MARCH 2020 PAPER – l
SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY (PAPER-I)
[Time : 2 Hours]
[Max. Marks : 50]
Note :
(i) All questions are compulsory.
(ii) Use of a calculator is not allowed.
(iii) The numbers to the right of the questions indicate full marks.
(iv) In case of MCQs (Q. No. 1(A)) only the first attempt will be evaluated and will be given credit.
(v) For each MCQ, the correct alternative (A), (B), (C), (D) with sub-question number is to be written as answer.
For Eg : (i) (A), (ii) (B), (iii) (C)
(vi) Scientifically correct, labelled diagrams should be drawn wherever necessary.
Q. 1. (A) Write the correct alternative:
(i) According to Mendeleev’s periodic law, properties of elements are periodic function of their………………………….. .
(A) Atomic number
(B) Atomic masses
(C) Densities
(D) Boiling points
Ans. (B) Atomic masses
(ii) The vapour content in the air is measured using a physical quantity called……………………… .
(A) Absolute humidity
(B) Relative humidity
(C) Dew point
(D) Humidity
Ans. (A) Absolute humidity
(iii) For the normal human eye, the near point is at…………………….. .
(A) 10
(B) 20
(C) 25
(D) 30
Ans. (C) 25
(iv) The astronomical object closest to us is ………………… is our galaxy.
(A) Mars
(B) Venus
(C) Jupiter
(D) Moon
Ans. (D) Moon
(v) In the Wilfley table method, the particles of gangue are separated by ………………….. separation method.
(A) Magnetic
(B) Froth floatation
(C) Hydraulic
(D) Gravitational
Ans. (D) Gravitational
(B) Answer the following :
(i) Find the odd one out :
Voltmeter, Ammeter, Thermometer, Galvanometer.
Ans. Thermometer is odd.
(ii) Complete the correlation :
Alkene : : Alkyne :……………………………. .
Ans. Alkene : : : Alkyne:
(iii) State true or false :
The frequency of is .
Ans. True.
(iv) Match the Columns :
Column ‘A’ | Column ‘B’ |
The wavelength of red light | (a) |
(b) | |
(c) |
Ans. The wavelength of red light is (b)
(v) Name the first artificial satellite sent by Russia in space.
Ans. Sputnik.
Q. 2. (A) Give scientific reasons (any two) :
(i) The weight of an object changes from place to place though its mass is constant. *
Ans.
Answer is not given due to reduced syllabus.
(ii) Stars twinkle but we do not see the twinkling of planets.
Ans.
Stars twinkle, but we do not see the twinkling of planets.
(1) Due to the motion of atmospheric air, changing air density and temperature, the apparent position of the star keeps changing a bit. Thus, the refractive index of air keeps on changing continuously. So, the position and brightness of the star keep changing continuously and hence the star appears to be twinkling.
(2) But planets are much closer to us as compared to stars. So, they do not appear as point sources. They appear as a collection of point sources. Due to the changes in atmospheric refractive index, the position as well as the brightness of individual point source change. But the average position and total average brightness remains unchanged. Hence, planets do not twinkle.
(iii) Elements belonging to the same group have the same valency.
Ans.
Elements belonging to the same group have the same valency.
(1) Valency of an element is defined as the number of electrons present in the outermost shell of its atoms, i.e. valence electrons.
(2) For all the elements in the same group, the number of electrons in the outermost shell are same.
(3) Hence, the elements belonging to the same group have the same valency.
(B) Answer the following (any three) :
(i) How much heat energy is necessary to raise the temperature of of water from to ?
Ans.
Given data: Mass of water .
Change in temperature
.
Calculation :
Energy to be supplied to water Energy gained by water
Heat energy necessary to raise the temperature of water .
(ii) Observe the given figure of Fleming’s Right Hand Rule and write the labels of A and B correctly.
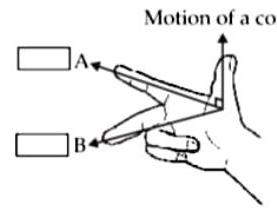
Ans.
(A) Direction of the magnetic field.
(B) Direction of the induced current.
(iii) Observe the given graph and answer the following questions :
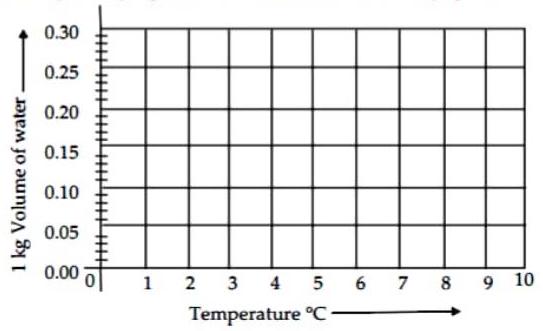
(a) Name the process represented in the figure.
Ans. The process represented in figure is Anomalous behaviour of water.
(b) At what temperature does this process take place?
Ans. This process takes place from to
(iv) Complete the given chemical reaction :
Name the type of the reaction.
Ans.
(1)
(2) The reaction is displacement reaction.
(v) Write a short note on Alloying.
Ans.
(1) An alloy is the homogenous mixture formed by mixing a metal with other metals or non-metals in a certain proportion and the process of making an alloy is called alloying.
(2) The main intension behind the alloying is to decrease the intensity of corrosion of metals.
(3) For example : Bronze is an alloy made from copper and tin. Statues made up of bronze are not affected by sun and rain.
(4) Stainless steel is an alloy formed from iron, chromium and carbon. Stainless steel does not get stains with air or water and also it does not rust.
(5) In recent times, for mining coins, various types of alloys are used.
Q. 3. Answer the following
(i) An element has its electronic configuration as 2, 8, 2. Now answer the following questions :
(a) What is the atomic number of this element?
Ans. Atomic number of the element with electronic configuration 2, 8, 2 is 12 . (The element is Magnesium).
(b) What is the group of this element?
Ans. Number of electrons in the outermost shell is 2. So, the element belongs to Group 2.
(c) To which period does this element belong ?
Ans. The element has 3 shells in its electronic configuration. Hence, it belongs to period 3.
(ii) Observe the given figure showing the orbit of a planet moving around the Sun and write the three laws related to it :
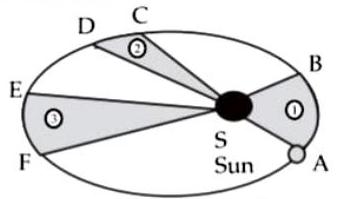
Planet
The orbit of a planet moving around the Sun
Ans.
The laws related to the given figure are Kepler’s laws.
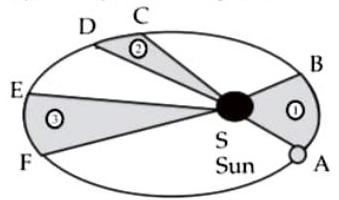
Planet
The orbit of a planet moving around the Sun
(1) Kepler’s first law : The orbit of a planet is an ellipse with the sun at one of the foci.The given figure shows an elliptical orbit of a planet revolving around the sun. In the figure indicates the position of the sun.
(2) Kepler’s second law : The line joining the planet and the sun sweeps equal areas in equal intervals of time.
In the figure and are the distances covered by the planet in equal time. The straight lines AS and CS sweep equal area in equal interval of time. That is, area ASB and area CSD are equal.
(3) Kepler’s third law : The square of its period of revolution around the sun is directly proportional to the cube of the mean distance of a planet from the sun.
If is the mean distance of the planet from the sun and is its period of revolution then.
(iii) Read the given passage and answer the following questions :
The home electrical connection consists of ‘live’, ‘neutral’ and ‘earth’ wires. The ‘live’ and the ‘neutral’ wires have potential difference of . The ‘earth’ is connected to ground. Due to a fault in the equipment or if the plastic coating on the ‘live’ and the ‘neutral’ wires gives a way the two wires come in contact with each other and a large current flows through it producing heat. If any inflammable material (such as wood, cloth, plastic, etc.) exists around that place it can catch fire. Therefore a fuse wire is used as a precautionary measure.
(a) Name the two wires having potential difference of .
Ans.
The ‘live’ and the ‘neutral’ wires have potential difference of .
(b) What is short circuit?
Ans.
Due to a fault in the equipment or if the plastic coating on the ‘live’ and the ‘neutral’ wires gives away, then the two wires come in contact with each other and a large current flows circuit through it producing heat. This is called as short circuit. If any inflammable material (such as wood, cloth, plastic, etc.) exists around that place, it can catch fire.
(c) Write the function of a fuse.
Ans.
Fuse wire is used as precautionary measure. As soon as high current flows in a circuit, the fuse wire melts and breaks the circuit and any mishap is avoided.
(iv) Observe the given figure and answer the following questions :
(a) Name the process represented by the figure.
Ans.
The given figure represents refraction.
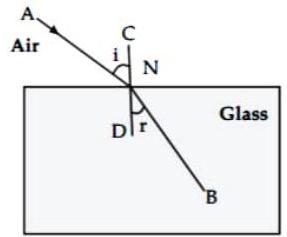
(b) State the two laws related to the process.
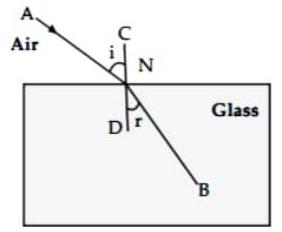
Ans.
Laws of refraction :
(1) Incident ray and the refracted ray at the point of incidence are on the opposite sides of the normal to the surface of the slab at that point i.e. CD, and the three the incident ray, refracted ray and the normal are in the same plane.
(2) For a given pair of media, (here air and glass), the ratio of to is constant, where ‘ ‘ is the angle of incidence and ‘ ‘ is the angle of refraction.
(v) What is an artificial satellite ? Name any two types of artificial satellite and state their functions.
Ans.
(1) If a manmade object revolves around the earth or any other planet in a fixed orbit, it is called an artificial satellites :
(2) The two types of artificial satellites.
(a) Weather satellite : Its function is study and prediction of weather.
(b) Broadcast satellite : Its function is to telecast television programs.
(vi) Answer the following questions :
(a) Define Hydrocarbons.
Ans.
The compounds which contain carbon and hydrogen as the only two elements are called hydrocarbons.
(b) Name the types of Hydrocarbons.
Ans.
Types of hydrocarbons are saturated hydrocarbons and unsaturated hydrocarbons. Unsaturated hydrocarbons have double or triple bond between the carbon atoms unlike the saturated hydrocarbons in which all hydrogen atoms and carbon atoms are bonded together with single bonds. Both these types are further classified as straight chain hydrocarbons, branched chain hydrocarbons and cyclic hydrocarbons.
(c) Name two carbon compounds used in day-to-day life.
Ans.
(1) Polythene which is used in production of carry bags and sports wear.
(2) Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) which is used in manufacture of PVC pipes, door mats, tubes and bags in hospital kits.
(vii) Observe the given figure of reactivity series of metals and answer the following questions :
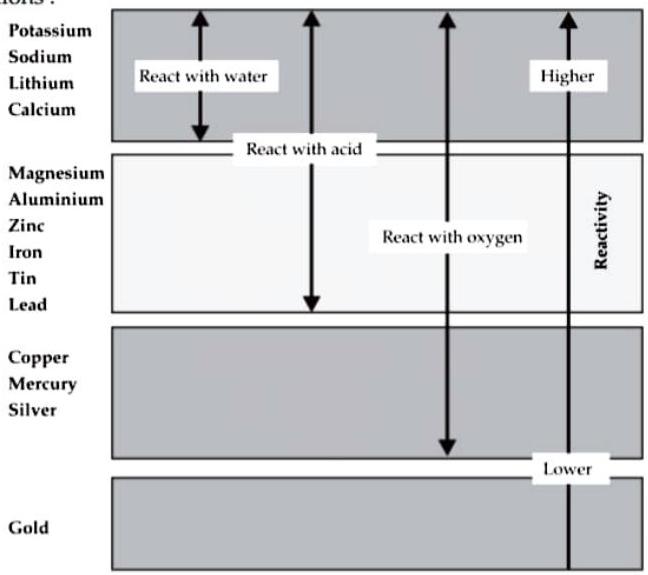
Reactivity series of metals
(a) Name two metals which react with water.
Ans.
(a) Sodium and calcium react with water.
(b) Name two moderately reactive metals.
Ans.
(b) Aluminium and zinc are the moderately reactive metals.
(c) Name the most highly reactive metal and the most less reactive metal.
Ans.
(c) The most highly reactive metal is Potassium and the most less reactive metal is Gold.
(viii) Complete the following table :
| Structural formula |
| Name | ||||
C | Methane | ||||||
……………….. | ……………….. | Ethane | |||||
……………….. | ……………….. | ||||||
 | ……………….. | ……………….. |
Ans.
| Structural formula |
| Name | ||||||||||||
C | Methane | ||||||||||||||
Ethane | |||||||||||||||
Propane | |||||||||||||||
 | Butane |
Q. 4. Answer any one of the following :
(i) Draw a scientifically correct labelled diagram of a human eye and answer the questions based on it :
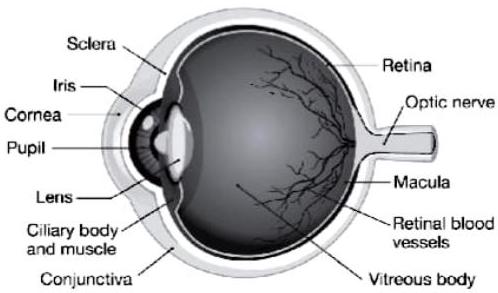
(a) Name the type of lens in the human eye.
Ans.
Lens in the human eye is double convex transparent crystalline lens.
(b) Name the screen at which the maximum amount of incident light is refracted ?
Ans.
Maximum amount of incident light is refracted inside the eye at the outer surface of the cornea.
(c) State the nature of the image formed of the object on the screen inside the eye.
Ans.
The image of the object formed on the screen inside the eye is real and inverted.
(ii) Observe the following picture and answer the following questions :
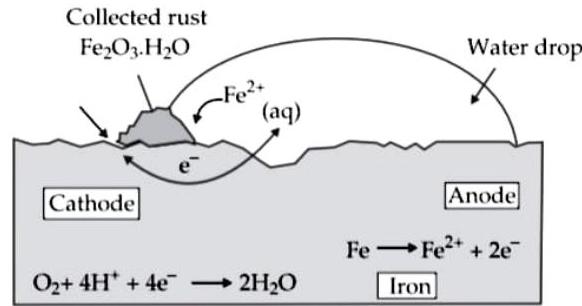
(a) What is a rust?
Ans.
A certain type of reddish coloured solid layer collec layer is called rust.
(b) Write the chemical formula of rust.
Ans.
Chemical formula of rust is
(c) Write the reaction of oxidation of iron at anode.
Ans.
Iron is oxidised to in the anode region.
(d) Write the reaction of oxidation of iron at cathode.
Ans.
is reduced to form water in the cathode region.
When ions migrate from the anode region, the get oxidised to form ions.
(e) What is corrosion?
Ans.
Due to various components of atmosphere, oxid consequently resulting in their damage. This is calle