Chapter 6 Ocean Resources
1. Complete the chain.
Question 1.
A | B | C |
(1) Continental Shelf | (1) Deeper Part | (1) Manganese Nodules |
(2) Oceanic Microorganisms | (2) Abyssal Plains | (2) Whales |
(3) Oceanic Trenches | (3) Fishing | (3) Sunda |
(4) Vast Flat Area | (4) Plankton | (4) Dogger Bank |
Answer:
A | B | C |
(1) Continental Shelf | (1) Fishing | (1) Dogger Bank |
(2) Oceanic Microorganisms | (2) Plankton | (2) Whales |
(3) Oceanic Trenches | (3) Deeper Part | (3) Sunda |
(4) Vast Flat Area | (4) Abyssal Plains | (4) Manganese Nodules |
2. Identify the correct correlation.
A : Assertion
R : Reasoning
Question 1.
A – Continental shelf is a storehouse of mineral oil and natural gas.
R – Continental shelf receives large quantities of load from continental areas.
(a) Only A is correct.
(b) Only R is correct.
(c) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
(d) Both A and R are correct but R is not the correct explanation of A.
Answer:
(d) Both A and R are correct but R is not the correct explanation of A.
Question 2.
A – More deposition occurs in the continental slope.
R – The slope is steeper here.
(a) Only A is correct.
(b) Only R is correct.
(c) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
(d) Both A and R are correct but R is not the correct explanation of A.
Answer:
(b) Only R is correct.
Question 3.
A – The islands are actually peaks of submerged mountains.
R – Some peaks of submerged mountains come above the sea level.
(a) Only A is correct.
(b) Only R is correct.
(c) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
(d) Both A and R are correct but R is not the correct explanation of A.
Answer:
(c) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
Question 4.
A – The abyssal plains are the deepest parts of the ocean.
R – They lie at the bottom of the ocean.
(a) Only A is correct.
(b) Only R is correct.
(c) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
(d) Both A and R are correct but R is not the correct explanation of A.
Answer:
(b) Only R is correct.
Question 5.
A – Sodium chloride and potassium are parts of inorganic oceanic resources.
R – Salt extraction is a major activity in coastal areas.
(a) Only A is correct.
(b) Only R is correct.
(c) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A.
(d) Both A and R are correct but R is not the correct explanation of A.
Answer:
(d) Both A and R are correct but R is not the correct explanation of A.
3. Give geographical reasons.
Question 1.
Fishing has developed in continental shelves.
Answer:
Fishing has developed in continental shelves because-
- The portion of the continents that is submerged under water and borders the coastal areas is known as a continental shelf.
- They are broad, shallow and gently-sloping plains covered by water.
- As the sunlight reaches this part of the ocean bed, plankton grows.
- These millions of microscopic organisms found in sea water are an important and favourite food for fish.
- Also, the sediments washed from the continental areas add to the food for fish. Thus, millions of fish thrive in this region.
Question 2.
Our knowledge regarding the oceanic trenches is limited.
Answer:
Our knowledge regarding the oceanic trenches is limited because-
- At places, deep, narrow and steeply sloping depressions are found on the ocean floor. These are called ocean deeps or ocean trenches.
- Generally, the shallow ones are called deeps whereas deeper ones are called ocean trenches. The oceanic trenches are the deepest parts of the oceans.
- These trenches can be thousands of meters deep. For example, The Mariana Trench in the Pacific Ocean is around 11 km deep while the Java Trench in the Indian Ocean is around 7.7 km deep.
- They generally occur along plate boundaries and are associated with active volcanoes and strong earthquakes.
- The knowledge of ocean trenches is limited because of their depth and their remoteness.
Question 3.
The ocean is a storehouse of minerals.
Answer:
The ocean is a storehouse of minerals because-
- The continental shelves contain the world’s largest reservoirs of natural oil and gas.
- The other deposits like diamonds, chromite, ilmenite, magnetite, platinum, gold and phosphorite are also found.
- Sand, gravel aggregates and industrial silica sand are the most important of hard minerals now extracted in the near offshore zone.
- The abyssal plains are often littered with nodules of manganese containing varying amounts of iron, nickel, cobalt, and copper.
- The most common resources obtained from oceans are sodium chloride, i.e., common salt.
- A large number of metallic and non-metallic minerals are found on the ocean floor, e.g., potassium occurs in large quantities.
- Gypsum forms during evaporation of sea water. The gypsum deposits are mined and converted into Plaster of Paris and used for construction.
- The most important minerals extracted from the sea floor are petroleum and natural gas.
Question 4.
Like the land, there are landforms below the ocean too.
Answer:
Like the land, there are landforms below the ocean too because-
- Continental shelf is mere continuation of coastal plain, sloping gently, they resemble gently sloping low-lying areas.
- As there are plains formed on the surface, similar feature in form of extensive flat land is found on the ocean floor, they are called abyssal plains.
- Mountains and ranges are found on the earth’s surface, as seamounts and ridges are found as part of ocean floor. For example, Mid-Indian Ridge.
- Some oceanic ridges have flat and extensive tops, they are called oceanic plateaus. For example, Chagos Plateau in the Indian Ocean.
- V shaped valleys on the surface of the earth are similar to the deep, narrow and steep sloping depressions, they are called deeps or sea trenches. For example, Kuril Trench in Pacific Ocean in Japan.
- Many canyons and gorges are also found on the earth’s surface and in the oceans too.
4. Write short notes on.
Question 1.
EEZ
Answer:
- Generally, a state’s exclusive economic zone is an area beyond and adjacent to the territorial sea, extending seaward to a distance of no more than 370 km out from its coastal baseline.
- The exception to this rule occurs when exclusive economic zones would overlap; that is, state coastal baselines are less than 740 km apart. When an overlap occurs, it is up to the states to delineate the actual maritime boundary.
- The exclusive economic zone stretches much further into sea than the territorial water, which ends at 22 km from the coastal baseline if following the rules set out in the UN Convention on the Law of the Sea). Thus, the exclusive economic zones include the contiguous zone.
- States also have rights to the seabed of what is called the continental shelf up to 650 km from the coastal baseline, beyond the exclusive economic zones, but such areas are not part of their exclusive economic zones.
- The legal definition of the continental shelf does not directly correspond to the geological meaning of the term, as it also includes the continental rise and slope, and the entire seabed within the exclusive economic zone.
- The idea of allotting nations with EEZs is to give them more control of maritime affairs outside territorial limits, gained acceptance in the late 20th Century.
Question 2.
Oceanic tourism
Answer:
- Ocean tourism is developed along the coastal areas of seas and oceans.
- Ocean tourism comes in many forms like cruises, scuba-diving, fishing, beach tourism, etc. Such activities are increasingly becoming popular.
- Generally, water sports activities such as scuba diving, surfing, water skiing, etc., are developed along the coastline. For example, sport activities along the coast of Goa.
- There is beautiful scenery along the coastline due greenery of trees along the coast, huge waterbody of sea or ocean, clean air and coolness due to nearness to water, therefore many resorts, hotels, marina, etc., are developed and coastal areas have become popular for tourism.
For example, tourism along Konkan coastline. The cruise tourism is also increasing.
Question 3.
Abundance of minerals in oceans
Answer:
- The continental shelves contain the world’s largest reservoirs of natural oil and gas.
- The other deposits like diamonds, chromite, ilmenite, magnetite, platinum, gold and phosphorite are also found.
- Sand, gravel aggregates and industrial silica sand are the most important of hard minerals now extracted in the near offshore zone.
- The abyssal plains are often littered with nodules of manganese containing varying amounts of iron, nickel, cobalt, and copper.
- The most common resources obtained from oceans are sodium chloride i.e. common salt.
- A large number of metallic and non-metallic minerals are found on the ocean floor, e.g., potassium occurs in large quantities.
- Gypsum forms during evaporation of sea water. The gypsum deposits are mined and converted into Plaster of Paris and used for construction.
- The most important minerals extracted from the sea floor are mineral oil and natural gas.
Question 4.
Deposition and Continental Slope
Answer:
- After the extent of continental shelf is over, there is a sharp drop in the ocean floor.
- The gradient of slope in this region can be between 2° to 5°. This is called continental slope.
- The depth of this slope extends from 200 m up to 4000 m from sea level.
- Due to its steepness, the continental slope stretches over a limited area.
- The deposition of sediments is also limited in this part.
- The continental slopes are generally considered as boundaries of continents. Methane hydrate, a compound of water and methane, is present on the continental slopes.
- On the slope, we find many traces of submarine landslide activity, ocean canyons and huge avalanche fans. For example, Congo Canyon is a submarine canyon found near Africa.
5. Answer in detail.
Question 1.
The marine pollution is ultimately going to be harmful to the man himself. Discuss.
Answer:
- Though the human activities are a major cause behind climate change, there are some natural causes for climate change. They are as follows:
- Importance of the ocean is increasing day by day in various ways, human dependence on oceans is likely to increase manifold in the days to come.
- Nowadays, the oceanic waters are getting polluted on a large scale.
- This causes deterioration of the natural quality of ocean water.
- The leakages of oil from oil transporting ships, oil extraction from coastal areas, disposal of solid waste containing radioactive matter, atomic tests etc., are causing large scale pollution of oceanic waters.
- The effluents brought by river discharges, the disposal of waste from coastal cities, the waste from industries and many other similar factors are polluting the oceanic waters.
- As a result, the very existence of marine life is threatened.
Question 2.
There is similarity in the relief on the land surface and the ocean bottom.
Answer:
Ocean tourism is developed along the coastal areas of seas and oceans-
Ocean tourism comes in many forms like cruises, scuba-diving, fishing, beach tourism, etc. Such activities are increasingly becoming popular.
Generally, water sports activities such as scuba diving, surfing, water skiing, etc., are developed along the coastline. For example, sport activities along the coast of Goa.
There is beautiful scenery along the coastline due greenery of trees along the coast, huge waterbody of sea or ocean, clean air and coolness due to nearness to water, therefore many resorts, hotels, marina, etc., are developed and coastal areas have become popular for tourism. For example, tourism along Konkan coastline. The cruise tourism is also increasing.
Question 3.
Discuss how development of oceanic tourism should be carried out without disturbing marine life.
Answer:
It is difficult to clean up mass pollution once it has occurred, so the best plan is prevention. Several changes can take place to help keep industry in check and encourage sustainable practices such as:
- Stricter government regulations on industry and manufacturing is one large scale solution. There are several laws to help protect beaches, reduce pollution from ships, reduce marine debris, and prohibit ocean dumping.
- Implement renewable energy sources, such as wind or solar power, to limit off-shore drilling.
- Limit agricultural pesticides and encourage organic farming and eco-friendly pesticide use.
- Proper sewage treatment and exploration of eco-friendly wastewater treatment options, such as recycling sewage sludge to carbon-phosphorous fertilizer, are other solutions.
- Cut down on industry and manufacturing waste and contain landfills so they do not spill into the ocean.
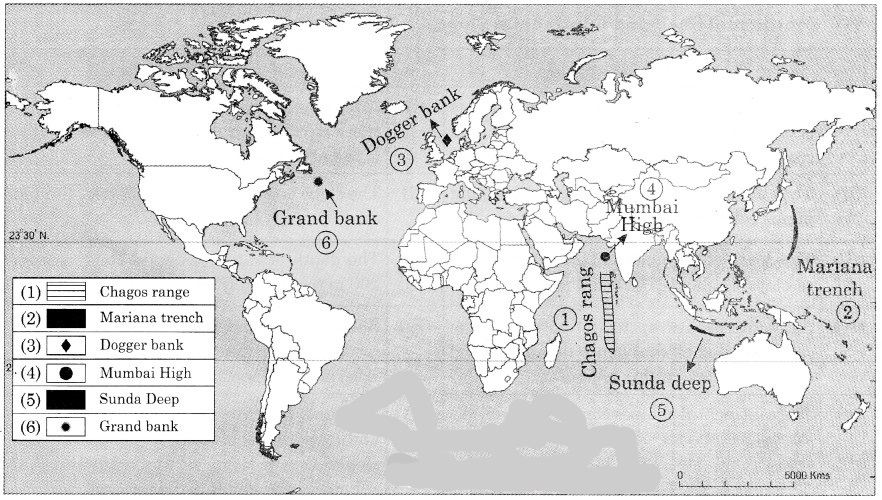
6. Show the following on the map of the World
1. Chagos Range
2. Mariana Trench
3. Dogger Bank
4. Mumbai High
5. Sunda Deep
6. Grand Banks
Answer:
11th Geography Digest Chapter 6 Ocean Resources Intext Questions and Answers
Use your brain power! (Textbook Page No. 68)
Collect information of the following and discuss in the class:
- Major journeys carried out by explorers in the last millennium
- Discovery of continents, countries and islands
- Spread of culture, trade and religions
Comment on how oceans have played a major role in all the three points mentioned above.
Answer:
[Students will find out the journeys and expeditions and comment on it in their own words.]
Try this.
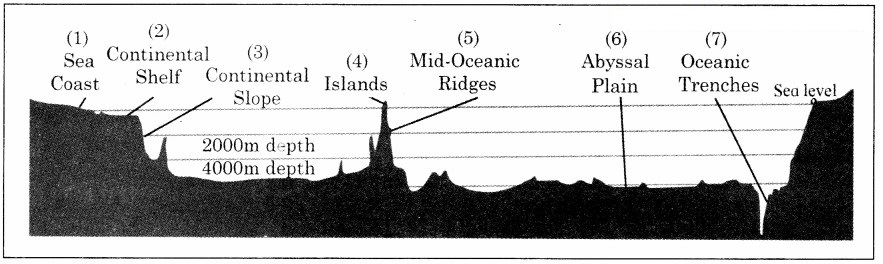
1. Look at figure 6.1 and answer the following question. (Textbook Page No. 68)
Question 1.
What does the figure show?
Answer:
The figure shows various landforms of the ocean floor.
Question 2.
In which part of the figure is the ocean shallow? Which human activities can be carried out here?
Answer:
The ocean is shallow at the continental shelf area. Fishing is carried out here as a major human activity.
Question 3.
In which part does deposition of sediments occur?
Answer:
Deposition of sediments occur on the continental shelf area as well as on the abyssal plains.
Question 4.
Where in the figure do you find islands formed due to submerged mountains?
Answer:
Islands formed due to submerged mountains are found in the oceanic ridges and plateau region.
Question 5.
Label the figure with correct names of landforms.
Answer:
Question 6.
Compare these features with the landforms on the earth.
Answer:
On the earth, different types of mountains and ranges are found, as they are found on the sea floor in the form of sea mounts and ridges, islands. Similarly, on the earth’s surface plains are formed as abyssal plains, which are found on the sea floor. Valleys and canyons on the earth’s surface represent oceanic deeps and trenches as a part of ocean floor.
2. Various institutes are presently working for exploration of ocean, its climate, resources and its impact on our lives. Prepare a list of such institutes which are in India. With the help of internet, complete the table below. (Textbook Page No. 72)
Answer:
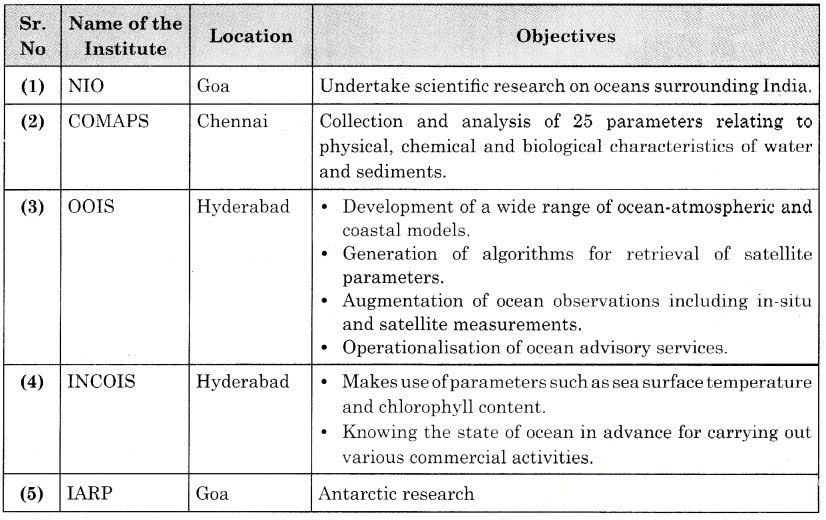
3. Do you know that India has got the right to mine manganese nodules from the bed of the Indian Ocean from that area which lies beyond the exclusive economic zone. Identify some other resources which are international in nature. (Textbook Page No. 73)
Answer:
India can mine Cobalt and Nickel from the Indian Ocean from the area which lies beyond the EEZ.
Find out! (Textbook Page No. 70)
Question 1.
Find out the name and locations of islands located in India and list them in the above given categories.
Answer:
- Continental Islands: Minicoy, Seven Islands of Bombay (Bombay is the present-day Mumbai.), Sundarbans, Amindivi, etc.
- Volcanic Island: Barren island part of Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Coral Island: Andaman and Nicobar, Gulf of Kutch, Gulf of Mannar, Lakshadweep, Tarkarli in Malvan, etc.
Question 2.
India also produces water from desalination plants. Find out their locations with the help of the internet.
Answer:
The Minjur Desalination Plant is the largest in India, located at Kattupalli village, a northern suburb of Chennai on the coast of the Bay of Bengal that supplies water to the city of Chennai.