
- Subsidiary cells are reservoirs of K+ ions. Starch is converted to malic acid which dissociate into malate and proton (H+) during day.
- Proton transported to subsidiary cells and K+ ions are taken from it. This forms potassium malate in guard cells.
- Potassium malate increases osmotic potential and endo osmosis occurs hence turgidity of guard cells. → stomata opens,
- The uptake of K+ and Cl– ions is stopped by abscissic acid formed during night. This changes permeability. Guard cells become hypotonic and loose water as they become flaccid stomata close.
Question 5.
What is hydroponics? How is it useful in identifying the role of nutrients?
Answer:
(1) Growing plants in aqueous (soilless) medium is known as hydroponics. [Greek word hudor = water and ponos = work]
(2) It is technique of growing plants by supplying all necessary nutrients in the water supply given to plant.
(3) A nutrient medium is prepared by dissolving necessary salts of micronutrients and macronutricnts In desired quantity and roots of plants are suspended in this liquid with appropriate support.
(4) Hydroponics is of great use in studying the deficiency symptoms of different mineral nutrients.
(5) The plants uptake mineral nutrients in the form of dissolved ions with the help of root hairs from the surrounding medium or nutrient solution supplied.
(6) While preparing the required nutricnt medium particular nutrient can be totally avoided and then the effect of lack of that nutrient can be studied in variation of plant growth.
(7) Any visible change noticed from normal structure and function of the plant is the symptom or hunger sign considered.
(8) For e.g. Yellowing of leaf is observed due to loss of chlorophyll pigments or Chiorosis is noticed if Magnesium is lacking as it is a structural componen of chlorophyll pigment.
Question 6.
Explain the active absorption of minerals.
Answer:
- Plants absorb minerals from the soil with their root system.
- MInerals are absorbed from the soil In the form of charged particles, positively charged cations and negatively charged anions.
- The absorption of minerals against the concentration gradient which requires expenditure of metabolic energy is called active absorption.
- The ATP energy derived from resp’ration in root cells Is utilized for active absrption.
- Ions get accumulated in the root hair against the concentration gradient.
- These ions pass into cortical cells and finally reach xylem of roots.
- Along with the water these minerals are carried to other parts of plant.